What is FOSL1 Protein
FOSL1, or Fos-like antigen 1, is a protein that plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes. Officially known as FOSL1, it is also recognized by other names, including Fra-1 (Fos-related antigen 1), Fosl1, and FRA, among others. Belonging to the Fos family of transcription factors, FOSL1 is a key component of the Activator Protein-1 (AP-1) complex, which regulates gene expression in response to a variety of stimuli.
FOSL1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, FOSL1 is characterized by its leucine zipper domain, which facilitates dimerization with other proteins, enabling the formation of the AP-1 transcription factor. Recent research advances have shed light on the unique regulatory role of FOSL1 in gene expression, contributing to our understanding of cellular responses to external signals.
FOSL1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of FOSL1 are diverse and vital for cellular homeostasis. As a transcription factor, FOSL1 regulates the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and response to various environmental stimuli. It is particularly implicated in processes such as embryonic development, immune response, and tissue repair.
At the molecular level, FOSL1 interacts with other members of the AP-1 complex to modulate target gene expression. It binds to specific DNA sequences, influencing the transcriptional activity of genes crucial for cellular function. The dynamic interplay between FOSL1 and its binding partners enables precise control over cellular processes, contributing to the maintenance of tissue integrity and functionality.
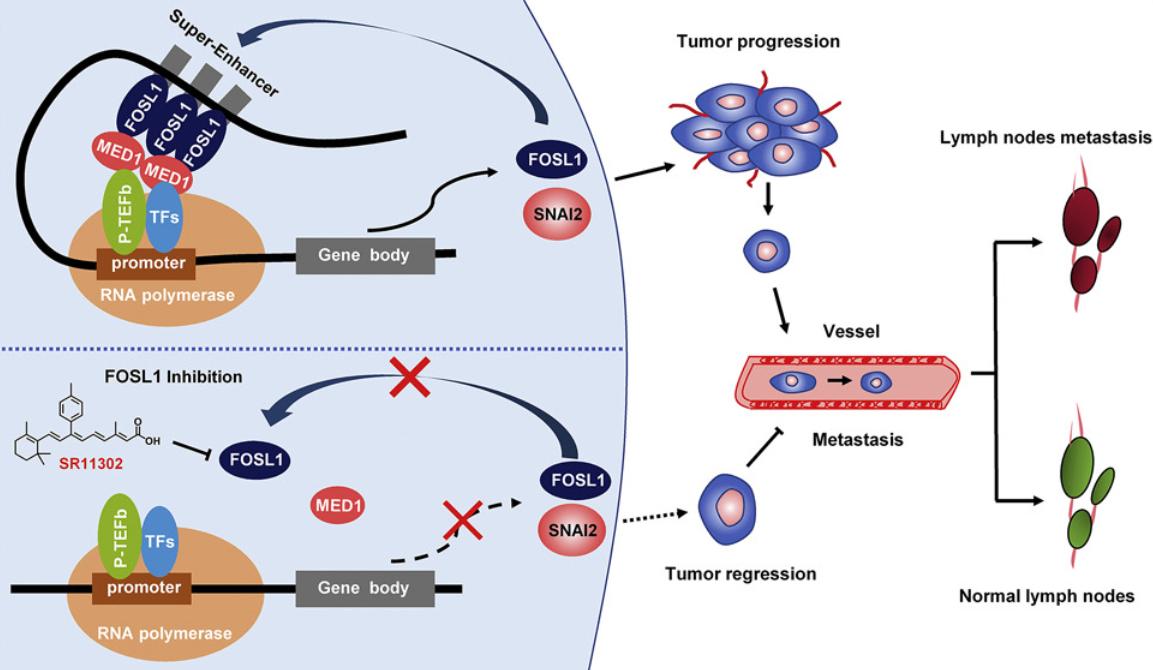
Figure 1. FOSL1 promotes metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. (Zhang M, et al., 2021)
FOSL1 Related Signaling Pathway
The FOSL1-related signal pathway is intricately connected to the MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) signaling cascade. Various extracellular stimuli, such as growth factors, cytokines, and environmental stressors, activate MAPK pathways, ultimately leading to the activation of the AP-1 complex, where FOSL1 plays a central role.
Activation of FOSL1 occurs through phosphorylation events initiated by upstream kinases in the MAPK pathway. Once activated, FOSL1 translocates to the nucleus, where it modulates gene expression by binding to target DNA sequences. The MAPK-FOSL1 axis is a critical signaling pathway that translates extracellular signals into transcriptional responses, influencing cellular behavior and fate.
FOSL1 Related Diseases
Dysregulation of FOSL1 expression has been associated with several diseases, highlighting its significance in maintaining cellular balance. Aberrant FOSL1 expression is observed in various cancers, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. In these contexts, FOSL1 promotes tumor progression by influencing cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis.
Additionally, FOSL1 is implicated in inflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases. Its role in modulating immune responses suggests a potential link between FOSL1 dysregulation and the development of autoimmune conditions. Understanding these associations provides avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions in diseases characterized by FOSL1 imbalances.
FOSL1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique regulatory role of FOSL1 in gene expression makes it a promising target for biomedical applications. Researchers are exploring the potential of FOSL1 in diagnostic development, leveraging its association with various diseases, especially cancers. Detection of FOSL1 expression levels may serve as a diagnostic marker, aiding in the early identification and monitoring of diseases.
Furthermore, FOSL1's involvement in immune responses positions it as a candidate for vaccine development. Understanding its role in modulating immune functions can inform the design of vaccines aimed at enhancing immune responses against specific pathogens.
In the realm of therapeutics, targeting FOSL1 and the AP-1 complex presents opportunities for novel treatment strategies. Small molecules and therapeutic agents designed to modulate FOSL1 activity could potentially be used to intervene in diseases characterized by FOSL1 dysregulation, offering a new frontier in precision medicine.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOSL1-12965H | Recombinant Human FOSL1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| FOSL1-1034H | Active Recombinant Human FOS-like Antigen 1 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| FOSL1-932H | Recombinant Human FOSL1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| FOSL1-001H | Recombinant Human FOSL1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| FOSL1-28947TH | Recombinant Human FOSL1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FOSL1-2065HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human FOSL1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| FOSL1-3365H | Recombinant Human FOSL1 Protein (Met1-Leu271), His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FOSL1-4427H | Recombinant Human FOSL1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| FOSL1-3366H | Recombinant Human FOSL1 Protein (Met1-Leu271), N-His tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| FOSL1-5042HF | Recombinant Full Length Human FOSL1 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
Reference
- Zhang M, et al. FOSL1 promotes metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through super-enhancer-driven transcription program. Molecular Therapy. 2021, 29(8): 2583-2600.

