RPS6KB1
-
Official Full Name
ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70kDa, polypeptide 1 -
Overview
p70S6K is responsible for the phosphorylation of 40Sribosomal protein S6, and is ubiquitously expressed inhuman adult tissues (1). p70S6K is activated by serumstimulation and this activation is inhibited by wortmanninand rapamycin. p70S6k activity changes during the cellcycle, and increases 20-fold in G1 cells released from G0(2). p70S6K activation requires sequential phosphorylationat proline-directed residues in the putative autoinhibitorypseudosubstrate domain, as well as threonine 389, a sitephosphorylated by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1(PDK-1). -
Synonyms
RPS6KB1;ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70kDa, polypeptide 1;ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 70kD, polypeptide 1 , STK14A;ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1;p70(S6K) alpha;PS6K;S6K1;P70S6K1;p70 S6KA;S6K-beta-1;p70 S6K-alpha;p70 S6 kinase, alpha 1;p70 S6 kinase, alpha 2;ribosomal protein S6 kinase I;serine/threonine kinase 14 alpha;serine/threonine-protein kinase 14A;70 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1;S6K;STK14A;p70-S6K;p70-alpha;p70(S6K)-alpha
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
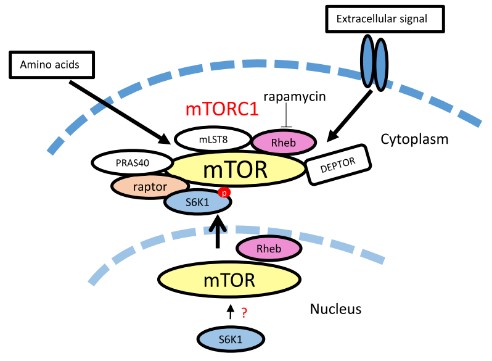
Fig1. Schematic of mTORC1 signalling in live cells showing possible S6K1 recruitment onto mTORC1. (Abdullah R Ahmed, 2019)
What is RPS6KB1 protein?
RPS6KB1 (ribosomal protein S6 kinase B1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q23. This gene encodes a member of the ribosomal S6 kinase family of serine/threonine kinases. The encoded protein responds to mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling to promote protein synthesis, cell growth, and cell proliferation. Activity of this gene has been associated with human cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been observed. The RPS6KB1 protein is consisted of 525 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 59.1 kDa.
What is the function of RPS6KB1 protein?
Activated RPS6KB1 promotes protein synthesis by phosphorylating multiple substrates, including ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) and other factors involved in mRNA translation, which affects cell growth and size. RPS6KB1 plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism, especially in the presence of adequate nutrition. It responds to cellular nutritional status and growth factor signals by regulating protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. RPS6KB1 is also involved in cellular responses to stress, such as oxidative stress and DNA damage. It may regulate cell survival and death by influencing the process of cell cycle and apoptosis. RPS6KB1 is involved in cell cycle regulation by phosphorylating cell cycle-related proteins, such as cycle-dependent kinase inhibitory protein p27^Kip1, which affects cell proliferation and differentiation.
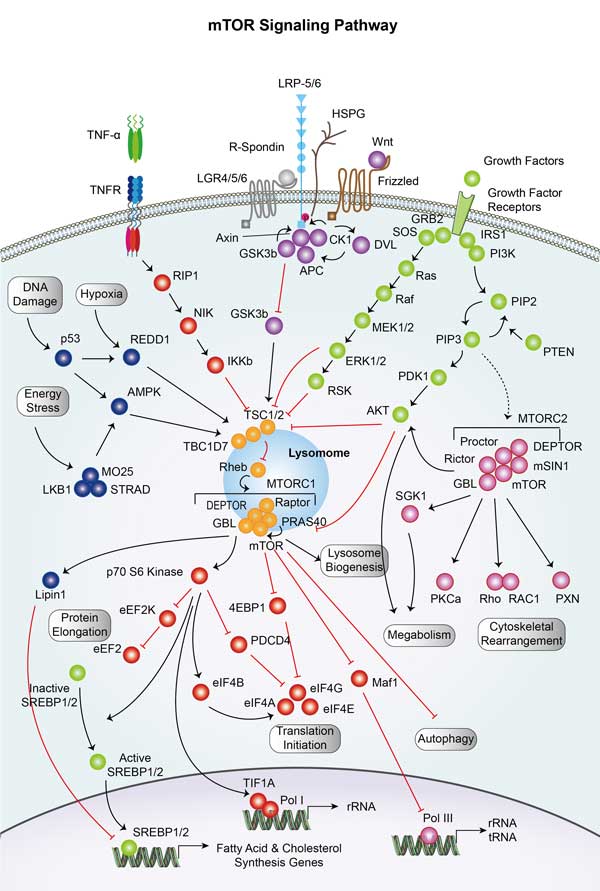
RPS6KB1 Related Signaling Pathway
RPS6KB1, also known as S6K1, is a serine/threonine kinase that is primarily involved in the mTOR signaling pathway. mTOR (Mammalian Target Protein) is a key protein kinase that integrates a variety of intracellular and extracellular signals, including growth factors, nutrient levels, energy status, and environmental stress, to regulate cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, and survival.
The role of S6K1 in the mTOR signaling pathway is primarily as a direct substrate for mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1). When mTORC1 is activated, it phosphorylates S6K1, which boosts its kinase activity. Activated S6K1 further phosphorylates its downstream substrates, including ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6), which is its best known substrate, a process that promotes protein synthesis and cell growth.
RPS6KB1 Related Diseases
RPS6KB1 is an important serine/threonine kinase, which is closely related to the occurrence and development of many diseases. Due to its role in protein synthesis, cell growth, and metabolic regulation, abnormal activity of RPS6KB1 has been associated with a variety of metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and obesity. In addition, RPS6KB1 also plays a key role in tumor biology, and its overactivation has been linked to the progression of multiple cancers such as breast cancer and lung cancer, making it a potential target for cancer therapy. RPS6KB1 is also associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis, and may be involved in the pathogenesis of these diseases by affecting cell signaling and cell survival pathways. In addition, RPS6KB1 is also associated with the pathological processes of rare diseases such as Tuberous Sclerosis and Lymphangioleiomyomatosis.
Bioapplications of RPS6KB1
As a marker of mTORC1 activity, S6K1 is often used to evaluate the effects of mTOR inhibitors and as a target or biomarker during drug screening and development. S6K1 is overactivated in many types of cancer, promoting the proliferation and survival of tumor cells. Therefore, the development of small molecule drugs that inhibit S6K1 activity could be used as a potential strategy for anti-cancer therapy, either alone or in combination with other treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kelsey Briggs, 2020
MuV is a member of the genus Rubulavirus, in the family Paramyxoviridae, and has a nonsegmented negative-strand RNA genome. The viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (vRdRp) of MuV consists of the large protein (L) and the phosphoprotein (P), while the nucleocapsid protein (NP) encapsulates the viral RNA genome. These proteins make up the replication and transcription machinery of MuV. The P protein is phosphorylated by host kinases, and its phosphorylation is important for its function. This study performed a large-scale small interfering RNA (siRNA) screen targeting host kinases that regulated MuV replication. The human kinase ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 (RPS6KB1) was shown to play a role in MuV replication and transcription. The role of RPS6KB1 in regulating MuV has been validated using siRNA knockdown, an inhibitor, and RPS6KB1 knockout cells. MuV grows better in cells lacking RPS6KB1, indicating that it downregulates viral growth. Furthermore, an interaction between the MuV P protein and RPS6KB1 was detected, suggesting that RPS6KB1 directly regulates MuV replication and transcription.
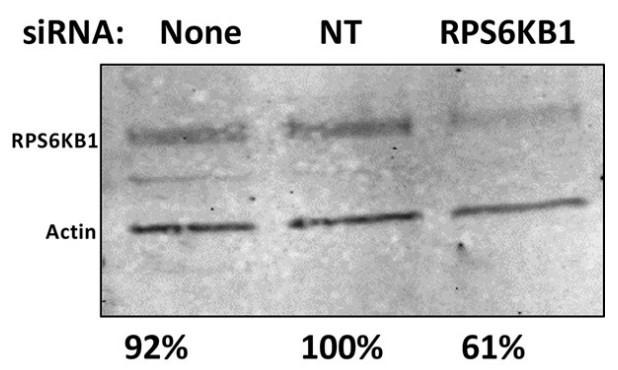
Fig1. Detection of RPS6KB1 using Western blot analysis.
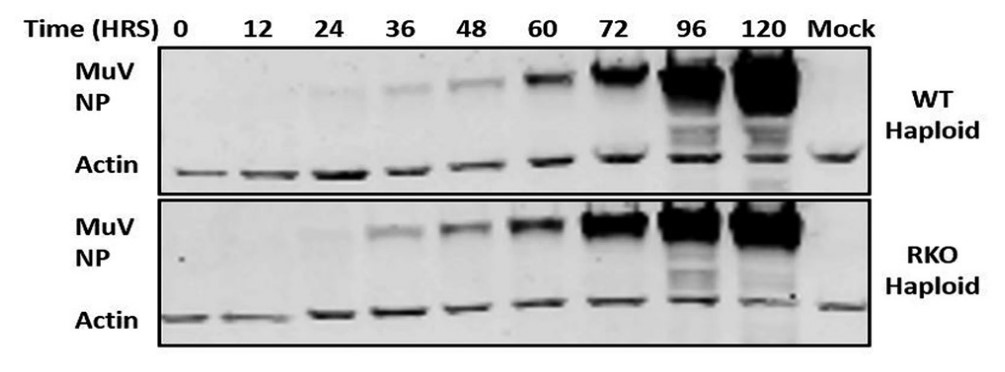
Fig2. Detection of MuV NP expression in WT and RPS6KB1-KO HapI cells.
Case Study 2: Abdullah R Ahmed, 2019
Knowledge of protein signalling pathways in the working cell is seen as a primary route to identifying and developing targeted medicines. In recent years there has been a growing awareness of the importance of the mTOR pathway, making it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in several diseases. Within this pathway the researchers have focused on S6 kinase 1 (S6K1), the downstream phosphorylation substrate of mTORC1, and specifically identify its juxtaposition with mTORC1. When S6K1 is co-expressed with raptor, S6K1 is translocated from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. By developing a novel biosensor they demonstrate in real-time, that phosphorylation and de-phosphorylation of S6K1 occurs mainly in the cytoplasm of living cells. Furthermore, the scaffold protein raptor, that typically recruits mTOR substrates, is not always involved in S6K1 phosphorylation.
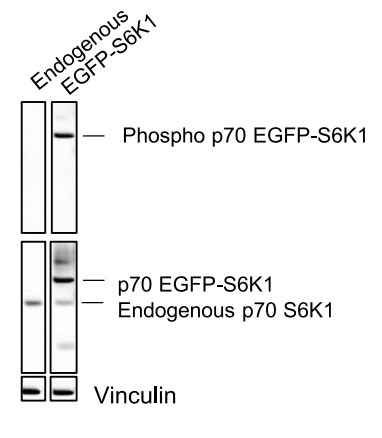
Fig3. Western blot validation of the functionality of the EGFP-S6K1 construct.
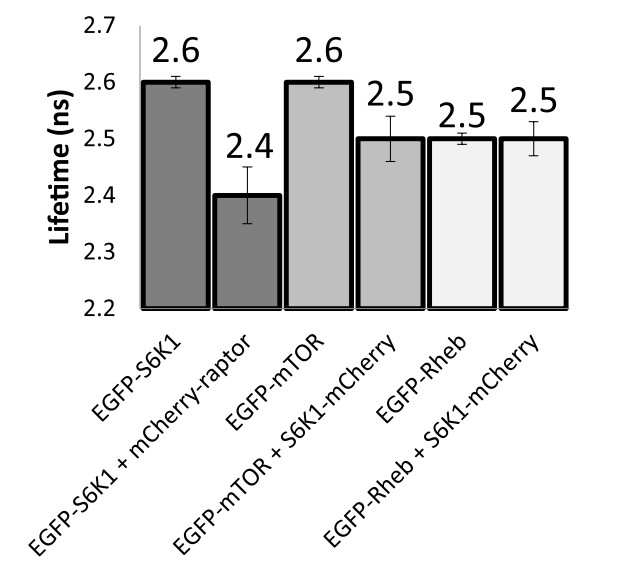
Fig4. Summary of FRET-FLIM studies for S6K1-mTORC1 interactions.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
RPS6KB1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RPS6KB1 participated on our site, such as ErbB signaling pathway,HIF- signaling pathway,mTOR signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RPS6KB1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Insulin resistance | PPP1CC,CREB3L3A,PIK3R1,PRKAG1,RPS6KAL,OGT,PRKAG2A,AKT2L,PYGM,NR1H2 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | FZD8,RHOA,PRKCG,SMO,GRB2,IGF2,PLAU,HOXD10,EZR,ARHGEF12 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | RHOA,SMAD2,SMAD6,BMP8B,TFDP1A,TGFBR1A,ID2A,NDR1,TGFBR2,NODAL |
| mTOR signaling pathway | PRKAA1,PRKCBB,TSC2,RPS6KA3A,EIF4E2,RPS6KA6,IGF1,TNF,CAB39,PRKCA |
| Insulin signaling pathway | PRKAR1AB,HRAS,INPP5K,CALM3A,G6PCA.2,FOXO1A,PTPRF,CALML5,CALML3,AKT3A |
| ErbB signaling pathway | SHC4,NRG2,MAPK8A,RAF1A,AKT2L,EGFRA,MAP2K7,MAP2K2A,ELK1,PIK3R5 |
| HIF- signaling pathway | IFNG,SLC2A1,NOX1,MAPK3,HK3,PDHB,PFKFB3,EP300,EGLN1,PIK3R2 |
| Fc gamma R-mediated phagocytosis | ASAP3,PRKCG,SYK,ARPC5L,MARCKSL1,PLA2G4F,LIMK2,PLA2G4D,MYO10,FCGR1 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | NGF,CCND3,IFNA1,IL4,FGF20,IFNA2,NFKB1,IFNA8,IL6R,F2R |
Protein Function
RPS6KB1 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,peptide binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RPS6KB1 itself. We selected most functions RPS6KB1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RPS6KB1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | DYRK1A,DYRK2,MAP2K2,RPS6KA1,CLK2,DYRK1AA,PRKCG,DSTYK,TESK1,PRKACA |
| ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity | RPS6KA1,RPS6KA3B,RPS6KB1B,RPS6KA2,RPS6KB2,RPS6KA3A,ALPK2,RPS6KA6,RPS6KA4,RPS6KA3 |
| ATP binding | MYO1EB,MAP3K3,EPHB4A,TTLL13,NTRK3,CDK19,MYLK2,STK25,MAPK12,DNA2 |
| protein kinase activity | PIK3C3,AKT3A,CAD,ARAF,AKT1,DYRK3,RIPK4,EPHB2B,CCL8,MAP2K4B |
| protein phosphatase 2A binding | PPP2R2A,PTPN1,MASTL,BCL2,AKT1,PPME1,STRN4,ARPP19,HMGCR,FOXO1 |
| protein binding | NUBP1,CETN3,MAGED1,C9orf142,CA2,FKBP6,MED24,XRCC5,NCOA3,HMG20B |
| peptide binding | Ctsl,HCRTR1,NPFFR1L2,OXTR,ANPEPA,TRHDE,PPYR1,PPIB,GPR37,ERAP2 |
Interacting Protein
RPS6KB1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RPS6KB1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RPS6KB1.
AKT1;EIF3B;COASY;PPP2R2B;MAPT;MAPT;PDK1;GLI1;HSP90AB1;STK11
RPS6KB1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References


.jpg)
.jpg)