What is XIAP Protein
The X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) protein, officially known as BIRC4 (Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 4), stands as a sentinel in the intricate world of cellular processes. Synonyms for XIAP include IAP-3, API3, MIHA, and ILP-1. As a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family, XIAP is recognized for its role in regulating programmed cell death, or apoptosis.
XIAP Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, XIAP harbors three Baculoviral IAP Repeat (BIR) domains and a RING (Really Interesting New Gene) domain. The BIR domains play a pivotal role in protein-protein interactions, enabling XIAP to engage with various partners in the cellular milieu. Classification-wise, XIAP falls into the class of anti-apoptotic proteins, countering the cell's natural inclination toward self-destruction.
XIAP Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
XIAP is renowned for its prowess in suppressing apoptosis, the controlled process of cell death crucial for development and tissue maintenance. The protein achieves this by inhibiting the activity of caspases, which are key executioners of apoptosis. XIAP's BIR domains interact with caspases, particularly caspase-3, -7, and -9, stifling their enzymatic activity and preventing the execution of the cell death program.
Beyond its role in apoptosis, XIAP has emerged as a multifunctional player in cellular dynamics. Recent insights indicate its involvement in autophagy, a process by which cells recycle and eliminate damaged components. XIAP appears to modulate autophagy by interacting with key autophagic proteins, shedding light on its broader impact on cellular quality control mechanisms.
Moreover, XIAP is implicated in inflammatory responses. Its interaction with signaling molecules involved in inflammation suggests a role in the intricate web of immune regulation. These multifaceted functions underscore XIAP's significance as a pivotal regulator of cellular fate.
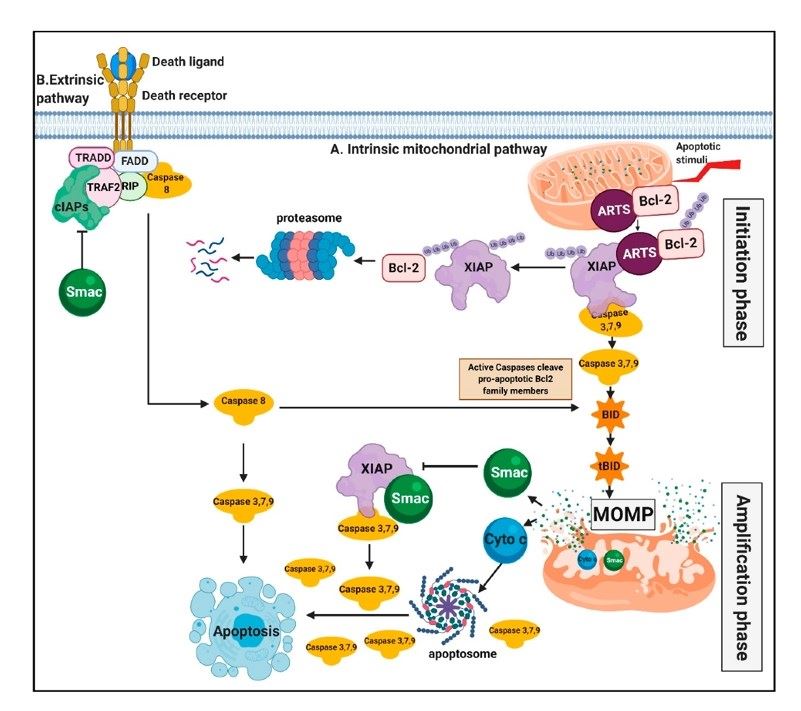
Figure 1. Targeting XIAP for promoting cancer cell death. (Abbas R, et al., 2020)
XIAP Related Signaling Pathway
XIAP is a key player in the regulation of apoptotic pathways, particularly the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. In the intrinsic pathway, XIAP inhibits caspase-9 activation, blocking the mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic cascade. In the extrinsic pathway, XIAP hinders caspase-3 activation, impeding the signal transduction initiated by death receptors.
Moreover, XIAP is involved in the NF-κB signaling pathway, influencing inflammation and immune responses. Through its interactions with signaling molecules, XIAP modulates the activation of NF-κB, affecting the transcription of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses.
XIAP Related Diseases
Dysregulation of XIAP has been associated with various diseases, marking it as a potential therapeutic target. In cancer, elevated levels of XIAP contribute to aberrant cell survival, promoting tumor growth and resistance to chemotherapy. Conversely, decreased XIAP expression has been observed in neurodegenerative disorders, hinting at its involvement in maintaining neuronal integrity.
Inflammatory conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, showcase an intricate interplay between XIAP and the immune system. Understanding these associations provides a foundation for developing targeted interventions to modulate XIAP levels and restore cellular balance in disease states.
XIAP's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatile nature of XIAP has spurred interest in its applications in biomedical research and development. In diagnostic development, XIAP's altered expression patterns in diseases make it a potential biomarker for early detection and prognosis assessment. Leveraging XIAP as a diagnostic tool holds promise for identifying conditions where its dysregulation plays a pivotal role.
In the realm of vaccine development, XIAP's role in modulating immune responses opens avenues for enhancing vaccine efficacy. Harnessing XIAP's ability to fine-tune the immune system could lead to the design of vaccines with improved immunogenicity and efficacy.
From a therapeutic standpoint, targeting XIAP presents a compelling strategy for diseases characterized by dysregulated apoptosis, such as certain cancers. Small molecules and therapeutic agents designed to modulate XIAP activity are under investigation, holding the potential to tilt the balance in favor of controlled cell death in cancer cells.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XIAP-3103H | Active Recombinant Human XIAP protein, Avi-tagged | Human | E.coli | Avi |
| XIAP-226H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| XIAP-245H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein, GST/StrepII-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST/StrepII |
| XIAP-410H | Recombinant Human XIAP, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| XIAP-399H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| XIAP-247H | Recombinant Human XIAP protein, His-SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His-SUMO |
| XIAP-2365H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| XIAP-0712H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein (Y120-P260), GST tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| XIAP-2775H | Recombinant Human XIAP Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| XIAP-1757HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human XIAP Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
Reference
- Abbas R, Larisch S. Targeting XIAP for promoting cancer cell death—the story of ARTS and SMAC. Cells. 2020, 9(3): 663.

