What is FZR1 Protein
In the intricate world of molecular biology, proteins play a pivotal role in regulating various cellular processes. One such protein that has garnered significant attention is the FZR1 protein.
FZR1, also known as Fizzy-related protein 1, stands as a key player in the intricate machinery that controls the cell cycle. Encoded by a highly conserved gene, FZR1's ubiquity across various organisms underscores its evolutionary importance. As a critical component of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C) E3 ubiquitin ligase, FZR1 emerges as a linchpin in the finely tuned mechanisms governing cell division.
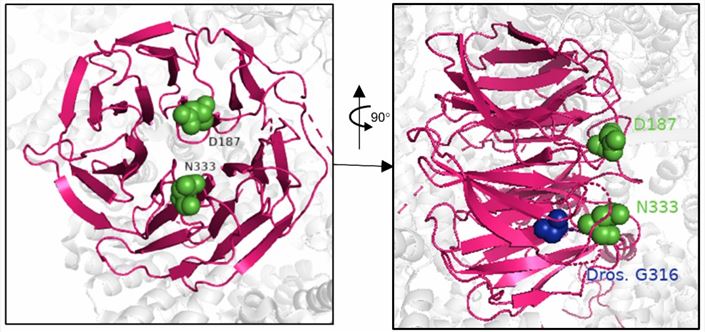 Figure 1. 3D structural model FZR1 as part of the Cdh1-APC. (Manivannan, S.N., et al. 2022)
Figure 1. 3D structural model FZR1 as part of the Cdh1-APC. (Manivannan, S.N., et al. 2022)The Function of FZR1 Protein
At the heart of FZR1's function lies its prowess in orchestrating the transition from metaphase to anaphase during cell division. Collaborating with the APC/C complex, FZR1 meticulously regulates the degradation of key cell cycle regulators. Cyclin B and securin, essential players in mitotic progression, succumb to FZR1-mediated ubiquitin tagging, ensuring a seamless exit from mitosis.
In the complex choreography of the cell cycle, FZR1 acts as a conductor, precisely cueing the degradation of cyclin B to halt mitotic progression. This degradation unleashes separase by liberating securin's inhibitory grasp, facilitating the orderly separation of sister chromatids. The pivotal role of FZR1 in these regulatory processes showcases its significance in maintaining the fidelity of cell division.
FZR1-Related Diseases
The spotlight on FZR1 intensifies as its dysregulation emerges as a potential harbinger of diseases, notably cancer. Perturbations in FZR1 expression or function can throw the delicate balance of cell division into disarray, propelling uncontrolled proliferation—a hallmark of malignancy. Studies have identified altered FZR1 levels in various cancer types, cementing its status as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker.
Beyond the realm of cancer, FZR1's fingerprints are evident in developmental disorders and neurodegenerative diseases. Its involvement in safeguarding genomic stability positions FZR1 as a guardian of cellular health, extending its relevance beyond the confines of the cell cycle.
FZR1 Related Signaling Pathways
FZR1 participates in the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) and mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC) pathways. SAC's vigilant monitoring of chromosome-spindle attachments prompts FZR1 to restrain APC/C activity when errors are detected. This enforced pause provides the cellular machinery with the opportunity to rectify anomalies before permitting cell cycle progression, showcasing FZR1's role as a sentinel for genomic integrity.
Delving deeper, FZR1's interaction with the tumor suppressor p53 intertwines its fate with the cellular response to DNA damage. The partnership between FZR1 and p53 underlines FZR1's involvement in broader cellular surveillance mechanisms, emphasizing its role in maintaining genetic stability.
Applications of FZR1 in Biomedical Research
The multifaceted role of FZR1 extends its influence into the realm of biomedicine, offering a trove of potential applications. Targeting FZR1 emerges as a promising strategy in cancer therapeutics. Modulating its expression or activity holds the key to restoring normal cell cycle regulation, inducing cell cycle arrest, or prompting apoptosis in cancer cells.
Beyond cancer, FZR1's involvement in DNA damage response positions it as a potential therapeutic target for diseases characterized by genomic instability. Manipulating FZR1 could potentially enhance DNA repair mechanisms, presenting a novel avenue for addressing conditions marked by DNA damage accumulation.
The diagnostic and prognostic potential of FZR1 takes center stage in biomedicine. Monitoring FZR1 levels in patient samples could unveil critical insights into the state of the cell cycle, aiding in disease diagnosis and prognostication. Furthermore, FZR1's interaction with p53 suggests its potential as a biomarker for assessing DNA damage and cellular stress responses, enriching the diagnostic landscape.
In the intricate tapestry of cellular processes, FZR1 emerges as a pivotal player, governing the precise execution of cell division and safeguarding genomic integrity. Its implication in diseases, intricate signaling pathways, and promising applications in biomedicine underscore the profound impact of unraveling the mysteries of FZR1. As research advances, the exploration of FZR1 unveils new possibilities, offering a deeper understanding of cellular dynamics and paving the way for innovative therapeutic interventions in the ever-evolving landscape of molecular biology.
Recommended Products for FZR1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FZR1-950H | Human | Recombinant Human FZR1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| FZR1-4601H | Human | Recombinant Human FZR1 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| FZR1-1160H | Human | Recombinant Human FZR1 Protein (1-493 aa), His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | His/SUMO |
| FZR1-5093HF | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human FZR1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| FZR1-1049HFL | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human FZR1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| Fzr1-3120M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Fzr1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| FZR1-1778R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus monkey FZR1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | His |
| FZR1-1599R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque FZR1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| FZR1-5730C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken FZR1 | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Manivannan, S.N., et al. De novo FZR1 loss-of-function variants cause developmental and epileptic encephalopathies. Brain. 2022, 145(5): 1684-1697.

