MMP7
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. The enzyme encoded by this gene degrades proteoglycans, fibronectin, elastin and casein and differs from most MMP family members in that it lacks a conserved C-terminal protein domain. The enzyme is involved in wound healing, and studies in mice suggest that it regulates the activity of defensins in intestinal mucosa. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP7;matrix metallopeptidase 7 (matrilysin, uterine);MMP-7;MPSL1;PUMP-1;matrilysin;matrin;pump-1 protease;uterine matrilysin;uterine metalloproteinase;matrix metalloproteinase-7;matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin, uterine);MAT
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cattle
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- NS0
- HEK293
- Yeast
- CHO
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- His
- T7
- Avi
- SUMO
- GGQ
- TG
Background
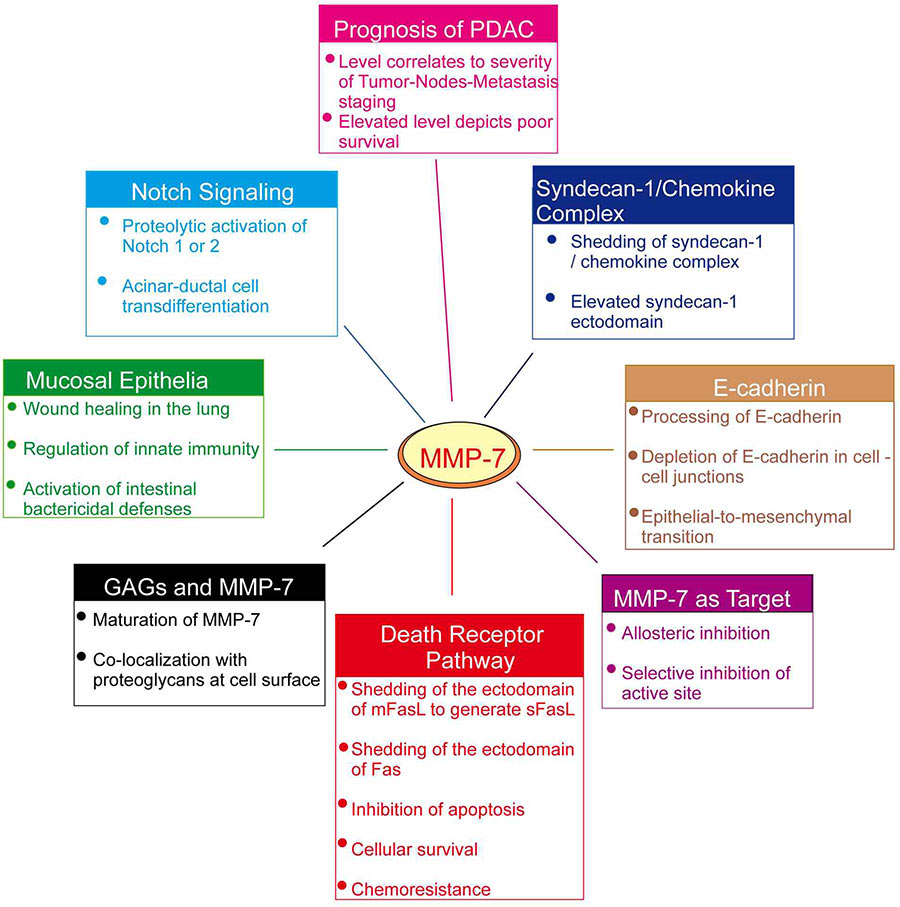
Fig1. MMP-7 roles, structure, function, and inhibition. (Steven R Van Doren, 2022)
What is MMP7 protein?
MMP7 gene (matrix metallopeptidase 7) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q22. This gene encodes a member of the peptidase M10 family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate the mature protease. This secreted protease breaks down proteoglycans, fibronectin, elastin and casein and differs from most MMP family members in that it lacks a conserved C-terminal hemopexin domain. The enzyme is involved in wound healing, and studies in mice suggest that it regulates the activity of defensins in intestinal mucosa. The MMP7 protein is consisted of 267 amino acids and MMP7 molecular weight is approximately 29.7 kDa.
What is the function of MMP7 protein?
MMP7 protein is a secreted zinc-dependent endopeptidase that plays a role in a variety of biological processes. MMP7 is capable of degrading extracellular matrix and through this degradation plays a regulatory role in physiological processes such as tissue repair, wound healing, bone growth and remodeling. In addition, MMP7 also plays an important role in the pathological process, especially in the occurrence and development of cancer, which can promote the proliferation, differentiation, metastasis and invasion of cancer cells. The expression of MMP7 is associated with clinical features in patients with multiple cancers, and its expression pattern can serve as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for a variety of human diseases.
MMP7 related signaling pathway
Matrix metalloproteinase-7 (MMP7), also known as matrilysin, belongs to the family of zinc-dependent endopeptidases. It cleaves various ECM components, such as type IV collagen, laminin, and elastin, thereby facilitating cell migration, invasion, and tissue remodeling. MMP7 is upregulated by various signaling pathways, including those involving growth factors like epidermal growth factor (EGF) and cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). Its activity is tightly regulated by endogenous inhibitors called tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
MMP7 related diseases
The MMP7 protein plays an important role in the occurrence and development of many diseases. The expression level of MMP7 is elevated in many types of cancer, including lung cancer, stomach cancer, colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, bladder cancer, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, etc., and its expression is closely related to tumor invasiveness, metastasis and prognosis. MMP7 is involved in tumor progression by promoting the proliferation, differentiation, migration and invasion of tumor cells. In addition, MMP7 also plays a role in non-neoplastic diseases such as chronic kidney disease and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and its abnormal expression may lead to tissue damage and fibrosis.
Bioapplications of MMP7
By harnessing its ability to degrade extracellular matrix (ECM) components, rhMMP7 can facilitate the development of novel treatments for conditions characterized by excessive ECM deposition, such as fibrotic diseases and atherosclerosis. In oncology, rhMMP7 holds potential as a therapeutic agent to enhance drug delivery across biological barriers or as a targeted therapy for cancers overexpressing specific MMP7 receptors. Additionally, due to its role in ECM remodeling, rhMMP7 can be utilized in regenerative medicine to promote wound healing and tissue engineering applications. Furthermore, its specificity for certain ECM proteins makes it a candidate for imaging agents to visualize ECM changes in disease states.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Suwen Ou, 2023
Colorectal cancer (CRC), the third most prevalent cancer, often harbors high levels of Fusobacterium nucleatum (F. nucleatum), which may promote metastasis. Researchers conducted a comprehensive analysis to identify key genes and pathways influenced by F. nucleatum. Using 16S rDNA sequencing and q-PCR, they confirmed its overabundance in CRC tissues and stools. The experiments showed that F. nucleatum enhances CRC cell migration by upregulating Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP7), which is linked to poor prognosis. Researchers also identified potential drugs from the HERB database that could target MMP7, suggesting new therapeutic strategies for CRC.
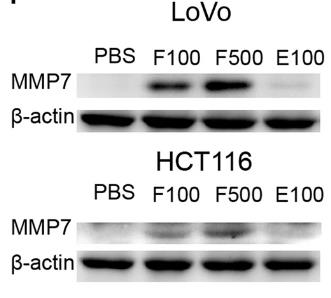
Fig1. The protein expression of MMP7 after PBS treatment.
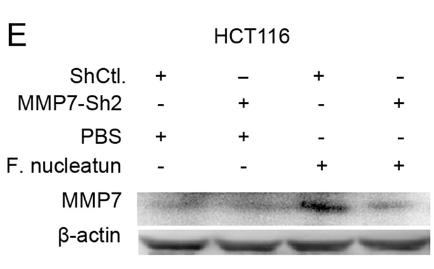
Fig2. WB results showed F. nucleatum promotes the migration of CRC cells by upregulating MMP7.
Case Study 2: Yue Yin, 2021
Long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) can lead to peritoneal membrane dysfunction and ultrafiltration failure. Mesothelial cells are crucial for peritoneal membrane health, and Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), particularly MMP-7, are key in maintaining extracellular matrix balance. This study found that MMP-7 levels rise in PD patients, correlating with reduced ultrafiltration. MMP-7 affects cell osmotic pressure and volume in mesothelial cells by activating the MAPKs-ERK pathway, which increases aquaporin-1 (AQP-1) expression. Blocking the ERK pathway can reverse MMP-7's effects on AQP-1 and cell homeostasis.
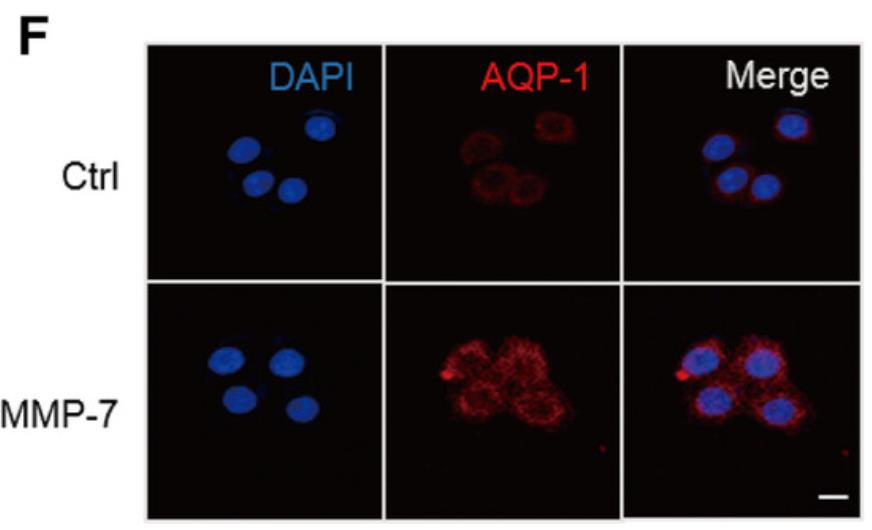
Fig3. The cells were treated with indicated MMP-7 for 12 hours and immunofluorescence assay was used to detect the expression of AQP-1.
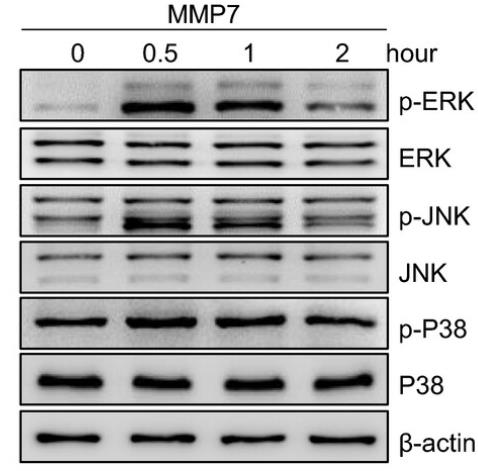
Fig4. HMrSV5 cells were stimulated with MMP-7 protein for indicated time points, and the phosphorylation level of ERK, JNK and p38 was detected by Western blotting.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP7-49H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MMP7-5434H)
Involved Pathway
MMP7 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP7 participated on our site, such as Wnt signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP7 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Wnt signaling pathway | CAMK2B1,WNT7AA,CXXC4,NLK1,FZD3B,CAMK2D2,NFATC3,TCF7L1A,FOSL1,PORCNL |
Protein Function
MMP7 has several biochemical functions, for example, heparin binding,metalloendopeptidase activity,zinc ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP7 itself. We selected most functions MMP7 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP7. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| zinc ion binding | TIMM9,TRIM11,LHX5,ZFP330,ADAM21,KDM2BA,BIRC7,RNF145B,EWSR1,MYLIP |
| heparin binding | ADAMTSL5,LPA,ZFP207,RSPO4,SOST,FGFR2,UBE4A,PRG2,ABI3BP,CXCL13 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | MMP23B,MMP20,UQCRC2,MEP1A.1,ADAMTS4,ZMPSTE24,ADAM22,ADAMTS5,MBTPS2,XRCC6BP1 |
Interacting Protein
MMP7 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP7 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP7.
ELN;FASLG
Resources
-
-cover.jpg)
Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
-

Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kim, GE; Lee, JS; et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in different immunohistochemical-based molecular subtypes of breast cancer. BMC CANCER 14:-(2014).
- Mitsui, H; Suarez-Farinas, M; et al. Gene Expression Profiling of the Leading Edge of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: IL-24-Driven MMP-7. JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY 134:1418-1427(2014).



