What is IDO1 Protein
The Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) protein, also known by its official full name as Indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase 1, plays a crucial role in regulating immune responses and maintaining immune tolerance. IDO1 is part of the larger dioxygenase family and is classified under the tryptophan pyrrolase subfamily. Its structural characteristics include a heme-containing catalytic domain, which is responsible for its enzymatic activity.
Recent research advances have shed light on the diverse functions of IDO1 beyond its traditional role in immune regulation. Studies have explored its implications in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and infectious diseases, making IDO1 an intriguing target for therapeutic interventions.
IDO1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
IDO1 primarily functions as a key player in tryptophan metabolism, catalyzing the oxidative cleavage of tryptophan to kynurenine. This enzymatic activity results in the depletion of tryptophan, an essential amino acid, and the accumulation of kynurenine and its metabolites. The modulation of tryptophan levels has profound effects on immune responses.
One of the main functions of IDO1 is its immunosuppressive role. By depleting tryptophan, IDO1 restricts the availability of this amino acid for T cells, leading to the inhibition of T cell proliferation and activation. This immunosuppressive environment is crucial for preventing excessive immune responses and maintaining immune tolerance, especially in conditions like pregnancy, where immune tolerance is essential for fetal development.
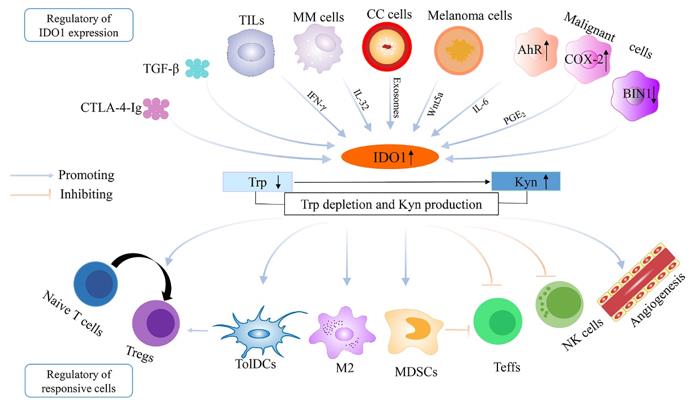
Figure 1. The regulation of IDO1 overexpression and the establishment of immune escape in the tumor microenvironment. (Song X, et al., 2021)
IDO1 Related Signaling Pathway
The molecular mechanisms underlying IDO1 function involve intricate signaling pathways. The interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) pathway is a major regulator of IDO1 expression. Upon activation by IFN-γ, cells upregulate IDO1 as part of the immune response. Additionally, other signaling pathways, including those involving Toll-like receptors and cytokines, can modulate IDO1 expression in different cellular contexts.
Understanding these signal pathways is essential for unraveling the complex regulatory networks that govern IDO1 activity. Targeting specific signaling components within these pathways presents opportunities for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating IDO1 function in various disease settings.
IDO1 Related Diseases
Research has linked dysregulation of IDO1 to various diseases. In cancer, IDO1 overexpression is observed in numerous tumor types, contributing to immune evasion by creating an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, studies have highlighted the involvement of IDO1 in chronic inflammatory conditions and autoimmune diseases, where aberrant IDO1 activity may contribute to the breakdown of immune tolerance.
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, have also been associated with altered IDO1 expression. The precise role of IDO1 in these conditions is still under investigation, but its potential impact on neuroinflammation and neuronal function is a subject of growing interest.
IDO1's Applications in Biomedicine
The multifaceted roles of IDO1 make it a promising target for biomedical applications. In diagnostics development, IDO1 expression levels can serve as biomarkers for certain diseases, aiding in early detection and prognosis. Researchers are exploring the use of IDO1 as a diagnostic tool in cancer and autoimmune diseases, where its dysregulation is prevalent.
Vaccine development is another area where IDO1 is garnering attention. By understanding the immunomodulatory functions of IDO1, scientists are exploring its potential as a component in vaccine formulations. This includes enhancing vaccine efficacy by incorporating IDO1 modulators to manipulate immune responses and improve vaccine-induced immunity.
In therapeutics, targeting IDO1 has become a strategy for treating conditions characterized by immune dysregulation, such as cancer. IDO1 inhibitors are being developed as potential anticancer agents, aiming to overcome the immunosuppressive barriers within the tumor microenvironment and enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy.
Recommended Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDO1-3920H | Recombinant Human IDO1, His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IDO1-7325H | Recombinant Human IDO1, None tagged | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IDO1-7190H | Active Recombinant Human IDO1 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IDO1-14054H | Recombinant Human IDO1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IDO1-3920HAF555 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | Human | E.coli | His |
| IDO1-7325HAF555 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, Gly/Pro-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | Human | E.coli | Gly/Pro |
| IDO1-3920HAF647 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | Human | E.coli | His |
| IDO1-3920HAF488 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, His-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | Human | E.coli | His |
| IDO1-7325HAF647 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, Gly/Pro-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | Human | E.coli | Gly/Pro |
| IDO1-7325HAF488 | Recombinant Human IDO1 Protein, Gly/Pro-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | Human | E.coli | Gly/Pro |
Reference
- Song X, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1: a promising therapeutic target in malignant tumor. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021, 12: 800630.

