What is MITF Protein
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) is a significant protein that plays an integral role in various cellular functions.
The identification of the MITF protein was initially linked to the characterization of the "microphthalmia" mouse phenotype, thus, defining its name. More extensive research led to the isolation of the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor gene, whose mutations were observed to result in microphthalmia in mice. This discovery was significant and marked the beginnings of understanding its complex role in various processes in the body.
MITF is a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper (bHLH-Zip) transcription factor that shares its structure with other proteins within the Myc-Max-Mad network. In terms of genetic composition, the MITF gene locates on chromosome 3p14.2-p14.1 in humans. The alternating gene structure comprises 9 exons and codes for different MITF isoforms. Given this alternate coding pattern, different MITF isoforms are expressed in various tissues, resulting in several cellular functions.
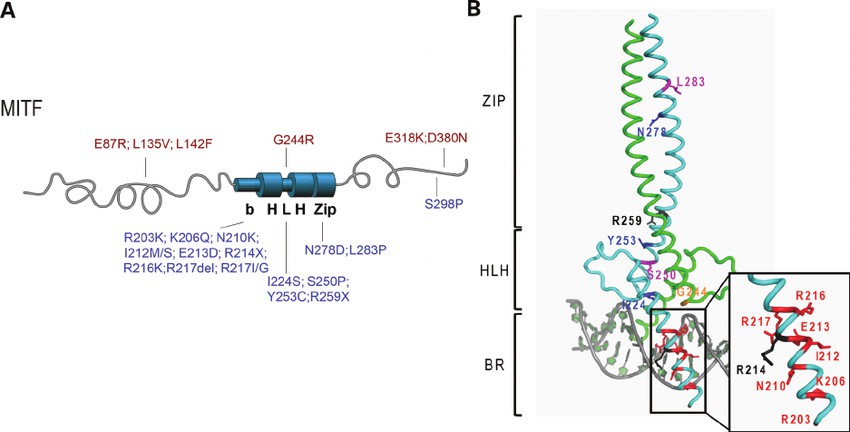
Fig1. MITF mutations found in melanoma (Grill, Christine, et al. 2013)
Functions of MITF
MITF protein plays a multi-faceted and essential role in the body. It primarily regulates the differentiation, development, and survival of melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigmentation in the skin, hair, and eyes. More specifically, MITF activates many genes that are required for specific steps in melanocyte development and pigment production. Beyond this role, it also regulates osteoclast development, contributing to bone remodeling and maintaining normal bone health.
MITF also possesses transcriptional activity, regulating gene expression and contributing to cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. In this context, it plays an essential role in early embryonic development and cellular responses to external stimuli, including oxidative stress and DNA damage.
MITF Protein-related signal pathways
MITF engages in distinct signal transduction pathways, most notably the MAPK/ERK pathway. MITF acts as a downstream effector in the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway where phosphorylation event activates its transcriptional activity. This implies that abnormal activation or mutation in these pathways can significantly affect cell proliferation and potentially lead to disease.
MITF protein and related diseases
When the function of the MITF protein is altered due to various reasons like gene mutation or dysregulation, it can lead to several disorders. These include Waardenburg Syndrome Type II, in which mutations in the MITF gene lead to hearing loss and changes in pigmentation. Another well-known disease related to MITF mutation is the Tietz Syndrome, characterized by profound hearing loss and universally pale skin and light hair color.
Most significantly, research findings suggest a crucial role for MITF in the occurrence of malignant melanoma. The correlation is tied to the protein's role in melanocyte development, and abnormal MITF activity can lead to unregulated proliferation and survival of melanocytes, resulting in melanoma.
MITF in biomedical applications
The understanding of MITF protein's role and functionality has significant implications in the biomedical field. For instance, it has potential use as a biomarker for various diseases due to its critical role in cell differentiation and proliferation. Moreover, targeting MITF in therapeutic approaches, particularly in the context of melanoma, has become a major objective. The modulation of MITF expression, either by pharmacological agents or innovative genetic strategies, holds the promise of treating melanoma effectively.
Consequently, albeit the complexity of the various ISO forms and the broad range of its activity, understanding the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor remains a prominent focus in biomedical research. The significant role that MITF protein plays in various developmental, physiological, and pathological processes underlines its relevance as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target. Extensive research on its molecular mechanisms is essential to completely unlock its potential in mitigating disease progression.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MITF-737H | Recombinant Human MITF Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| MITF-6272HF | Recombinant Full Length Human MITF Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| MITF-2446HB | Recombinant Human MITF Protein (Met1-Cys520), N-His tagged, Biotinylated | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| mitF-3722A | Recombinant Aspergillus fumigatus mitF protein, His-SUMO & Myc-tagged | Aspergillus fumigatus | E.coli | His-SUMO & Myc |
| MITF-2597R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque MITF Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rhesus Macaque | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Grill, Christine & Bergsteinsdottir, Kristin & Ogmundsdottir, Margret & Pogenberg, Vivian & Schepsky, Alexander & Wilmanns, Matthias & Pingault, Véronique & Steingrímsson, Eiríkur. (2013). MITF mutations associated with pigment deficiency syndromes and melanoma have different effects on protein function. Human molecular genetics. 22. 10.1093/hmg/ddt285.

