Common Gamma-Chain Family
Creative BioMart Common Gamma-Chain Family Product List
Immunology Background
About Granulocyte Markers
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system by defending the body against foreign invaders such as bacteria and fungi. They are characterized by the presence of granules within their cytoplasm, which contain various enzymes and antimicrobial substances that aid in their function.
Granulocyte markers are proteins or molecules that are expressed on the surface of granulocytes and can be used to identify and differentiate them from other cell types. These markers serve as important tools in both research and clinical settings, allowing for the identification and characterization of granulocytes in various physiological and pathological conditions.
Some commonly used granulocyte markers include CD15, CD16, and CD66b. CD15, also known as the Lewis X antigen, is expressed on the surface of neutrophils and plays a role in cell adhesion and migration. CD16, also known as FcγRIII, is a receptor for the Fc portion of immunoglobulins and is expressed on the surface of neutrophils and some monocytes. CD66b, also known as CEACAM8, is a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of neutrophils and eosinophils.
In addition to these markers, other markers such as CD10, CD11b, and CD13 can also be used to identify granulocytes. CD10, also known as CALLA, is expressed on the surface of early myeloid cells, including granulocyte precursors. CD11b, also known as Mac-1, is an integrin that is expressed on the surface of neutrophils and is involved in their adhesion and migration. CD13, also known as aminopeptidase N, is expressed on the surface of granulocytes and monocytes and is involved in peptide metabolism.
The use of granulocyte markers is essential for studying granulocyte biology, understanding their role in immune responses, and diagnosing various diseases such as infections, leukemias, and autoimmune disorders. These markers offer valuable information about the presence, activation, and function of granulocytes in different physiological and pathological conditions, allowing for accurate and precise characterization of granulocyte populations.
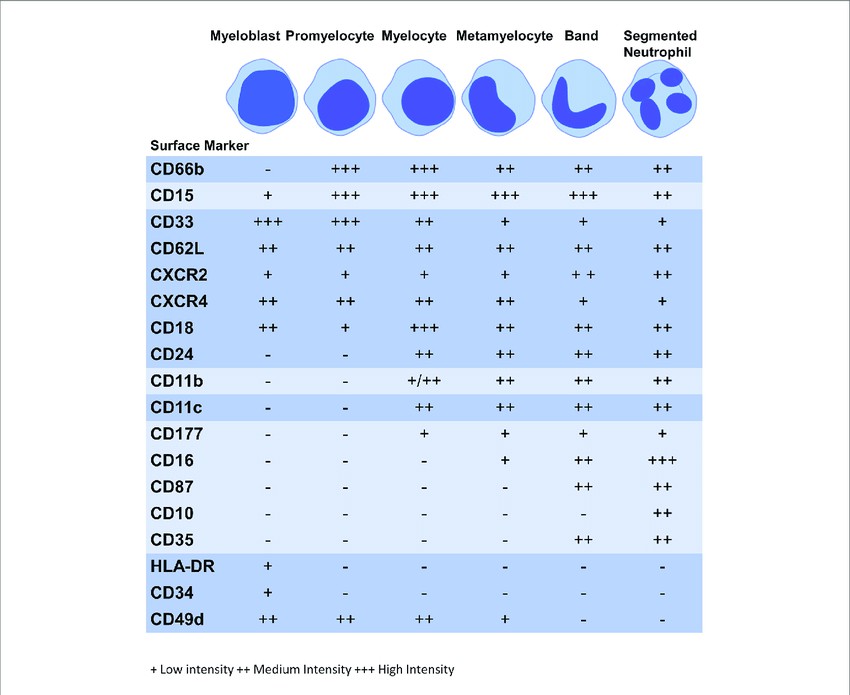 Fig.1 Expression of surface markers during granulopoiesis. (McKenna E, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Expression of surface markers during granulopoiesis. (McKenna E, et al., 2021)
Figure illustrates the surface marker expression at each stage of granulopoiesis; myeloblast, promyelocyte, myelocyte, metamyelocyte, band cell and segmented neutrophil. The intensity of the surface marker is shown whereby; low intensity (+), medium intensity (++) and high intensity (+++).
Applications of Granulocyte Markers
Research on Granulocyte Biology: Granulocyte markers are widely used in research studies to understand the biology, development, and function of granulocytes. By studying the expression patterns and behavior of granulocyte markers, researchers can gain insights into various cellular processes and mechanisms involved in granulocyte function.
Cell Isolation and Purification: Granulocyte markers are used to isolate and purify granulocytes from complex mixtures of cells. By specifically targeting granulocyte markers, researchers can separate granulocytes from other cell types for further analysis, such as functional assays, gene expression studies, or proteomics.
Immune Cell Profiling: Granulocyte markers are part of many immune cell profiling panels, which help in characterizing and quantifying various immune cell types. This profiling is essential for understanding the immune response in different diseases, including cancer, autoimmunity, and infectious diseases.
Immunophenotyping: Granulocyte markers are used in flow cytometry and immunophenotyping studies to identify and quantify granulocyte populations in biological samples. This helps in characterizing the composition and activation status of granulocytes in different conditions, such as infections, allergies, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
Functional Studies: Granulocyte markers are used to investigate the functional properties of granulocytes. By isolating granulocytes based on specific markers, researchers can study their phagocytic activity, chemotaxis, degranulation, cytokine production, and other functional responses in various experimental setups.
Biomarker Discovery: Granulocyte markers can serve as potential biomarkers for specific diseases or conditions. By analyzing the expression levels or patterns of granulocyte markers in patient samples, researchers can identify diagnostic, prognostic, or predictive biomarkers that can help guide treatment decisions or monitor disease progression.
Drug Development and Therapy: Granulocyte markers are used in preclinical and clinical studies of granulocyte-targeted therapies. By understanding the expression patterns and functional characteristics of granulocytes in different diseases, researchers can develop targeted therapies that specifically modulate granulocyte activity or selectively deliver therapeutic agents to these cells.
Disease Diagnosis and Monitoring: Granulocyte markers can aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of specific diseases. For example, elevated levels of specific granulocyte markers, such as CD15 or CD66b, may indicate the presence of infections, inflammatory disorders, or certain types of leukemia. Monitoring changes in granulocyte marker expression over time can provide insights into disease progression and response to treatment.
Available Resources for Granulocyte Markers
Creative BioMart is dedicated to providing a rich and diverse range of products related to granulocyte markers, including recombinant proteins and others. We also provide customized services to meet the specific needs of researchers in academia and the biopharmaceutical industry. In addition to our products and customized services, we offer a wealth of resources covering all aspects of granulocyte markers. These resources include involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, overviews of research areas, and in-depth discussions of other relevant topics.
Creative BioMart is committed to supporting your research and development efforts in the field of granulocyte markers. Please feel free to explore our products, take advantage of our customization services, and leverage the detailed resources we offer to advance your scientific pursuits.
Our Featured Products
- Recombinant Human ITGAX, flag & His tagged
- Recombinant Human FCGR3B protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human FCGR3B, None tagged
- Active Recombinant Human FCGR3B Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated
- Recombinant Human CD45, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD45 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD147, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD44 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD44 protein, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human CD44 Protein, hFc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated
- Recombinant Human CD44 Protein, hFc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated
- Active Recombinant Rat Cd44 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated
- Active Recombinant Human ITGA4 & ITGB1 Protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated
- Active Recombinant Mouse Ltbr Protein, Fc-tagged
- Recombinant Mouse Spn protein, Fc-tagged, APC labeled
- Recombinant Mouse Spn Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated
- Recombinant Human CD164, His tagged
- Active Recombinant Human CD24 protein, Fc-tagged
- Recombinant Human FCGR2C, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human FCGR2B, His & AVI tagged
- Recombinant Human S100A4 protein, hFc-tagged
- Active Recombinant Human S100A8, His tagged
- Active Recombinant Human Calprotectin Protein
- Recombinant Human CEACAM5 Protein, His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated
- Recombinant Human LAMP1, His tagged
- Recombinant Human CEACAM5 Protein, Fc/His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated
- Recombinant Human CEACAM5 Protein, Fc/His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated
- Recombinant Human CD93, His-tagged
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- McKenna E, Mhaonaigh AU, Wubben R, Dwivedi A, Hurley T, Kelly LA, Stevenson NJ, Little MA, Molloy EJ. Neutrophils: Need for Standardized Nomenclature. Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 15;12:602963.
- Kwok I, Becht E, Xia Y, et al. Combinatorial Single-Cell Analyses of Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitor Heterogeneity Reveals an Early Uni-potent Neutrophil Progenitor. Immunity. 2020;53(2):303-318.e5.

