CCL5
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 -
Overview
This gene is one of several chemokine genes clustered on the q-arm of chromosome 17. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, functions as a chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T helper cells and eosinophils. It causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. This cytokine is one of the major HIV-suppressive factors produced by CD8+ cells. It functions as one of the natural ligands for the chemokine receptor chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5), and it suppresses in vitro replication of the R5 strains of HIV-1, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants that encode different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2013] -
Synonyms
CCL5;chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5;SISd;eoCP;SCYA5;RANTES;TCP228;D17S136E;SIS-delta;C-C motif chemokine 5;beta-chemokine RANTES;T-cell specific protein p288;eosinophil chemotactic cytokine;small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 5;regulated upon activation, normally T-expressed, and presumably secreted
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rabbit
- Swine
- Cynomolgus
- Mouse
- Cotton Rat
- Canine
- Feline
- Rat
- Bovine
- Pig
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Dog
- Horse
- Guinea pig
- Cattle
- Rhesus
- Human Cells
- Yeast
- HEK293
- Mouse
- E.coli
- CHO
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- GST
- S
- T7
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- mucin
Background
What is CCL5 protein?
CCL5 gene (C-C motif chemokine ligand 5) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q12. Chemokines form a superfamily of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The superfamily is divided into four subfamilies based on the arrangement of the N-terminal cysteine residues of the mature peptide. This chemokine, a member of the CC subfamily, functions as a chemoattractant for blood monocytes, memory T helper cells and eosinophils. It causes the release of histamine from basophils and activates eosinophils. It functions as one of the natural ligands for the chemokine receptor chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 5 (CCR5), and it suppresses in vitro replication of the R5 strains of HIV-1, which use CCR5 as a coreceptor. The CCL5 protein is consisted of 91 amino acids and CCL5 molecular weight is approximately 10.0 kDa.
What is the function of CCL5 protein?
CCL5 can attract immune cells such as T lymphocytes, monocytes, basophils and eosinophils, and regulate inflammatory response and immune response. In the nervous system, CCL5 supports nerve activity and nerve growth and may function as a trophic factor. CCL5 is associated with synaptic plasticity, cognition and spatial memory in the hippocampus, and has a positive effect on memory function. CCL5 promotes glucose uptake and mitochondrial function, enhancing the energy supply of cells, and is particularly important for nerve cells. CCL5 is involved in regulating the formation and maintenance of synapses and is essential for learning and memory processes. CCL5 may have a dual role in the tumor microenvironment, both attracting immunosuppressive cells to promote immune tolerance and promoting the recruitment of immune effector cells.
CCL5 related signaling pathway
In general, the CCL5/CCR5 axis influences cell behavior and gene expression by activating a variety of downstream signaling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, HIF-α, RAS-ERK-MEK, YAK-stat, and TGF-β-smad. CCL5 binds to CCR5 and activates G-protein-coupled receptors, triggering downstream signaling pathways that lead to migration and chemotaxis of immune cells such as T cells, monocytes, and macrophages. The CCL5/CCR5 signaling pathway promotes the release of inflammatory factors and exacerbates the inflammatory response by activating PI3K/AKT, NF-κB, HIF-α, RAS-ERK-MEK, YAK-stat and TGF-β-smad signaling pathways. CCR5 inhibitors such as Maravero (MVC) can block CCL5/CCR5 signaling, reduce abnormal activation of mTORC1, increase the number of autophagosomes, and reduce the aggregation of neurotoxic proteins, showing potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
CCL5 related diseases
CCL5 is a cytokine, also known as macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), which plays an important role in immune response and inflammation. CCL5 has been linked to a variety of diseases, including autoimmune diseases, tumors, cardiovascular diseases, neurological diseases, and more. In autoimmune diseases, CCL5 can promote the infiltration and activation of inflammatory cells, leading to tissue damage and increased inflammatory response. In tumors, CCL5 can promote the growth and spread of tumor cells. In cardiovascular disease, CCL5 can promote the proliferation and migration of vascular endothelial cells, resulting in thickening of blood vessel walls and hardening of blood vessels. In neurological diseases, CCL5 can promote neuronal death and neurodegeneration.
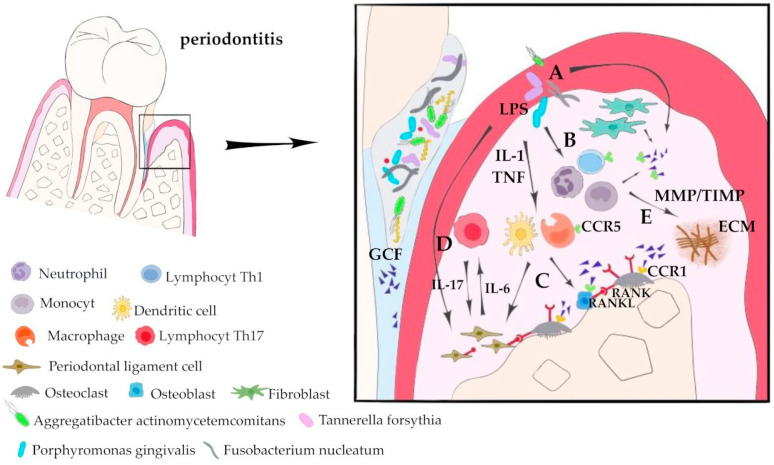
Fig1. Involvement of CCL5 in pathological processes in periodontitis. (Katarzyna Barczak, 2023)
Bioapplications of CCL5
In terms of disease treatment, CCL5 can be used as a therapeutic target to treat related diseases by inhibiting or regulating its expression. For example, in rheumatoid arthritis, inhibiting CCL5 expression can reduce inflammatory responses and joint pain; In cancer therapy, inhibition of CCL5 expression can prevent the growth and spread of tumor cells. In addition, CCL5 can be used as a target for drug development. At present, there are several drugs targeting CCL5 in development, such as anti-CCL5 monoclonal antibodies and CCL5 inhibitors. These drugs can be used to treat autoimmune diseases, tumors, cardiovascular disease and many other conditions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Nahzli Dilek, 2012
Researchers investigated the role of myelo-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) and regulatory T cells (Treg) in renal transplantation tolerance. By DNA microarray analysis, it was found that the expression of CCL5 in MDSC and plasma CCL5 level of rats were decreased after tolerance treatment. Since CCL5 attracts Treg, researchers conclude that changes in CCL5 levels may affect the distribution of Treg in the graft. In the experiment, by supplementing CCL5 to change the plasma concentration, the reduction of Treg in the graft resulted in rejection of the transplanted kidney. There was no effect on the kidney function of isogeneic transplantation.
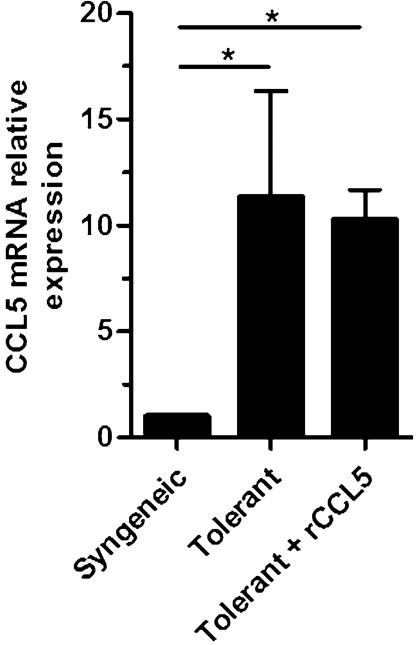
Fig1. qRT-PCR measurement of CCL5 mRNA in kidney grafts 3 mo posttransplantation.
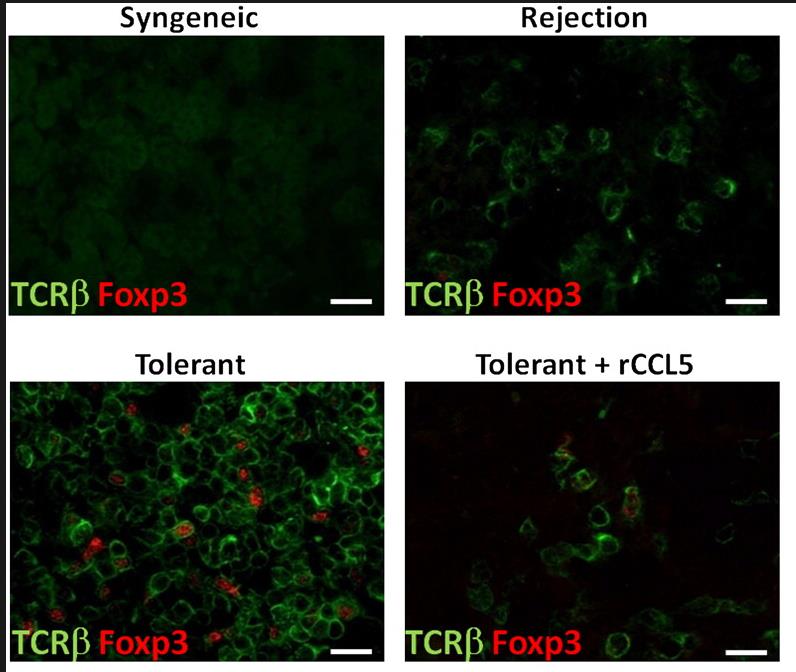
Fig2. Increased Treg infiltration in tolerated kidney allografts.
Case Study 2: Jean-Eric Alard, 2015
In acute and chronic inflammation, neutrophils and platelets are often activated simultaneously and promote recruitment of monocytes. Researchers investigated how secretory products from these cells work together to enhance recruitment of monocytes. Results showed that human neutrophil peptide 1 (HNP1, alpha-defencin) and platelet-derived CCL5 from neutrophils form heterodimers that promote monocyte adhesion through CCR5 binding. They further characterized the structure of the HNP1-CCL5 heterodimer and designed a stabilizing peptide that interferes with the pro-inflammatory HNP1-CCL5 interaction. In a mouse model of myocardial infarction, this peptide mitigated recruitment of monocytes and macrophages.

Fig3. Representative dot blot with hCCL5, Pltsup, and PMNsup spotted on a membrane.
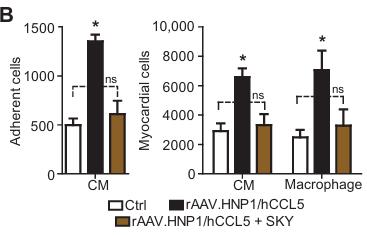
Fig4. The SKY peptide abrogates monocyte recruitment into the heart evoked by HNP1 and hCCL5.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CCL5-301H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CCL5-773H)
Involved Pathway
CCL5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CCL5 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CCL5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| TNF signaling pathway | VEGFC,MAPK9,TAB2,ATF4,RPS6KA4,IKBKG,IL15,TNFRSF1B,MAP3K7,MAPK10 |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | IL8L2,MAPK12B,CRFB2,MAP2K4A,CCL3L1,CXCL11,TLR8,NFKBIAB,MAP2K2A,IRAK1 |
| Herpes simplex infection | NXF3,HLA-C,IFNB1,C3A.1,HLA-DMA,CASP3A,CUL1,CUL1B,SRPK1A,LTA |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CCL20A.3,IL9,CSF2,IL6ST,INHBE,CCR1L1,OSM,CCL13,CXCL5,CXCL6 |
| Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway | TREX1,IL33,NFKBIB,POLR2L,RIPK3,IFNA7,ZBP1,OSTN,IFNA3,POLR2E |
| Prion diseases | NCAM1,PRKACA,Hc,ELK1,C8B,IL1A,HSPA5,LOC100033925,C1QB,NOTCH1 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | TLR4,Ctsl,IL18,ATP6V1C1,ATP6V1E1,GM-CSF,CD80,CCL20,HLA-DOB,TNF |
| Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | ATP6V1H,PAK1,F11R,ATP6V1A,ATP6V1G2,ATP6V1C1,LYN,PLCG1,ATP6V0D1,MAPK11 |
| Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | CD3G,TRAF6,MAPK10,CCL2,BDKRB2,IFNGR1,FASLG,CASP8,TLR4,IKBKG |
Protein Function
CCL5 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR1 chemokine receptor binding,CCR4 chemokine receptor binding,CCR5 chemokine receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CCL5 itself. We selected most functions CCL5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CCL5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase activity | MAP3K2,GM711,PRKCDA,RIPK4,MAP3K5,BMPR1BA,CLK4B,NLK2,CDK12,MAK |
| chemokine activity | Ccl21c,Ccl21a,CXCL18B,IL8L2,CCL20,CXCL2,CCL14,CCL15,CCL38A.5,CXCL9 |
| CCR1 chemokine receptor binding | CREB3,CCL4,CCL7,CCL3,CCL23 |
| phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity | PLCD3A,CHRM5,PLCH1,CCKBR,CCR1,CHRM1,CASR,BDKRB2,EDNRA,PLCB1 |
| chemokine receptor binding | CCL25,CCL21B,XCL1,CCRL2,S100A14,CCL19,CXCL12,CCL21,Ccl21c,Ccl21a |
| heparin binding | APPA,LAMC2,BMP7,APOB,APOH,PCOLCE2,SERPINC1,SLIT2,LXN,NELL2 |
| protein self-association | ZSWIM2,CCDC88C,AXIN1,NKX3,LDB1,PABPN1,TNFAIP3,VAMP2,ABCD3,CNTN2 |
| CCR5 chemokine receptor binding | CNIH4,STAT3,CCL4,CCL3,JAK1 |
| chemoattractant activity | FGF10,FGF2,CCL16,HGF,CCL3,SAA3,VEGFA,HMGB1,SAA1,FGF7 |
Interacting Protein
CCL5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CCL5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CCL5.
DPP4;CCR5;BCAR3;BAG4;CHEK2;KRAS;TGFB1;CDH1;PTPN1;WT1;SLC2A5;APC;PHB;RANGAP1;RELA;TRIP6
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Yin, Q; Fan, Q; et al. Spinal NF-kappa B and Chemokine Ligand 5 Expression during Spinal Glial Cell Activation in a Neuropathic Pain Model. PLOS ONE 10:-(2015).
- Ricciardi, A; Dalton, JP; et al. Evaluation of the immune response and protective efficacy of Schistosoma mansoni Cathepsin B in mice using CpG dinucleotides as adjuvant. VACCINE 33:346-353(2015).




