Activin Modulator
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Activin Modulator Research
At Creative BioMart you can find a wide range of products related to activin modulators, including recombinant proteins and other key products. In addition, we offer customized services to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you get the product you need.
In addition to our products and services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. Our resources cover all aspects of activin modulators, including the involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources will be invaluable to researchers wishing to deepen their understanding of activin modulators and their role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FST-6937H | Active Recombinant Human FST protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| FST-3848H | Recombinant Human FST, Fc tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| FST-01H | Recombinant Human FST Protein, His-Tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| FSTL1-714H | Recombinant Human FSTL1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
About Activin Modulator
An activin modulator is a therapeutic agent that specifically targets the activin signaling pathway to regulate its activity. Activin is a protein that belongs to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) superfamily and plays a role in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cellular proliferation and differentiation.
Applications of Activin Modulators
Activin modulators have a range of potential applications in various fields. Here are some notable applications of activin modulators:
- Cancer treatment
- Fibrosis treatment
- Regenerative medicine
- Reproductive medicine
- Musculoskeletal disorders
- Neurological disorders
- Metabolic disorders
It's important to note that while activin modulators show promise in preclinical and clinical studies, further research and clinical trials are needed to evaluate their safety, efficacy, and optimal therapeutic applications in specific diseases.
Importance of Activin Modulator in Cell Signaling
Activin modulators play a significant role in cell signaling by specifically targeting the activin pathway. Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of activin modulators in cell signaling:
- Regulating Cellular Processes: Activin signaling is involved in the regulation of diverse cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Activin modulators can fine-tune these processes by either enhancing or inhibiting activin signaling, depending on the specific therapeutic application. By modulating activin activity, these agents can exert control over cellular responses, influencing tissue development, homeostasis, and repair.
- Disease Modulation: Dysregulation of activin signaling has been implicated in various diseases, making activin modulators valuable tools for therapeutic intervention. Activin agonists can stimulate activin signaling in conditions characterized by reduced activin activity, such as tissue damage and impaired tissue regeneration. By promoting activin-mediated cellular responses, these modulators can potentially enhance tissue repair and regeneration. On the other hand, activin antagonists are used to counteract excessive activin signaling, which is observed in certain diseases like cancer and fibrosis. By inhibiting activin activity, these modulators can help suppress pathological processes associated with abnormal activin signaling, such as tumor growth, metastasis, and fibrotic tissue remodeling.
- Specificity and Selectivity: Activin modulators offer the advantage of targeting a specific signaling pathway, namely the activin pathway, while minimizing interference with other signaling pathways. This specificity allows for more precise control over cellular responses and reduces the risk of off-target effects. By selectively modulating activin signaling, these agents can have a more tailored impact on cellular processes, making them potentially safer and more effective in therapeutic applications.
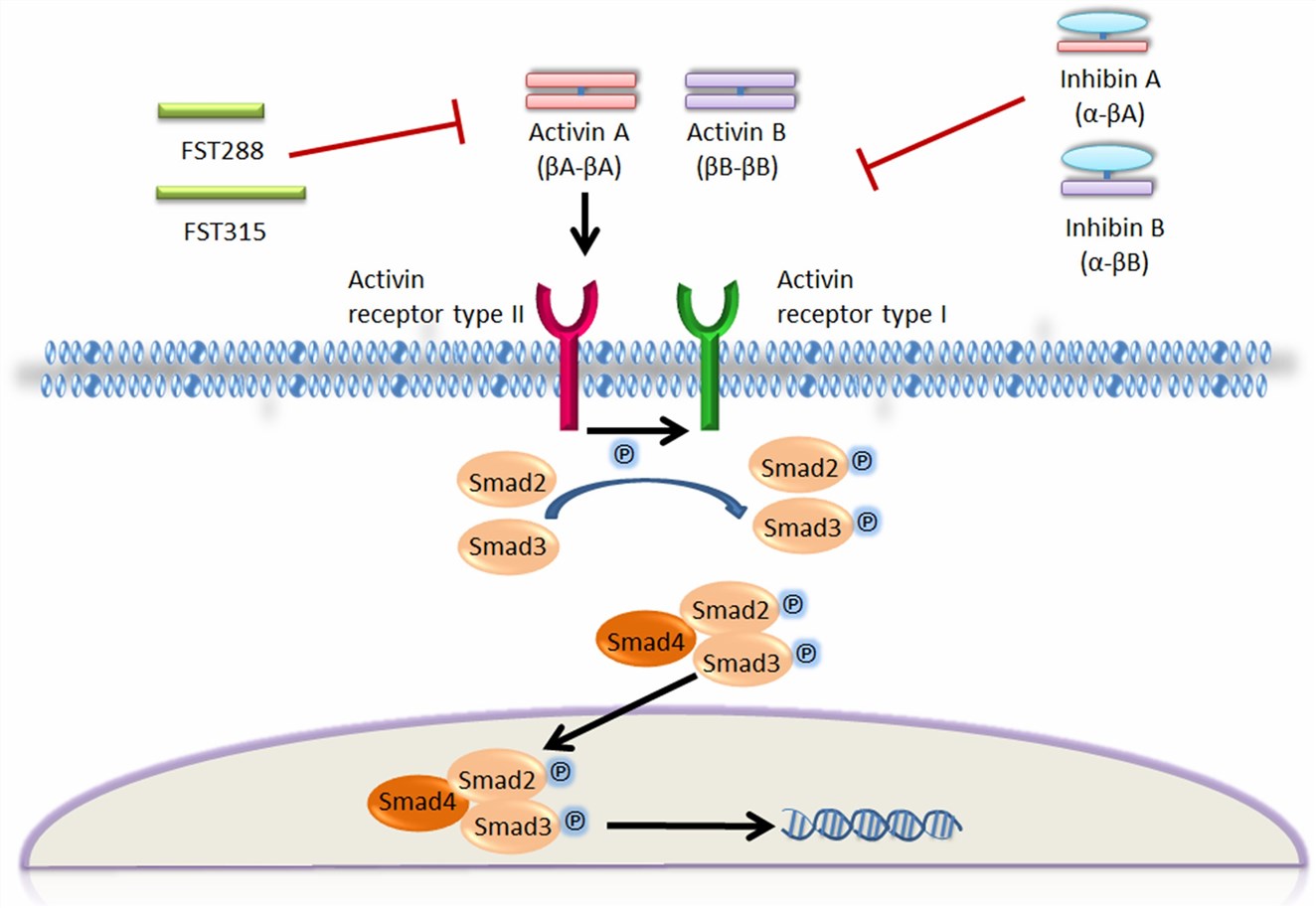 Fig.1 The activin signalling pathway. (R. Wijayarathna, et al., 2016)
Fig.1 The activin signalling pathway. (R. Wijayarathna, et al., 2016)
Activin binds to a type II receptor on the target cell surface. The type II receptor then binds to a type I receptor and causes phosphorylation of serine-threonine kinase residues. This leads to phosphorylation of SMAD2 and SMAD3, which form heteromeric transcription factor complexes with the common mediator, SMAD4. This complex is translocated to the nucleus, where they modulate target gene transcription. FST: follistatin.
Mechanism of Action of Activin Modulator
The mechanism of action of an activin modulator depends on whether it acts as an activin agonist or antagonist.
Activin Antagonists
Activin antagonists, also known as activin inhibitors, block or reduce the activity of activin signaling. They can target different steps in the activin signaling pathway to inhibit the binding of activin to its receptors or interfere with downstream signaling events. By inhibiting activin signaling, these antagonists can counteract the effects of excessive or dysregulated activin activity in certain diseases.
- Blocking Receptor Binding: Some activin antagonists work by binding to the activin ligand, preventing it from binding to its receptors. This prevents the initiation of downstream signaling events. Examples of activin antagonists that block receptor binding include soluble forms of activin receptors or antibodies that specifically bind to activin.
- Interfering with Downstream Signaling: Other activin antagonists can act downstream of receptor binding to disrupt intracellular signaling pathways. They may target components of the signaling cascade, such as receptor-associated proteins or downstream transcription factors, to inhibit activin-mediated gene expression and cellular responses.
Activin Agonists
Activin agonists, on the other hand, enhance or stimulate activin signaling. They work by promoting activin binding to its receptors and enhancing downstream signaling events. Activin agonists can be used when there is a deficiency or reduced activin activity in certain disease conditions.
- Enhancing Receptor Binding: Activin agonists can increase the binding affinity of activin to its receptors, allowing for more efficient receptor activation and signaling. This can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as modifying the activin ligand structure or designing molecules that interact with the receptor complex to enhance binding.
- Amplifying Downstream Signaling: Activin agonists can also amplify downstream signaling events by promoting the activation of intracellular signaling cascades involved in activin signaling. This can lead to increased gene expression and cellular responses mediated by activin.
The specific mechanism of action of an activin modulator can vary depending on the compound and its target within the activin signaling pathway. The goal of activin modulation is to restore or rebalance activin activity in a disease-specific manner, either by inhibiting excessive activin signaling or by enhancing reduced activin signaling.
Activin modulators hold potential for therapeutic applications in various diseases, including cancer, fibrosis, reproductive disorders, and regenerative medicine. However, further research and clinical studies are needed to evaluate their effectiveness, safety, and optimal usage in different disease contexts.
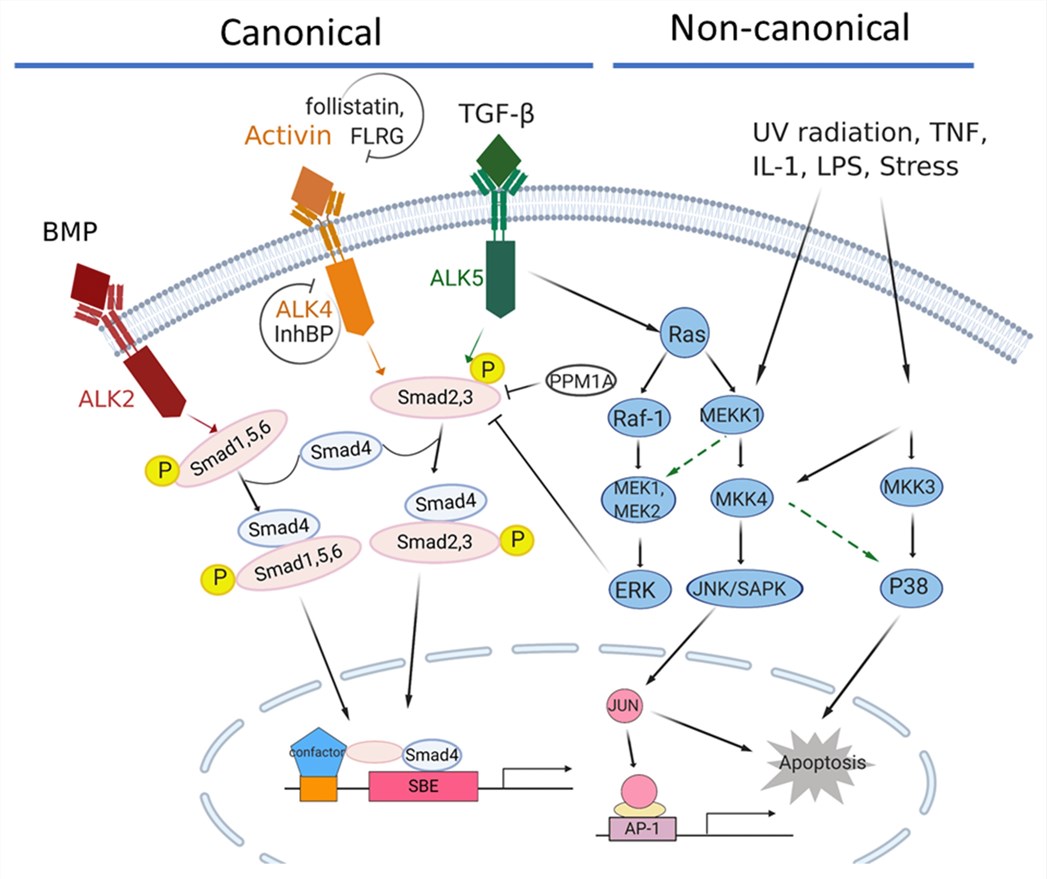 Fig.2 The activin/TGFβ signaling network in pancreatic cancer. (Qiu W, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 The activin/TGFβ signaling network in pancreatic cancer. (Qiu W, et al., 2021)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- R. Wijayarathna, D.M. de Kretser, Activins in reproductive biology and beyond, Human Reproduction Update, Volume 22, Issue 3, May/June 2016, Pages 342–357, https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmv058.
- Qiu W, Kuo C-Y, Tian Y, Su GH. Dual Roles of the Activin Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(7):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9070821

