What is CXCL12 Protein
CXCL12, officially known as C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12, is a crucial member of the chemokine family. Also recognized by the aliases SDF-1 (stromal cell-derived factor 1) and PBSF (pre-B cell growth-stimulating factor), CXCL12 plays a pivotal role in various biological processes. This protein is encoded by the CXCL12 gene, and its significance extends beyond its nomenclature.
CXCL12 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Belonging to the CXC chemokine subfamily, CXCL12 showcases distinct structural characteristics. It consists of a conserved cysteine motif, represented by the CXC motif, which defines its classification within the chemokine family. Recent advances in research have shed light on the intricate structural details of CXCL12, providing a deeper understanding of its molecular architecture and how it contributes to its diverse functions.
CXCL12 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of CXCL12 are multifaceted, reflecting its significance in various physiological processes. One of its primary roles is to regulate the migration and homing of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. This chemokine is a key player in the immune system, orchestrating the movement of immune cells to specific sites of inflammation or injury.
On a molecular level, CXCL12 interacts with its receptor, CXCR4, initiating downstream signaling cascades. This interaction is pivotal in mediating chemotaxis, a process crucial for immune cell recruitment. Additionally, CXCL12 has been implicated in angiogenesis, influencing the formation of new blood vessels.
CXCL12 Related Signal Pathway
The CXCL12 signaling pathway is intricately woven, involving the interaction between CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4. Upon binding, CXCL12 activates downstream signaling cascades, including the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. These pathways play a pivotal role in mediating cellular responses such as proliferation, survival, and migration.
Understanding the CXCL12-related signal pathway is crucial for developing targeted therapeutic interventions. Researchers are exploring ways to modulate this pathway to treat diseases characterized by aberrant CXCL12 signaling, providing a promising avenue for drug development.
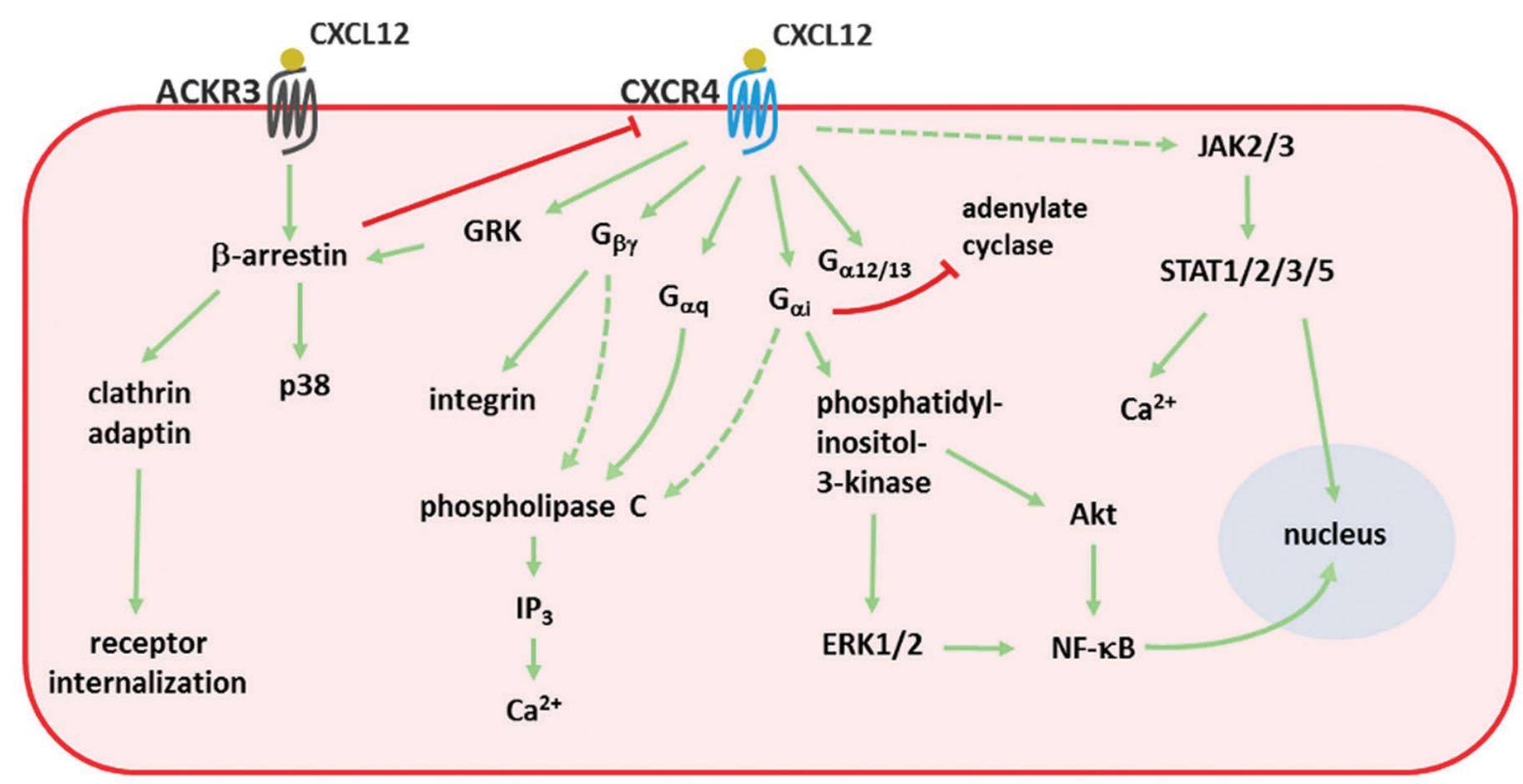
Figure 1. Signal transduction pathways activated by CXCL12. (Janssens R, et al., 2018)
CXCL12 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of CXCL12 has been linked to several diseases, emphasizing its role in maintaining homeostasis. Cancer, a condition characterized by uncontrolled cell growth, often involves alterations in CXCL12 signaling. Elevated levels of CXCL12 have been observed in certain cancers, promoting tumor progression and metastasis.
Furthermore, CXCL12 is implicated in inflammatory disorders, where its dysregulated expression contributes to the persistence of inflammation. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, showcase aberrant CXCL12 signaling, highlighting its involvement in immune dysregulation.
CXCL12's Applications in Biomedical
CXCL12's versatility extends beyond its physiological functions, making it a valuable asset in biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, the detection of CXCL12 levels can serve as a biomarker for certain diseases, aiding in early diagnosis and prognosis.
In vaccine development, CXCL12's ability to modulate immune responses is leveraged to enhance the efficacy of vaccines. Researchers are exploring its potential as an adjuvant to stimulate robust immune reactions, paving the way for the development of more effective vaccines.
In therapeutics, targeting the CXCL12 pathway holds promise for the treatment of various diseases, including cancer and inflammatory disorders. Pharmacological interventions that selectively modulate CXCL12 signaling are under investigation, offering new avenues for precision medicine.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cxcl12-2510M | Recombinant Mouse Cxcl12 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Cxcl12-018C | Active Recombinant Mouse Cxcl12 Protein (72 aa) | Mouse | E.coli | |
| CXCL12-24M | Recombinant Mouse CXCL12 Protein | Mouse | E.coli | |
| Cxcl12-62M | Active Recombinant Mouse CXCL12 Protein | Mouse | E.coli | |
| CXCL16-35M | Recombinant Mouse CXCL12 Protein, Biotin-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | Biotin |
| Cxcl12-63M | Active Recombinant Mouse CXCL12 Protein | Mouse | E.coli | |
| Cxcl12-2391M | Recombinant Mouse Cxcl12 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| Cxcl12-11719M | Recombinant mouse Cxcl12, GST-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | GST |
| Cxcl12-42M | Recombinant Mouse Cxcl12 protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| CXCL12-4351R | Recombinant Rabbit CXCL12 Protein | Rabbit | Yeast | N/A |
Reference
- Janssens R, et al. The unique structural and functional features of CXCL12. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2018, 15(4): 299-311.

