GRN
-
Official Full Name
granulin -
Overview
Granulins are a family of secreted, glycosylated peptides that are cleaved from a single precursor protein with 7.5 repeats of a highly conserved 12-cysteine granulin/epithelin motif. The 88 kDa precursor protein, progranulin, is also called proepithelin and PC cell-derived growth factor. Cleavage of the signal peptide produces mature granulin which can be further cleaved into a variety of active, 6 kDa peptides. These smaller cleavage products are named granulin A, granulin B, granulin C, etc. Epithelins 1 and 2 are synonymous with granulins A and B, respectively. Both the peptides and intact granulin protein regulate cell growth. However, different members of the granulin protein family may act as inhibitors, stimulators, or have dual actions on cell growth. Granulin family members are important in normal development, wound healing, and tumorigenesis. -
Synonyms
GRN;granulin;GEP;GP88;PEPI;PGRN;PCDGF;progranulin;Acrogranin;Granulin-1;Granulin G;Granulin-2;Granulin F;Granulin-3;Granulin-4;Granulin-5;Granulin-6;Granulin-7;Granulin A;Granulin C;Granulin D;Granulin E;granulin-epithelin;proepithelin;PC cell-derived growth factor
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Flag
- Non
- S
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is GRN protein?
GRN gene (granulin precursor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. Granulins are a family of secreted, glycosylated peptides that are cleaved from a single precursor protein with 7.5 repeats of a highly conserved 12-cysteine granulin/epithelin motif. The 88 kDa precursor protein, progranulin, is also called proepithelin and PC cell-derived growth factor. Cleavage of the signal peptide produces mature granulin which can be further cleaved into a variety of active, 6 kDa peptides. These smaller cleavage products are named granulin A, granulin B, granulin C, etc. Epithelins 1 and 2 are synonymous with granulins A and B, respectively. Both the peptides and intact granulin protein regulate cell growth. However, different members of the granulin protein family may act as inhibitors, stimulators, or have dual actions on cell growth. The GRN protein is consisted of 593 amino acids and GRN molecular weight is approximately 63.5 kDa.
What is the function of GRN protein?
GRN protein, also known as progranulin, is a secreted glycoprotein that plays a variety of roles in the body, including the regulation of cell growth, inflammation, wound healing, and cell proliferation. In the context of the brain, progranulin is considered neuroprotective and has a role in neuroinflammation. It is primarily found in lysosomes, which are cellular compartments responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and materials. Within lysosomes, progranulin can be cleaved into smaller proteins called granulins, which are thought to share similar functions with progranulin. It also functions as a growth factor that acts on dermal fibroblasts and endothelial cells, promoting division, migration, and the formation of capillary-like tubule structures.
GRN Related Signaling Pathway
GRN is able to activate these pathways to promote cell mitosis. In nerve cells, GRN promotes the survival of neurons during toxic damage by activating the MAPK and PI3K-AKT pathways. GRN may exert its physiological function through Wnt signaling pathway. In neural stem cells knocked out by the GRN gene, the expression of multiple members of the Wnt signaling pathway changed, indicating that the pathway was activated. GRN can inhibit caspase pathway and reduce cell apoptosis. In GRN knockout mouse cortical neurons, caspase activation was increased and apoptosis was increased. GRN can bind to tumor necrosis factor receptor TNFR2 as an anti-inflammatory factor to affect TNF-mediated inflammatory signaling pathways.
GRN Related Diseases
When the GRN gene is mutated or its expression levels are abnormal, it is associated with a variety of diseases, especially neurodegenerative diseases. Grn-related diseases mainly include frontotemporal lobular degeneration (FTLD), a degenerative encephalopathy affecting the frontal and temporal lobes, often caused by heterozygous mutations in the GRN gene and associated with pathological aggregation of the TDP-43 protein. In addition, loss of function of GRN is also associated with an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD). In non-neurodegenerative diseases, abnormal expression of GRN is also associated with inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis (OA). PGRN plays a role in the pathogenesis of these diseases by influencing pathways such as autophagy, metabolism, inflammatory response, and cell survival.
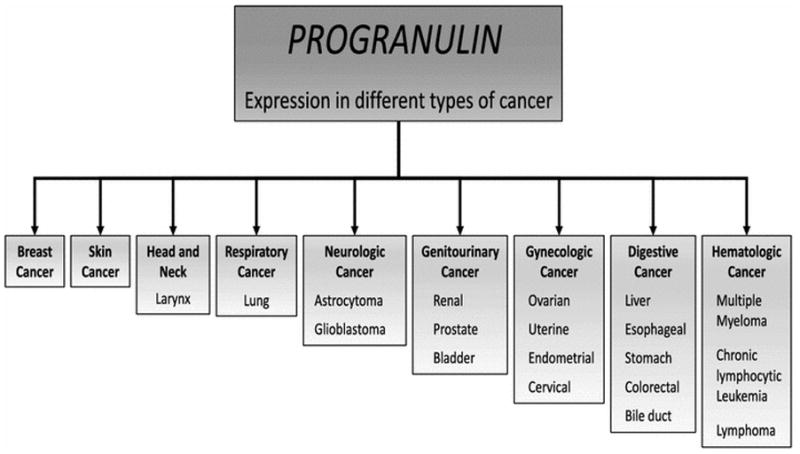
Fig1. Progranulin expression in cancer. (Fabian Arechavaleta-Velasco, 2017)
Bioapplications of GRN
As a neuroprotective factor, GRN's role in regulating inflammation, promoting cell survival, and participating in tissue repair makes it a potential therapeutic target for treating neurodegenerative and other inflammatory diseases. In terms of clinical diagnosis, changes in the level of GRN or its related proteins, such as the neurofilament light chain NfL, can be used as biomarkers to reflect disease activity and monitor disease progression.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Christopher Lee, 2023
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) refers to a group of neurodegenerative disorders that are characterized by pathology predominantly localized to the frontal and temporal lobes. Approximately 40% of FTD cases are familial, and up to 20% of these are caused by heterozygous loss of function mutations in the gene encoding for progranulin (PGRN), GRN. The mechanisms by which loss of PGRN leads to FTD remain incompletely understood. Here, researchers utilized human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-derived neural tissue carrying a homozygous GRN R493X-/- knock-in mutation to investigate in vitro whether GRN mutant astrocytes have a non-cell autonomous effect on neurons. Using microelectrode array (MEA) analysis, they demonstrate that the development of spiking activity of neurons cultured with GRN R493X-/- astrocytes was significantly delayed compared to cultures with WT astrocytes. Histological analysis of synaptic markers in these cultures showed an increase in GABAergic synaptic markers and a decrease in glutamatergic synaptic markers during this period when activity was delayed.
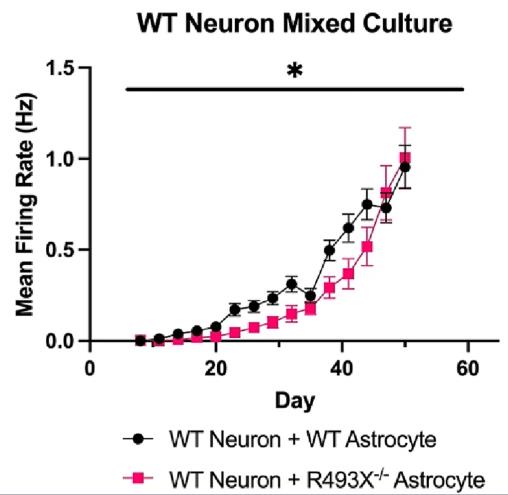
Fig1. Compared to WT astrocytes, R493X−/− astrocytes delayed development of excitatory electrical signaling in both WT neurons.
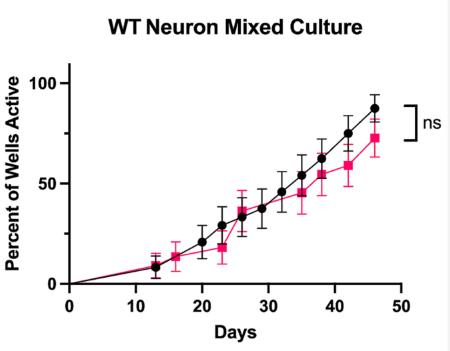
Fig2. Percent active wells was assessed using the Active Electrodes metric and represented as a percent of total wells for WT neuron mixes.
Case Study 2: Lianlian Liu, 2020
Macrophage M1 polarization plays a pivotal role in inflammatory diseases. Progranulin (PGRN) has potential anti-inflammation action, however, the effect of PGRN on macrophage M1 polarization has been poorly studied. This study aimed to investigate the effect of PGRN on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage M1 polarization and clarify the underlying mechanisms. RAW264.7 cells were polarized to M1 macrophage by LPS with or without recombinant PGRN (rPGRN) and tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody (anti-TNF-α). The phenotype of polarized cells was identified, and the expression level of signaling molecules in key pathways was determined. The results showed that in RAW264.7 cells, rPGRN at concentrations below 80 ng/ml significantly promoted cell proliferation in dose dependent fashion. rPGRN significantly inhibited LPS-induced change of phenotype (CD86/CD206 ratio) and function (tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expressions).
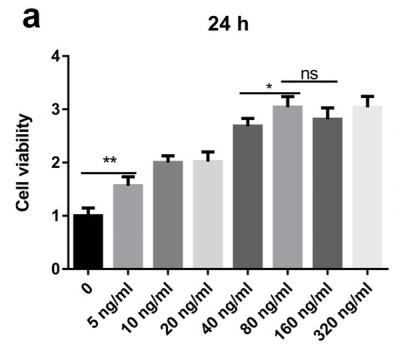
Fig3. The effect of 5, 10, 20, 40, 80,160 and 320 ng/ml rPGRN on RAW264.7 after treatment for 24 h.
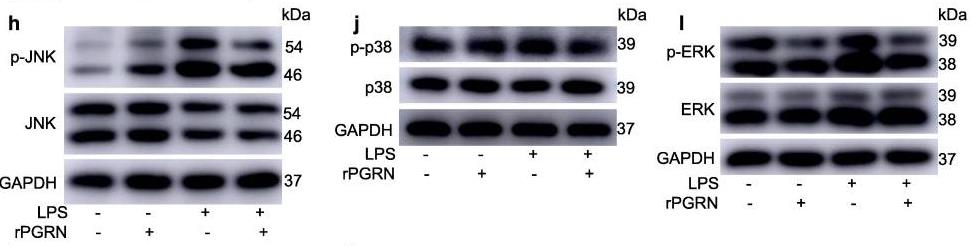
Fig4. Effects of PGRN on LPS-induced activation of MAPK pathways.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GRN-7847H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GRN-3063H)
Involved Pathway
GRN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GRN participated on our site, such as Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GRN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Integrated Breast Cancer Pathway | LGALS13,NAB1,NOXA1,USP38,ZMIZ1,GDI1,CCNB1IP1,SMARCA4,AHR,DCAKD |
Protein Function
GRN has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,growth factor activity,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GRN itself. We selected most functions GRN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GRN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | TOX4,ZNF567,CYC1,AP5S1,PTPLAD1,PRPF8,TSC22D3,PYROXD1,PRSS21,RCOR3 |
| growth factor activity | BMP1,IL7,EPGN,IGF3,BMP15,IL8L2,FGF12A,INHBAA,VEGFC,FGF10A |
| poly(A) RNA binding | SNRNP200,NUSAP1,APOBEC3B,KPNA2,FAM103A1,U2AF1,POLR2A,UBAP2L,LSM14A,DDX24 |
| cytokine activity | GPR19,IFNK,TNFSF15,GDF11,HMGB1B,CMTM8,IL34,IL8L2,IL23,NAMPT |
Interacting Protein
GRN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GRN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GRN.
GLRX3;HOXA1;TNFRSF1A;TNFRSF1B;80125
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Igarashi, K; Ochiai, K; et al. Orchestration of plasma cell differentiation by Bach2 and its gene regulatory network. IMMUNOLOGICAL REVIEWS 261:116-125(2014).
- Evans, RL; Pottala, JV; et al. Classifying Patients for Breast Cancer by Detection of Autoantibodies against a Panel of Conformation-Carrying Antigens. CANCER PREVENTION RESEARCH 7:545-555(2014).




