What is FURIN Protein
FURIN, officially known as "Furin, Paired Basic Amino Acid Cleaving Enzyme," is a pivotal member of the proprotein convertase (PC) family. This protease, encoded by the FURIN gene, plays a crucial role in cellular homeostasis and the regulation of various biological processes. Synonyms for FURIN include PACE, SPC1, and KEX2. Structurally, FURIN is characterized by its modular organization, featuring a signal peptide, propeptide, catalytic domain, P domain, and a C-terminal domain. It belongs to the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase (SPC) family, known for their ability to cleave precursor proteins into their active forms. Recent research has shed light on FURIN's dynamic role, emphasizing its involvement in diverse cellular functions.
FURIN Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
At the crux of cellular function, FURIN orchestrates the proteolytic activation of diverse substrates. Its main function lies in cleaving precursor proteins at paired basic amino acid motifs, initiating the maturation of various bioactive molecules. FURIN substrates range from growth factors and receptors to viral glycoproteins, underscoring its influence on both physiological and pathological processes. The molecular mechanisms underlying FURIN's actions involve precise substrate recognition, followed by catalytic cleavage, ultimately modulating cellular responses. Its ability to fine-tune the activation of proteins underscores FURIN's significance in cellular signaling cascades.
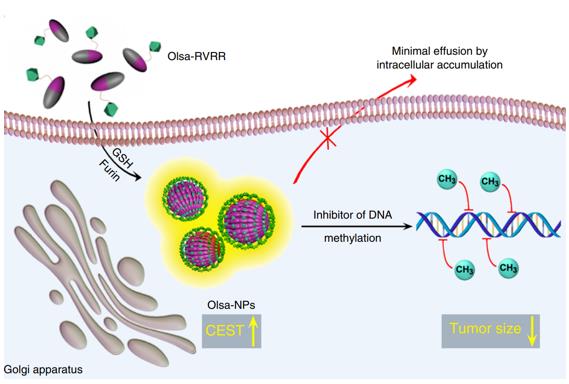
Figure 1. Furin-mediated intracellular self-assembly of olsalazine nanoparticles. (Yuan Y, et al., 2019)
FURIN Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways associated with FURIN are complex and multifaceted. FURIN's involvement in the activation of growth factors like transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) highlights its role in regulating cell growth and differentiation. Furthermore, FURIN participates in the processing of membrane receptors, influencing downstream signaling events. Deciphering the intricate network of FURIN-related signal pathways is paramount for comprehending its impact on cellular behavior and disease development.
FURIN Related Diseases
While FURIN's role in normal cellular processes is indispensable, dysregulation of its activity has been linked to several diseases. Notably, FURIN has been implicated in cancer progression, where its overexpression contributes to increased cell proliferation and invasiveness. Additionally, FURIN is involved in the activation of certain bacterial toxins, emphasizing its role in infectious diseases. Understanding the delicate balance of FURIN activity is critical in unraveling its implications in disease pathogenesis.
FURIN's Applications in Biomedicine
Harnessing FURIN's unique enzymatic properties has paved the way for its applications in biomedical research and development. In diagnostics, FURIN serves as a biomarker for certain diseases, aiding in early detection and prognosis. Moreover, the proteolytic activity of FURIN is integral in vaccine development, as it facilitates the generation of immunogenic epitopes. In therapeutics, targeting FURIN has emerged as a strategy for modulating specific pathways implicated in disease, presenting a promising avenue for drug development. The multifaceted applications of FURIN underscore its versatility in advancing biomedical frontiers.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FURIN-13036H | Recombinant Human FURIN, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FURIN-605H | Active Recombinant Human FURIN Protein | Human | Drosophila melanogaster Schneider 2 cells | N/A |
| FURIN-720H | Recombinant Human Furin (Paired Basic Amino Acid Cleaving Enzyme) | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | N/A |
| FURIN-4553H | Active Recombinant Human FURIN Protein | Human | Insect Cell | N/A |
| FURIN-130H | Recombinant Human FURIN protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FURIN-4554H | Recombinant Human FURIN Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| FURIN-5158HF | Recombinant Full Length Human FURIN Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| FURIN-6584H | Recombinant Human FURIN Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| FURIN-946H | Recombinant Human FURIN Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| FURIN-131H | Recombinant Human FURIN protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Yuan Y, et al. Furin-mediated intracellular self-assembly of olsalazine nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and tumour therapy. Nature Materials. 2019, 18(12): 1376-1383.

