What is KPNB1 Protein
What is KPNB1 Protein?
KPNB1, or Importin β1, belongs to the karyopherin family, playing a pivotal role in nuclear transport processes. As a molecular shuttle, KPNB1 collaborates with Importin α to form a heterodimeric complex that recognizes and transports cargo proteins bearing a nuclear localization signal (NLS). This intricate import process is a linchpin in cellular homeostasis, ensuring the precise localization of proteins within the cellular compartments.
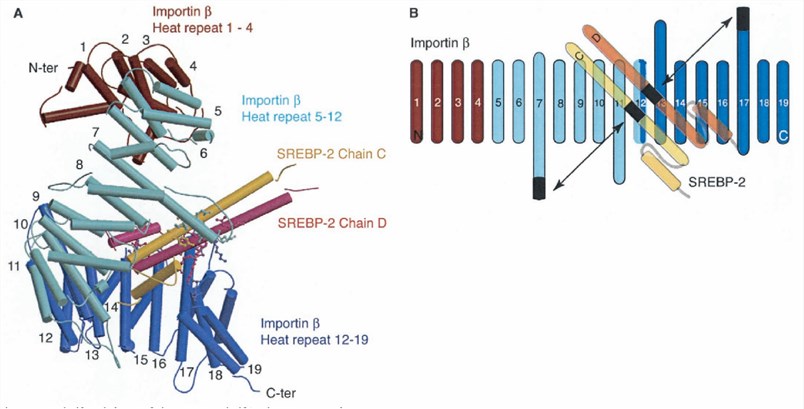
Figure 1. The Structure of Importin-ß Bound to SREBP-2. (Lee, S.J., et al. 2003)
The Function of KPNB1 Protein
- Gene Expression Regulation
Central to KPNB1's function is its role in gene expression regulation. By facilitating the transport of transcription factors into the nucleus, KPNB1 governs the initiation and modulation of gene transcription, thus influencing diverse cellular activities.
- Cell Cycle Control
KPNB1 contributes to the orchestration of the cell cycle by ensuring the nuclear import of proteins pivotal for cell cycle checkpoints and DNA replication. This regulatory role underscores the significance of KPNB1 in the seamless progression of cellular events.
- Signal Transduction
Critical signaling pathways hinge on the timely and accurate transport of signaling molecules into the nucleus. KPNB1's involvement in this process positions it as a linchpin in signal transduction cascades, impacting cellular responses and downstream events.
KPNB1-Related Diseases
- Cancer
In the realm of diseases, KPNB1 has emerged as a key player, particularly in cancer. Dysregulation of KPNB1 expression and function has been implicated in various cancers, where mislocalization of tumor suppressor proteins or oncogenes contributes to malignant transformation.
- Neurodegenerative Disorders
Linkages between KPNB1 dysfunction and neurodegenerative disorders have surfaced. Aberrant nuclear transport may underlie the accumulation of toxic aggregates in neurons, providing a potential avenue for understanding and intervening in conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
- Viral Infections
Exploiting the cellular machinery, viruses hijack KPNB1 for their replication. Understanding the interplay between viruses and KPNB1 sheds light on potential antiviral strategies, emphasizing the broad implications of KPNB1 in infectious diseases.
KPNB1 Related Signaling Pathways
- Wnt Signaling Pathway
KPNB1's involvement in the Wnt signaling pathway further highlights its significance in cellular processes. The nuclear import facilitated by KPNB1 influences downstream gene expression, contributing to the regulation of embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cancer.
- Notch Signaling Pathway
The Notch signaling pathway, crucial for cell fate determination, relies on KPNB1 for the nuclear import of Notch intracellular domain (NICD). Dysregulation of this pathway due to KPNB1 abnormalities has implications for developmental disorders and cancer.
- NF-κB Signaling Pathway
KPNB1's role in the nuclear import of NF-κB, a transcription factor central to inflammation and immune response, underscores its impact on inflammatory diseases and cancer. Dysregulation of NF-κB signaling due to aberrant KPNB1 function provides insights into potential therapeutic interventions.
Applications of KPNB1 in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Biomarker
The dysregulation of KPNB1 in various diseases positions it as a potential diagnostic biomarker. Detection of aberrant KPNB1 levels or activity could serve as an early indicator of disease progression, allowing for timely diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
- Target for Therapeutic Intervention
Considering its implications in cancer and other diseases, KPNB1 emerges as a promising therapeutic target. Researchers are actively exploring small molecules or peptides that can modulate KPNB1 activity, offering a novel avenue for the development of targeted therapies.
- Drug Delivery
Exploiting KPNB1's nuclear import function, researchers are investigating its potential in drug delivery. Conjugating drugs to molecules recognized by the KPNB1 import machinery could enhance their nuclear localization, presenting a promising strategy to improve therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
As our understanding of KPNB1 deepens, so does the potential for innovative diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, paving the way for advancements in personalized medicine and targeted therapies.
Recommended Products for KPNB1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KPNB1-1316H | Human | Recombinant Human Karyopherin (importin) Beta 1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| KPNB1-728H | Human | Recombinant Human KPNB1 Protein, DDK-tagged | Sf9 Insect Cell | DDK |
| KPNB1-4369H | Human | Recombinant Human KPNB1 Protein (Met1-Ala876), N-His tagged | E.coli | N-His |
| KPNB1-4891H | Human | Recombinant Human KPNB1 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| KPNB1-5841HF | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human KPNB1 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| KPNB1-8803M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse KPNB1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| KPNB1-4901M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse KPNB1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| KPNB1-3304R | Rat | Recombinant Rat KPNB1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| KPNB1-2960R | Rat | Recombinant Rat KPNB1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| KPNB1-3594Z | Zebrafish | Recombinant Zebrafish KPNB1 | Mammalian Cell |
Reference
- Lee, S.J., et al. The structure of importin-beta bound to SREBP-2: nuclear import of a transcription factor. Science. 2003, 302(5650): 1571-1575.

