What is FGF1 Protein
Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 (FGF1), also known as acidic FGF or aFGF, is a crucial member of the fibroblast growth factor family. This family comprises a diverse group of signaling proteins that play pivotal roles in various biological processes, including cell growth, development, tissue repair, and angiogenesis. FGF1, with its official full name as Fibroblast Growth Factor 1, has synonyms such as heparin-binding growth factor 1 and HBGF-1. Recent research advances have shed light on its intricate structural characteristics and classification, deepening our understanding of its multifaceted functions.
FGF1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, FGF1 is characterized by a conserved core β-trefoil structure, which is a threefold symmetric arrangement of 12 antiparallel β-strands. This unique architecture is crucial for its interaction with cell surface receptors and modulating downstream signaling cascades. FGF1 is classified as an intracellular protein, contrary to other FGF family members, as it lacks a signal peptide for secretion. However, upon cellular stress or specific stimuli, FGF1 can be translocated to the cell surface and exert its functions extracellularly.
FGF1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of FGF1 are diverse and essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Primarily, FGF1 acts as a potent mitogen, stimulating cell proliferation and differentiation. It plays a pivotal role in embryonic development, tissue repair, and angiogenesis, contributing to the formation of new blood vessels. The molecular mechanisms underlying FGF1's actions involve binding to high-affinity FGF receptors (FGFRs) on the cell surface. This interaction triggers intracellular signaling cascades, including the Ras-MAPK pathway and PI3K-Akt pathway, regulating gene expression and cellular responses.
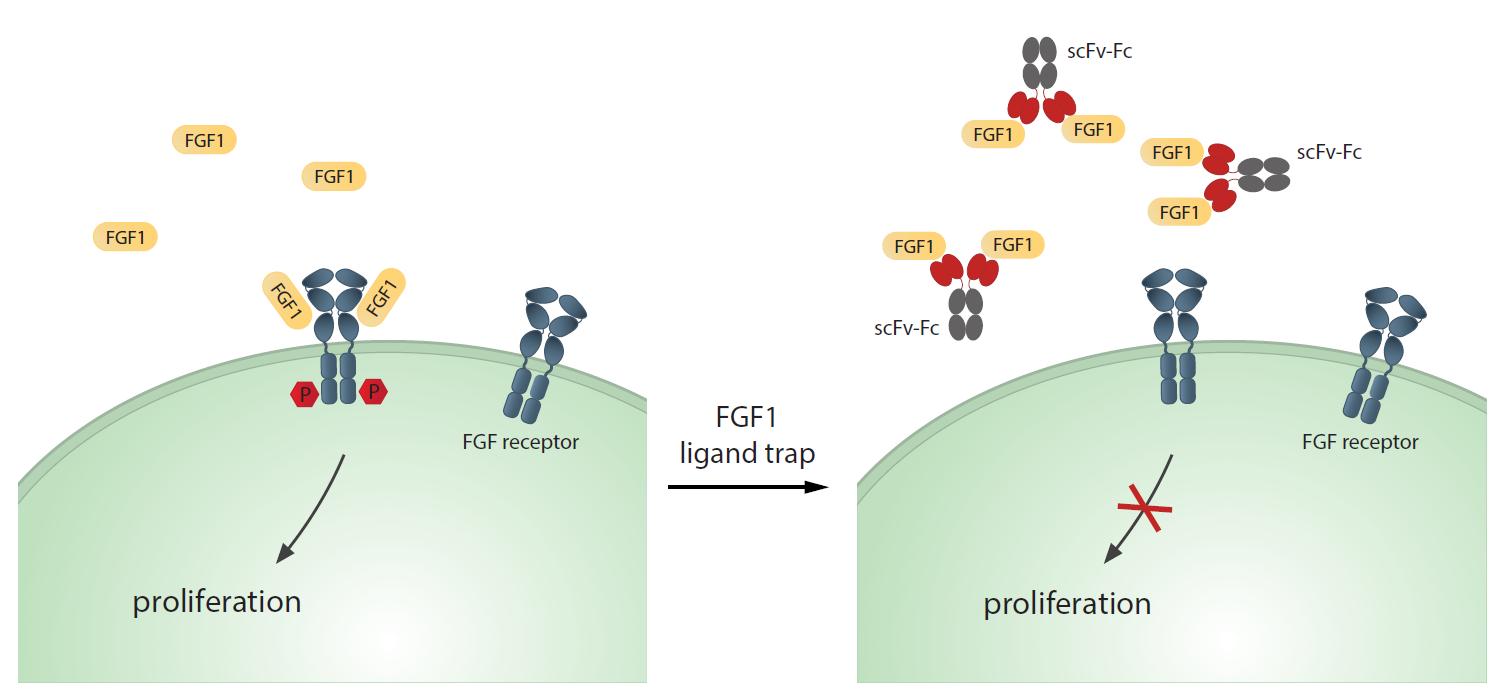
Figure 1. Specific antibody fragment ligand traps blocking FGF1 activity. (Chudzian J, et al., 2018)
FGF1 Related Signaling Pathway
The FGF1 signaling pathway is a complex network of interactions that govern cellular responses. Upon binding to FGFRs, FGF1 activates downstream effectors, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. These pathways regulate processes such as cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. Understanding the intricacies of the FGF1 signal pathway is crucial for developing targeted therapies for diseases associated with FGF1 dysregulation.
FGF1 Related Diseases
While FGF1 is crucial for normal physiological processes, dysregulation of its signaling pathways can contribute to various diseases. Aberrant FGF1 expression has been implicated in cancer, where its mitogenic properties may drive uncontrolled cell growth. Additionally, FGF1 has been associated with inflammatory disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting its intricate role in both health and pathology.
FGF1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of FGF1 make it a promising candidate for various biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, FGF1 can serve as a biomarker for diseases where its expression is dysregulated. Its involvement in angiogenesis also positions it as a potential target for therapeutic interventions in conditions characterized by abnormal blood vessel formation, such as certain cancers.
Moreover, FGF1 holds promise in vaccine development, as it plays a role in immune responses. Harnessing its immunomodulatory properties may contribute to the design of novel vaccines with enhanced efficacy. In therapeutics, FGF1-based treatments are being explored for conditions like tissue injury and ischemic diseases, where its ability to promote cell proliferation and angiogenesis could facilitate tissue regeneration.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF1-12861H | Recombinant Human FGF1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| FGF1-2528H | Recombinant Human FGF1 Protein (Phe16-Asp155) | Human | E.coli | Tag Free |
| FGF1-26555TH | Recombinant Human FGF1, His-tagged | Human | His | |
| FGF1-255H | Recombinant Human FGF1 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| FGF1-547H | Recombinant Human FGF1 protein, His & GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| FGF1-3224M | Recombinant Mouse FGF1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Fgf1-403F | Active Recombinant Mouse Fgf1 Protein (140 aa) | Mouse | E.coli | |
| Fgf1-056M | Active Recombinant Mouse Fgf1 Protein | Mouse | E.coli | |
| Fgf1-496M | Recombinant Mouse Fgf1, His-tagged | Mouse | Mouse | His |
| Fgf1-558M | Recombinant Mouse Fgf1 protein | Mouse | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Chudzian J, et al. Specific antibody fragment ligand traps blocking FGF1 activit. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018, 19(9): 2470.

