What is CAPZA1 Protein
CAPZA1, officially known as Capping Actin Protein of Muscle Z-line Alpha Subunit 1, is a pivotal member of the actin-capping protein family. Also recognized by its aliases, such as CP alpha-1 and CapZ alpha-1, this protein plays a crucial role in the regulation of actin dynamics within the cell. As a member of the CAPZ family, it works in concert with its counterparts to control the growth and organization of actin filaments, fundamental components in cellular architecture.
CAPZA1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, CAPZA1 exhibits a conserved alpha/beta-tubulin domain and is classified as an alpha/beta subunit, distinct from its beta counterparts. Recent research has shed light on the significance of CAPZA1 in cellular processes, unraveling its intricate role in maintaining cytoskeletal integrity.
CAPZA1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of CAPZA1 are multifaceted, reflecting its importance in cellular homeostasis. At its core, CAPZA1 acts as a capping protein, binding to the barbed ends of actin filaments, a crucial step in modulating actin dynamics. By capping these ends, CAPZA1 prevents further polymerization, contributing to the stabilization of actin filaments. This function is instrumental in cellular processes such as cell motility, shape maintenance, and cell division.
Molecularly, CAPZA1 interacts with actin monomers, preventing their addition to the growing filament. This regulation of actin dynamics is fundamental in processes like cell migration, where the controlled assembly and disassembly of actin filaments dictate the cell's movement. Moreover, CAPZA1 is implicated in the regulation of muscle contraction, emphasizing its diverse roles in different cellular contexts.
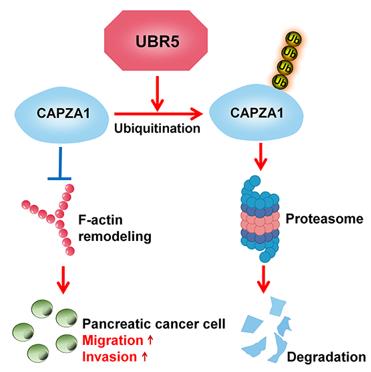
Figure 1. UBR5 mediates the ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation of CAPZA1. (Li J, et al., 2021)
CAPZA1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway involving CAPZA1 is intricately linked to actin dynamics and cellular communication. CAPZA1 is modulated by various signaling molecules, including Rho GTPases and other actin-binding proteins. These interactions orchestrate the precise control of actin polymerization and depolymerization, influencing cellular processes like cell adhesion, migration, and morphogenesis.
In particular, the Rho GTPase family members, such as RhoA, have been implicated in CAPZA1 regulation. Activation of RhoA stimulates actin polymerization by releasing CAPZA1 from the barbed ends, promoting filament elongation. Understanding these signal pathways is crucial in unraveling the broader cellular context in which CAPZA1 operates.
CAPZA1 Related Diseases
Alterations in CAPZA1 expression or function have been linked to various diseases, highlighting its significance in maintaining cellular health. Studies have implicated CAPZA1 in certain cancers, including breast and lung cancers, where dysregulation of actin dynamics plays a role in tumor progression. The exact mechanisms linking CAPZA1 to cancer are complex and multifactorial, involving disruptions in cell migration, invasion, and cytoskeletal organization.
Neurological disorders also show associations with CAPZA1, suggesting its involvement in maintaining synaptic function and neuronal integrity. Research is underway to elucidate the precise role of CAPZA1 in these diseases, offering potential avenues for targeted therapies.
CAPZA1's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatility of CAPZA1 extends beyond its cellular functions, holding promise in biomedical applications. Researchers are exploring its potential in diagnostics, leveraging its involvement in diseases to develop diagnostic markers. The dysregulation of CAPZA1 in certain cancers, for instance, may serve as a prognostic indicator or a target for therapeutic interventions.
Furthermore, CAPZA1's role in modulating actin dynamics makes it a potential player in vaccine development. Actin is involved in various stages of the immune response, and understanding how CAPZA1 influences these processes could open new avenues for vaccine design.
In the realm of therapeutics, targeting CAPZA1 may offer novel strategies for diseases associated with its dysregulation. Small molecules or biological agents that selectively modulate CAPZA1 could be developed to restore normal cellular function and counteract the aberrant processes seen in diseases.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAPZA1-2913H | Recombinant Human Capping Protein (Actin Filament) Muscle Z-line, Alpha 1 CAPZA1, T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | T7 |
| CAPZA1-118H | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 protein, T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | T7 |
| CAPZA1-0382H | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CAPZA1-26237TH | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 | Human | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| CAPZA1&CAPZB-869H | Active Recombinant Human CAPZA1/CAPZB Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CAPZA1-0841H | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 Protein (Met1-Ala286), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| CAPZA1-499H | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CAPZA1-1870H | Recombinant Human CAPZA1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| CAPZA1-2847HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CAPZA1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CAPZA1-1381HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CAPZA1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
Reference
- Li J, et al. E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR5 promotes the metastasis of pancreatic cancer via destabilizing F-actin capping protein CAPZA1. Frontiers in Oncology. 2021, 11: 634167.

