What is FGF2 Protein
Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2), also known as basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bFGF), is a multifunctional protein that plays a pivotal role in various physiological processes. Its official full name is precisely Fibroblast Growth Factor 2, and it goes by several synonyms such as bFGF, HBGF-2, and FGF-β. This essential protein belongs to the fibroblast growth factor family, a group of signaling proteins crucial for embryonic development, tissue repair, and overall homeostasis.
FGF2 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, FGF2 consists of a conserved core beta-trefoil structure and exhibits a high affinity for heparin, a glycosaminoglycan. This characteristic property enables FGF2 to interact with cell surface receptors and modulate downstream signaling pathways. Recent research advances have shed light on the diverse roles of FGF2, uncovering its implications in cellular proliferation, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration.
FGF2 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of FGF2 are remarkably diverse, reflecting its significance in orchestrating cellular activities. As a growth factor, FGF2 stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of various cell types, contributing to tissue development and repair. One of its key functions is its involvement in angiogenesis, the process of forming new blood vessels. FGF2 acts as a potent mitogen for endothelial cells, promoting the growth of blood vessels and facilitating wound healing.
At the molecular level, FGF2 exerts its effects by binding to specific cell surface receptors, known as fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). This interaction triggers a cascade of intracellular events, including the activation of downstream signaling pathways such as the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. These pathways play crucial roles in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and migration.
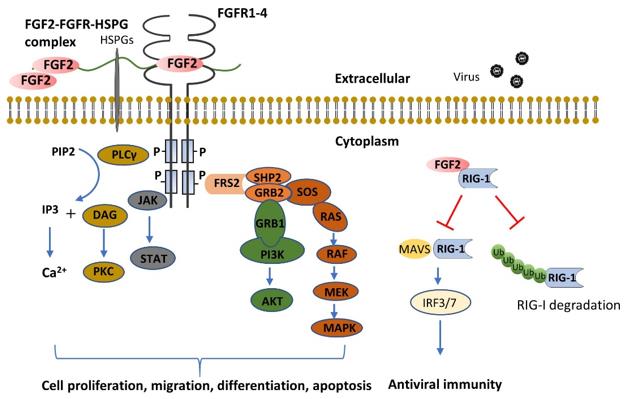
Figure 1. FGF2 functions through FGFR dependent or independent pathways. (Tan Y, et al., 2020)
FGF2 Related Signaling Pathway
The FGF2 signaling pathway is a complex network of molecular events that govern cellular responses to FGF2 stimulation. Upon binding to FGFRs, FGF2 activates downstream signaling cascades, including the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway. These pathways converge to regulate gene expression, cell cycle progression, and cell survival.
The MAPK/ERK pathway is particularly crucial, influencing cellular proliferation and differentiation. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the regulation of cell survival and metabolism. The tight control of these pathways is essential for maintaining normal cellular functions, and disruptions in FGF2 signaling can lead to various pathological conditions.
FGF2 Related Diseases
While FGF2 is indispensable for normal physiological processes, aberrant expression or dysregulation of this protein is associated with several pathological conditions. In cancer, FGF2 is implicated in promoting tumor growth and angiogenesis. Its pro-proliferative and pro-survival effects contribute to the aggressive nature of certain cancers, making it a potential target for anti-cancer therapies.
Additionally, FGF2 is linked to cardiovascular diseases, where its dysregulation can disrupt vascular homeostasis and contribute to conditions such as atherosclerosis. Neurological disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, have also been associated with abnormal FGF2 expression, highlighting the intricate role of this protein in maintaining neuronal health.
FGF2's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatile nature of FGF2 has led to its exploration in various biomedical applications. In diagnostics development, FGF2 has been investigated as a potential biomarker for certain diseases, including cancer. Its presence or altered levels in biological fluids may serve as indicators of disease progression or response to therapy.
In vaccine development, FGF2's ability to stimulate angiogenesis and tissue repair makes it an intriguing candidate for enhancing the efficacy of regenerative therapies. By harnessing its potential, researchers aim to develop innovative vaccines that not only target pathogens but also facilitate tissue regeneration, offering new avenues for combating diseases with a regenerative component.
In therapeutics, FGF2-based treatments are being explored for their potential in promoting tissue repair and regeneration. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of FGF2 in conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and musculoskeletal disorders. The goal is to leverage FGF2's biological functions to develop targeted therapies that address the underlying mechanisms of diseases and promote healing.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF2-13H | Active Recombinant Human FGF2 Protein, Biotinylated | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| FGF2-11H | Recombinant Human Fibroblast Growth Factor-basic | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| FGF2-482H | Recombinant Human FGF2, None tagged | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| FGF2-001H | Recombinant Human FGF2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FGF2-18H | Active Recombinant Human FGF2 Protein (143-288aa), Non-tagged | Human | E.coli | Tag Free |
| FGF2-4387R | Recombinant Rabbit FGF2 Protein | Rabbit | Yeast | N/A |
| FGF2-4381B | Recombinant Bovine FGF2 Protein | Bovine | Yeast | N/A |
| FGF2-019B | Active Recombinant Bovine FGF2 protein, His-tagged | Bovine | E.coli | His |
| FGF2-40B | Active Native Bovine FGF2 Protein | Bovine | Bovine brain | N/A |
| FGF2-12B | Recombinant Bovine FGF2 Protein | Bovine | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Tan Y, et al. FGF2, an immunomodulatory factor in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2020, 8: 223.

