What is CTSL1 Protein
The CTSL1 protein, or Cathepsin L1, is a key player in the intricate world of cellular function and regulation. This protease, belonging to the cathepsin family, holds significant importance in various biological processes.
What is CTSL1 Protein?
The CTSL1 protein, classified as a lysosomal cathepsin, stands as a pivotal player in cellular homeostasis. Residing within lysosomes, it is a cysteine protease featuring a distinct structure. Comprising a propeptide region, catalytic domain, and occluding loop, CTSL1's intricate architecture plays a crucial role in its functions.
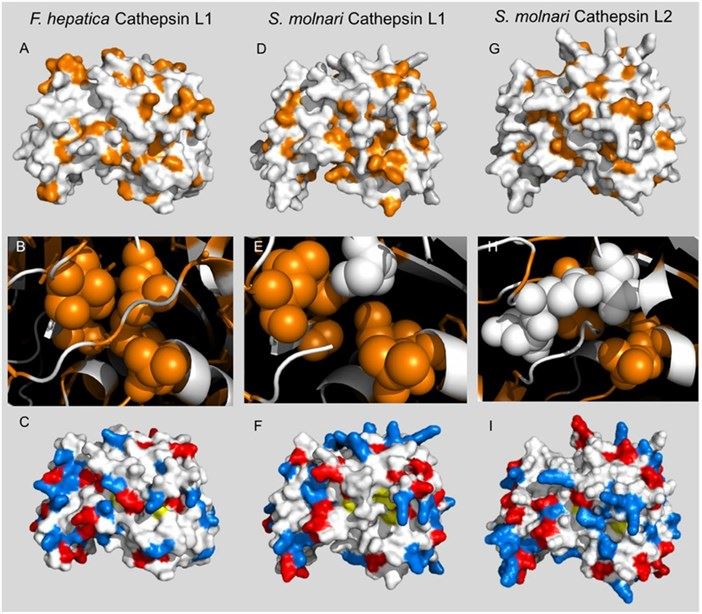
Figure 1. Predicted tertiary structure of SMBS Cathepsin L 1 and 2 and comparison with Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L. (Hartigan, A., et al. 2020)
The Function of CTSL1 Protein
CTSL1's primary function lies in peptide bond hydrolysis within proteins, contributing to cellular waste degradation and biomolecule recycling. Beyond this, CTSL1 plays a pivotal role in immune responses through antigen presentation. It aids in the processing of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules, essential for immune system recognition of foreign antigens.
CTSL1-Related Diseases
Aberrations in CTSL1 expression have been associated with various diseases. In cancer, heightened CTSL1 levels correlate with increased invasiveness and metastasis. The protease's involvement in the degradation of extracellular matrix proteins facilitates cancer cell migration. Additionally, CTSL1's dysregulation is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, where it contributes to the accumulation of misfolded proteins, leading to neuronal dysfunction.
CTSL1 Related Signaling Pathways
Understanding the signal pathways associated with CTSL1 activation and regulation is crucial for unraveling its cellular involvement.
- Wnt Signaling Pathway
CTSL1 emerges as a downstream effector of the Wnt signaling pathway, influencing cell fate decisions and tissue development. Its role in modulating protein turnover within this pathway showcases its regulatory significance.
- Notch Signaling Pathway
CTSL1 is involved in the processing of Notch receptors, impacting their activation and downstream signaling events. Dysregulation of this pathway, facilitated by CTSL1, contributes to various developmental disorders and cancers.
- mTOR Signaling Pathway
CTSL1's link to the mTOR signaling pathway underscores its involvement in cellular growth and metabolism regulation. Modulating the balance between cellular growth and autophagy, CTSL1 plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Applications of CTSL1 in Biomedical Research
The distinctive properties of CTSL1 make it a compelling candidate for various biomedical applications.
- Diagnostic Biomarker
CTSL1's aberrant expression in diseases positions it as a potential diagnostic biomarker. Monitoring CTSL1 levels in biological samples could offer insights into early detection, particularly in cancers and neurodegenerative disorders.
- Therapeutic Target
Given its involvement in cancer progression, CTSL1 emerges as a valuable therapeutic target. Inhibitors designed to target CTSL1 are under investigation for their potential in impeding tumor invasion and metastasis. These targeted therapies present a paradigm shift in cancer treatment, minimizing side effects associated with traditional treatments.
- Drug Development
Understanding the molecular intricacies of CTSL1 activation and regulation provides a foundation for drug development. Researchers are exploring small molecules and peptides that can modulate CTSL1 activity, offering novel avenues for drug discovery across various diseases.
- Immunotherapy Applications
CTSL1's role in antigen presentation and immune responses positions it as a potential target for immunotherapy. Modulating CTSL1 activity could enhance or suppress immune responses, presenting innovative strategies for treating autoimmune diseases or fortifying the immune system against infections.
As scientists continue to unravel the mysteries surrounding CTSL1, it is poised to become a key player in diagnostics, therapeutics, and drug development, potentially revolutionizing the landscape of biomedical research and clinical practice.
Recommended Products for CTSL1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTSL1-91H | Human | Recombinant Human cathepsin L1 | E.coli | N/A |
| CTSL1-26491TH | Human | Recombinant Human CTSL1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| CTSL1-11690H | Human | Recombinant Human CTSL1, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| CTSL1-896H | Human | Recombinant Human CTSL1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| CTSL1-1668R | Rat | Recombinant Rat CTSL1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| CTSL1-1327R | Rat | Recombinant Rat CTSL1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| CTSL1-441C | Chlorocebus Aethiops | Recombinant Chlorocebus Aethiops CTSG Protein (114-333 aa), His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | His/SUMO |
Reference
- Hartigan, A., et al. Transcriptome of Sphaerospora molnari (Cnidaria, Myxosporea) blood stages provides proteolytic arsenal as potential therapeutic targets against sphaerosporosis in common carp. BMC Genomics. 2020, 21: 404.

