What is MMP7 Protein
The matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7) protein, also termed matrilysin, is an enzyme encoded by the MMP7 gene in the human body. Initially discovered in the 1980s, this protein has attracted significant attention owing to its relationship with various physiological and pathological events.
The MMP7 protein is encoded by the gene located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q22.3. It measures about 19 kilodaltons and is considered one of the smallest in the matrix metalloproteinase family. Structurally, MMP7 is composed of a propeptide domain, a catalytic domain, and a hemopexin-like C-terminal domain, absent in MMP7. Its expression is regulated at the transcriptional level, which explains its high concentration in diverse pathological conditions.
Function of MMP7 Protein
MMP7 plays pivotal roles in the body's various physiological and homeostatic processes. It degrades components of the extracellular matrix (ECM), influencing tissue remodeling during development, wound healing, and physiological angiogenesis. ECM degradation by MMP7 can result in the release of bioactive ECM-sequestered molecules, influencing multiple signal transduction pathways. MMP7 also acts upon non-matrix proteins such as E-cadherin, pro-α-defensins, and the precursor of the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor.
MMP7 Protein Related Signal Pathway
One of the essential signaling pathways involving the MMP7 protein is the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In cancer, abnormal activation of this pathway induces MMP7 gene expression, contributing to cell invasion and metastasis. Notably, regulated intramembrane proteolysis releases the intracellular domain of E-cadherin, which then translocates to the nucleus to drive MMP7 gene expression. Furthermore, MMP7 is upregulated consistently in interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) pathways involved in inflammation, cell proliferation, and tissue remodeling.
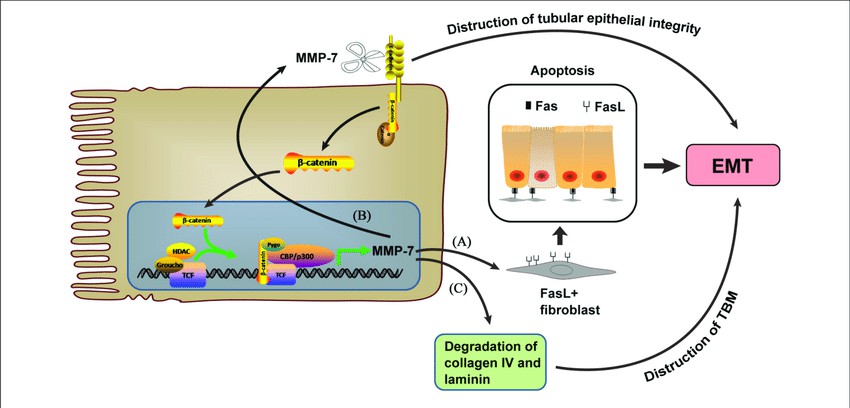
(Ke, Ben & Fan, et al. 2017)
MMP7 Protein Related Diseases
MMP7 is associated with various pathological events, including inflammation and cancer. For instance, in inflammatory bowel disease, upregulation of MMP7 contributes to tissue injury and remodeling. In cancer, MMP7 overexpression has been found in many malignant tumors, including those of the breast, prostate, colon, stomach, pancreas, and lung. Its overexpression is associated with poor prognosis, enhanced invasiveness, and metastasis, largely due to its capacity for ECM remodeling and modulation of cell-cell adhesion, angiogenesis, and tissue invasion.
MMP7 Protein's Applications in biomedical
Given its involvement in different physiological and pathological processes, MMP7 serves as an attractive target for biomedical research and therapeutic intervention. Its quantifiable level in various biological fluids makes it a valuable biomarker for several pathological conditions, such as colorectal cancer and acute kidney injury.
In cancer therapy, efforts are being made to design inhibitors that block MMP7 activity, thereby preventing malignant progression. Some of these include small molecules, antibodies, and engineered tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). The recombinant human MMP7, used in various experimental models, sheds light on the causes and mechanisms of related diseases, which can further lead to the development of potential clinical applications.
In conclusion, MMP7 is indeed a versatile protein that plays a critical role in various physiological operations of the human body. Its involvement in pathological conditions, particularly cancer, makes it a valuable target for therapeutic intervention. Advances in our understanding of this protein's structure and function, along with the burgeoning potential for its clinical use, bring promises of improved diagnostics and treatments for devastating diseases. The future of research into the MMP7 protein is indeed promising as the unraveling of its full spectrum of biological roles continues.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP7-810H | Recombinant Human MMP7, Fc tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| MMP7-395H | Recombinant Human MMP7 Protien, GST-tagged | Human | E. coli | GST |
| MMP7-22H | Active Recombinant Human MMP7 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| MMP7-5435H | Recombinant Human MMP7 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| MMP7-6280HF | Recombinant Full Length Human MMP7 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| Mmp7-203M | Active Recombinant Mouse Mmp7 | Mouse | Mammalian cells | N/A |
| Mmp7-10595M | Recombinant Mouse Mmp7 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| MMP7-3374R | Recombinant Rat MMP7 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Ke, Ben & Fan, Chuqiao & Yang, Liping & Fang, Xiangdong. (2017). Matrix Metalloproteinases-7 and Kidney Fibrosis. Frontiers in Physiology. 8. 10.3389/fphys.2017.00021.

