What is TREM1 Protein
In the intricate world of molecular biology, the TREM1 protein stands out as a key player with multifaceted roles. Also known as triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1, TREM1 has gained increasing attention in the scientific community due to its diverse functions and implications in various physiological and pathological processes.
TREM1, a sentinel on the surface of myeloid cells, boasts a unique structure. Comprising an extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain, a transmembrane section, and a succinct cytoplasmic tail, TREM1 plays a pivotal role in immune modulation. Expressing primarily on macrophages and neutrophils, TREM1 acts as a gatekeeper, sensing microbial challenges and orchestrating the ensuing immune responses.
The Function of TREM1 Protein
At its core, TREM1 operates as an amplifier of inflammatory responses. Upon encountering microbial products like lipopolysaccharides (LPS), TREM1 engages in a complex interplay, activating downstream signaling pathways. The interaction with the adaptor protein DAP12 sets the stage for the recruitment of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk), unleashing a cascade of events.
The MAPK pathway, a linchpin in TREM1 signaling, witnesses the phosphorylation of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK. Simultaneously, the NF-κB pathway comes into play, translocating NF-κB into the nucleus. This orchestrated activation results in an exaggerated immune response, essential for pathogen elimination but potentially perilous if uncontrolled.
TREM1-Related Diseases
The dual nature of TREM1, as a defender against pathogens and a potential instigator of tissue damage, is evident in its association with various diseases. In conditions such as sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), dysregulation of TREM1 has been implicated.
In sepsis, TREM1 takes center stage as its expression escalates, signifying its potential as a biomarker for disease severity. Meanwhile, in rheumatoid arthritis, TREM1 contributes to the perpetuation of inflammation and joint damage. The intricate involvement of TREM1 in IBD underlines its role in the dysregulated immune response characteristic of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
TREM1 Related Signaling Pathways
Understanding the signal pathways associated with TREM1 activation is crucial for developing targeted therapies to modulate its effects in various diseases. The binding of TREM1 to its ligands initiates a cascade of intracellular events, ultimately leading to the amplification of inflammatory responses.
One of the key players in TREM1 signaling is the adaptor protein DAP12. Upon ligand binding, TREM1 associates with DAP12, resulting in the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic tail of DAP12. This event recruits Syk, a tyrosine kinase, and triggers downstream signaling pathways.
The MAPK pathway is activated, leading to the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK. These activated kinases translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate the expression of genes involved in inflammation and immune responses.
Simultaneously, the NF-κB pathway is activated, leading to the translocation of NF-κB into the nucleus. NF-κB regulates the expression of a wide array of genes involved in inflammation, immune response, and cell survival. The coordination of these pathways results in the robust amplification of the immune response mediated by TREM1.
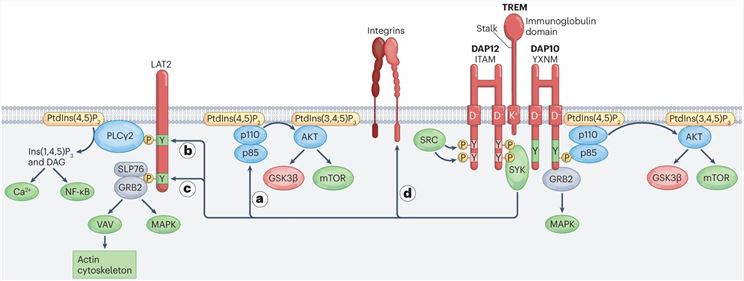 Figure 1. TREM activating signals through DAP12 and DAP10. (Colonna, M. 2023)
Figure 1. TREM activating signals through DAP12 and DAP10. (Colonna, M. 2023)Applications of TREM1 in Biomedical Research
The burgeoning landscape of biomedical research is witnessing a surge in interest surrounding TREM1, paving the way for innovative applications and therapeutic avenues.
- Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases
Targeting TREM1 emerges as a promising strategy in mitigating inflammatory diseases. Inhibition of TREM1 signaling holds the potential to curtail excessive inflammation, offering a beacon of hope for conditions like sepsis, rheumatoid arthritis, and IBD.
- Biomarker for Disease Severity
TREM1's upregulation in diseases like sepsis positions it as a potential biomarker for disease severity. Monitoring TREM1 expression levels could serve as a valuable tool for clinicians in assessing disease progression and tailoring interventions accordingly.
- Immunotherapy Approaches
The intricate interplay between TREM1 and the tumor microenvironment has kindled interest in exploring its role in cancer immunotherapy. Targeting TREM1 could pave the way for novel strategies to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapies in the fight against cancer.
- Pharmacological Modulation of TREM1
The quest for precision in biomedical interventions has led to the exploration of small molecules or biologics that selectively modulate TREM1 activity. These pharmacological interventions hold promise in offering precise control over TREM1-mediated immune responses.
TREM1 protein, with its pivotal role in amplifying immune responses, has emerged as a fascinating subject of study in the realm of molecular biology. From its structural features to its involvement in signal pathways and implications in diseases, TREM1 continues to captivate researchers worldwide. The ongoing exploration of TREM1's applications in biomedical research holds promise for innovative therapeutic strategies and diagnostic approaches. As our understanding of TREM1 deepens, we move closer to unraveling the intricate web of immune regulation and inflammation, paving the way for transformative advancements in medicine.
Recommended Products for TREM1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TREM1-7203H | Human | Recombinant Human Triggering Receptor Expressed On Myeloid Cells 1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| TREM1-285H | Human | Recombinant Human Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| TREM1-3842H | Human | Recombinant Human TREM1, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| TREM1-886H | Human | Recombinant Human TREM1, Fc-His tagged | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| TREM1-167H | Human | Recombinant Human TREM1 protein, T7/His-tagged | E.coli | T7/His |
| TREM1-116H | Human | Recombinant Human TREM1 Protein, C-His-tagged | E.coli | C-His |
| Trem1-213M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Trem1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| Trem1-17319M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Trem1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| TREM1-1779R | Rhesus monkey | Recombinant Rhesus Monkey TREM1 Protein | HEK293 | N/A |
| TREM1-1781R | Rhesus monkey | Recombinant Rhesus Monkey TREM1 Protein, hIgG4-tagged | HEK293 | hIgG4 |
Reference
- Colonna, M. The biology of TREM receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023, 23: 580–594.

