What is EOMES Protein
EOMES, short for Eomesodermin, stands as a formidable transcription factor encoded by the EOMES gene, featuring prominently in the T-box family.
At its core, EOMES protein is a transcription factor characterized by a conserved DNA-binding domain, the T-box. This evolutionarily conserved feature enables EOMES to exert precise control over gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences. The EOMES gene, found in humans, encodes this protein, playing a crucial role in orchestrating cellular processes during embryonic development and immune system modulation.
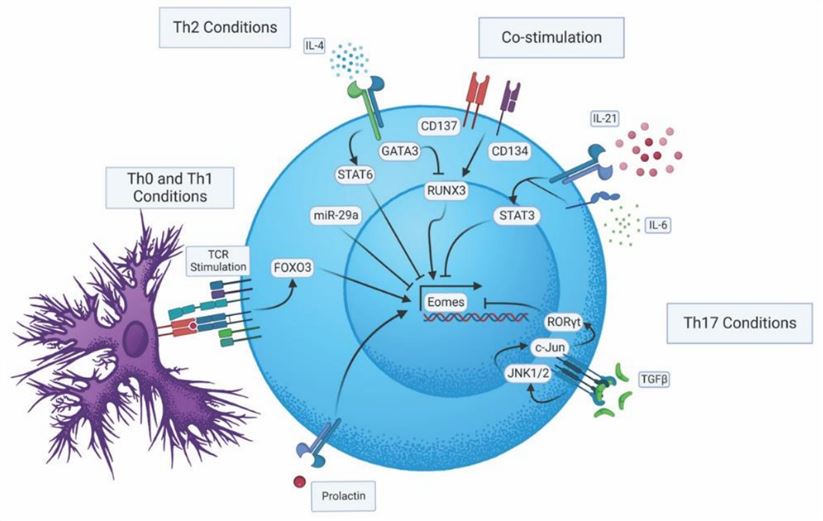 Figure 1. Regulatory pathways impacting Eomes expression in CD4 T cells. (Dhume, K., et al. 2022)
Figure 1. Regulatory pathways impacting Eomes expression in CD4 T cells. (Dhume, K., et al. 2022)The Function of EOMES Protein
- Embryonic Development
EOMES is a linchpin in the intricate dance of embryonic development. During this crucial phase, it emerges as a key player in the differentiation of cells, particularly in the mesoderm and endoderm. The regulatory influence of EOMES is instrumental in the formation of vital tissues and organs. Its absence or dysregulation can lead to profound developmental abnormalities, emphasizing its non-negotiable role in embryogenesis.
- Immune System Regulation
Transitioning to the immune system, EOMES takes center stage in the differentiation and function of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells. In CD8+ T cells, EOMES is indispensable for the development of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), crucial in eliminating infected or aberrant cells. Moreover, EOMES regulates NK cells, enhancing their cytotoxic activity against target cells. This dual role underscores the protein's significance in orchestrating a robust immune response.
EOMES-Related Diseases
- Cancer
EOMES's involvement in cancer extends beyond a mere correlation. Dysregulation of EOMES expression has been documented in cancer cells, impacting essential processes such as proliferation, migration, and invasion. Understanding these mechanisms could pave the way for targeted therapeutic interventions, offering a glimmer of hope in the fight against cancer.
- Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases
EOMES's regulatory role in T cell responses positions it as a potential player in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Aberrations in EOMES expression may contribute to inappropriate immune responses, serving as a potential trigger for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease. Unraveling these connections could provide novel avenues for therapeutic interventions.
EOMES Related Signaling Pathways
- TGF-β Signaling Pathway
Central to EOMES's modulatory prowess is its interaction with the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. TGF-β, a pivotal cytokine, regulates fundamental cellular processes. EOMES, by intertwining with this pathway, modulates the differentiation of embryonic cells and contributes to the delicate balance between effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the immune system.
- Wnt Signaling Pathway
The intricate crosstalk between EOMES and the Wnt signaling pathway further accentuates its regulatory complexity. This pathway, crucial in embryonic development and tissue homeostasis, finds a partner in EOMES. As research progresses, deciphering the nuances of this interaction promises a deeper understanding of EOMES's regulatory reach.
Applications of EOMES in Biomedical Research
- Cancer Immunotherapy
EOMES's implications in cancer extend beyond mere observation. Researchers are actively exploring avenues to leverage its regulatory functions for therapeutic gains. Cancer immunotherapy stands out, with strategies aimed at manipulating EOMES expression to enhance the anti-tumor activity of cytotoxic T cells. This precision-focused approach holds promise in revolutionizing cancer treatment.
- Regenerative Medicine
In the realm of regenerative medicine, EOMES emerges as a potential guide in directing the differentiation of stem cells. Its ability to influence cell fate during embryonic development suggests a role in steering stem cells toward specific lineages. This application holds immense potential in treating degenerative diseases and injuries, where targeted tissue regeneration is paramount.
EOMES protein, a molecular maestro orchestrating crucial facets of embryonic development and immune regulation, emerges as a promising focal point in both understanding diseases and advancing biomedical applications. From cancer to regenerative medicine, the multifaceted nature of EOMES positions it at the forefront of scientific inquiry, promising innovative breakthroughs in the pursuit of improved human health.
Recommended Products for EOMES Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOMES-3344H | Human | Recombinant Human EOMES Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| EOMES-389H | Human | Recombinant Human EOMES Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| EOMES-3345H | Human | Recombinant Human EOMES Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| EOMES-1649H | Human | Recombinant Human EOMES protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| EOMES-301271H | Human | Recombinant Human EOMES protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| EOMES-5228M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse EOMES Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| EOMES-2807M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse EOMES Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Dhume, K., Kaye, B., McKinstry, K.K. Regulation of CD4 T Cell Responses by the Transcription Factor Eomesodermin. Biomolecules. 2022, 12(11): 1549.

