What is PPM1G Protein
The field of Proteomics has been significantly enriched with the discovery of various proteins that play an integral part in the human body's biological processes. Among these proteins, the PPM1G protein (Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent 1G), has attracted significant attention due to its critical role in numerous cellular activities and its association with diverse diseases.
The PPM1G protein, also known as PP2C gamma, is a member of the PP2C family of Ser/Thr protein phosphatases, initially discovered due to its regulatory roles in diverse cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and in RNA splicing. It was identified as part of the human genome project, which discovered and located thousands of genes on different human chromosomes. PPM1G is encoded by the PPM1G gene which is located in the gene locus on the short arm of chromosome 16 at position 16p13.3.
The PPM1G protein, of length 496 amino acids, displays a structure consisting of a rossman fold and hydrolase domain. Its structural configuration enables it to bind selectively to ions, specifically Magnesium or Manganese. It can dephosphorylate serine and threonine residues in other proteins, performing a regulatory role in various biological functions.
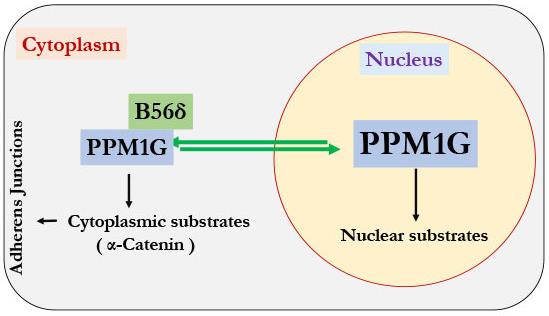
Fig1. PPM family phosphatases are thought to act as monomers. (Parveen Kumar, et al. 2019)
Function of PPM1G Protein
PPM1G is a ubiquitous protein in human tissues predominantly found in the nucleus, but it is also well-distributed in the cells' cytoplasm. It has several functions, mainly revolving around cell cycle progression and RNA processing.
PPM1G has a critical role in RNA splicing, a process through which the non-coding introns are removed from the pre-messenger RNA, and the coding exons are joined together to produce a mature messenger RNA molecule. This process allows the creation of multiple different proteins from a single gene due to alternative splicing patterns. PPM1G dynamically associates with the spliceosome, and it is believed that it might contribute to the spliceosome's catalytic activities.
Another significant function of the PPM1G protein is in cell cycle transitions. It is involved in the progression of the cell cycle by dephosphorylating CDK1, an essential protein required for starting various tasks associated with cell division, implying that the protein plays a critical role in cell division.
PPM1G Protein related Signal Pathway
In cellular signal transduction pathways, PPM1G involves the regulation of the Akt (protein kinase B) signaling pathway. It acts as a negative regulator by dephosphorylating and inactivating the Akt, which is critical in many cellular processes like glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration.
PPM1G Protein related Diseases
Given the PPM1G's significant function in multiple cellular pathways, alterations in its behavior can lead to or be associated with various diseases. Mutations in the PPM1G gene have been linked with idiopathic basal ganglia calcification (IBGC), also known as Fahr's disease. This neurodegenerative disorder is characterized by abnormal calcium deposits in the brain, which lead to a variety of neurological symptoms including dementia, headache, psychosis, and seizures.
Moreover, recent research has demonstrated the PPM1G protein's importance in cancer pathogenesis, specifically hematological malignancies. PPM1G has been shown to be critical in the self-renewal of acute myeloid leukemia cells, suggesting that drugs targeting PPM1G could be promising for treating this disease.
PPM1G Protein's Applications in Biomedical
The importance of PPM1G protein in various biological functions and disease pathways makes it a potentially useful target in biomedical research. Its influence in the cell cycle progression, RNA splicing, and signal pathway regulation are important aspects studied in cancer research and neuroscience.
Targeting the PPM1G protein could lead to the development of novel therapies for certain types of cancers. Additionally, understanding the precise role of PPM1G in RNA splicing and cell cycle progression may elucidate the molecular basis of certain neurodegenerative disorders, potentially leading to innovative therapeutic strategies.
Overall, the PPM1G protein is an important and dynamic molecular entity in our body's cellular machinery, playing key roles in vital processes. Its contribution to disease development provides an intriguing target for further biomedical research and therapeutic development.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPM1G-1151H | Recombinant Human PPM1G, His tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PPM1G-1896H | Recombinant Human PPM1G, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PPM1G-1352H | Recombinant Human PPM1G Protein, Flag-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Flag |
| PPM1G-001H | Recombinant Human PPM1G Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Insect cell | GST |
| PPM1G-560HFL | Active Recombinant Full Length Human PPM1G Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| PPM1G-1745H | Recombinant Human PPM1G Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| PPM1G-6992M | Recombinant Mouse PPM1G Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| PPM1G-3372R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque PPM1G Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rhesus Macaque | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Parveen Kumar, Prajakta Tathe, Neelam Chaudhary, Subbareddy Maddika. PPM1G forms a PPP-type phosphatase holoenzyme with B56δ that maintains adherens junction integrity. EMBO Reports (2019)20:e46965https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201846965

