What is GNA13 Protein
GNA13, also known as Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13, stands as a pivotal player in cellular signaling. Belonging to the G protein family, this protein operates in a dynamic network of molecular interactions that regulate a myriad of cellular processes. Synonymous with its official full name, GNA13 is encoded by the GNA13 gene.
GNA13 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, GNA13 comprises distinct domains that contribute to its functional significance. It boasts a nucleotide-binding domain and an alpha-helical domain, playing a key role in its interaction with guanine nucleotides. As a member of the G protein family, GNA13 is classified as a heterotrimeric G protein, existing as a complex with beta and gamma subunits. Recent research has shed light on the intricate details of GNA13's structure and classification, providing a deeper understanding of its molecular behavior.
GNA13 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of GNA13 are diverse and vital for cellular homeostasis. This protein serves as a molecular switch, toggling between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound states in response to extracellular signals. GNA13 orchestrates signaling cascades initiated by G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), transmitting messages from the extracellular environment to the cell's interior.
One of the primary functions of GNA13 is its involvement in cytoskeletal dynamics and cell migration. By interacting with effectors such as Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors (RhoGEFs), GNA13 plays a pivotal role in regulating actin cytoskeleton rearrangement. This function is particularly crucial during processes like cell migration and tissue morphogenesis.
Additionally, GNA13 contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation and survival pathways. Its interaction with downstream effectors modulates signaling pathways that influence cell fate decisions, making it a central player in cellular physiology.
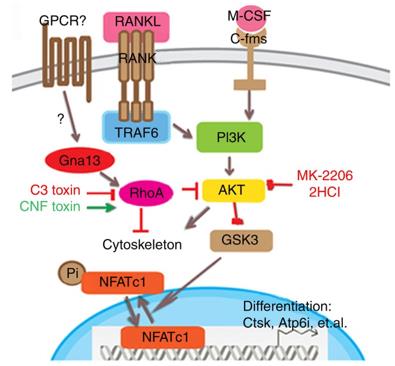
Figure 1. Working model of Gα13 as a negative regulator in osteoclast. (Wu M, et al., 2017)
GNA13 Related Signaling Pathway
The signal pathway orchestrated by GNA13 is complex and interconnected with various cellular processes. Primarily associated with GPCRs, GNA13 transduces signals from extracellular ligands to intracellular effectors. The Rho family of GTPases, particularly RhoA, serves as a downstream mediator of GNA13 signaling, influencing cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular migration.
Moreover, GNA13 is intricately involved in the Hippo signaling pathway, impacting cell proliferation and organ size regulation. The dynamic crosstalk between GNA13 and other signaling pathways adds layers of complexity to cellular responses, emphasizing the need for comprehensive investigations to decipher the molecular intricacies.
GNA13 Related Diseases
As with many proteins, dysregulation of GNA13 is implicated in various diseases. Aberrant GNA13 signaling has been associated with cancer progression, with alterations in its expression or activity contributing to the invasive and metastatic characteristics of cancer cells. Furthermore, GNA13 mutations have been identified in certain cancers, highlighting its potential role as a therapeutic target.
In addition to cancer, GNA13 dysregulation is linked to cardiovascular diseases. Studies have revealed its involvement in vascular development and maintenance, and disruptions in GNA13 signaling have been implicated in conditions like atherosclerosis and hypertension. Understanding the precise role of GNA13 in these diseases opens avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
GNA13's Applications in Biomedicine
Harnessing the knowledge of GNA13's functions has paved the way for its applications in biomedical research and development. In diagnostics, GNA13 may serve as a biomarker for certain cancers, aiding in early detection and prognosis assessment. The identification of GNA13 mutations in cardiovascular diseases holds promise for developing targeted diagnostic tools to assess individual risk profiles.
In the realm of vaccine development, understanding GNA13's involvement in immune responses can guide the design of more effective vaccines. Targeting GNA13-related pathways may enhance vaccine efficacy, providing a novel approach to bolstering immune responses.
Therapeutically, drugs targeting GNA13 signaling pathways are under exploration for their potential in cancer and cardiovascular disease treatment. The intricate involvement of GNA13 in cellular processes makes it a promising target for precision medicine approaches, tailoring interventions to the specific molecular characteristics of individual patients.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNA13-27H | Recombinant Human GNA13 protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| GNA13-13343H | Recombinant Human GNA13, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| GNA13-187H | Recombinant Human GNA13 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| GNA13-616HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GNA13 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| GNA13-2591R | Recombinant Rat GNA13 Protein | Rat | Mammalian Cell | His |
| GNA13-2246R | Recombinant Rat GNA13 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Wu M, et al. Gα13 negatively controls osteoclastogenesis through inhibition of the Akt-GSK3β-NFATc1 signalling pathway. Nature Communications. 2017, 8(1): 13700.

