What is PTK7 Protein
PTK7 (Protein Tyrosine Kinase 7), also known as the colon carcinoma kinase-4, is a conserved transmembrane protein that belongs to the family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Discovered in the early 1990s, PTK7 protein has drawn great attention due to its atypical nature. Unlike conventional RTKs, PTK7 lacks intrinsic catalytic activity because of its kinase dead nature which makes it unable to phosphorylate other proteins. However, it doesn't make PTK7 any less important or influential in cellular processes.
Function of PTK7 Protein
Despite lacking a typical kinase domain, PTK7 protein is instrumental in several critical processes. This includes cell adhesion, migration, and the regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), an essential mechanism associated with developmental processes, tissue repair, and pathological conditions like cancers and fibrosis. Interestingly, PTK7 does this through the intricate process of intricate signal transduction.
PTK7 Protein Related Signaling Pathways
Several signaling pathways are associated with PTK7 protein, particularly the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway and the Wnt signaling pathway - both very critical for normal embryonic development. The PCP pathway is fundamental in governing the organization of cells in the plane of epithelial sheets, which is essential for organ development. PTK7 has been found to influence the PCP pathway, affecting the asymmetric distribution of PCP components.
Similarly, in the Wnt signaling pathways, PTK7 acts as an important modulator. Wnt signaling is an intricate network that regulates cell-to-cell interactions during embryogenesis and also affects cell proliferation, motility, and morphogenesis. PTK7 plays a role both in canonical and non-canonical Wnt pathways, impacting cell polarity and movement.
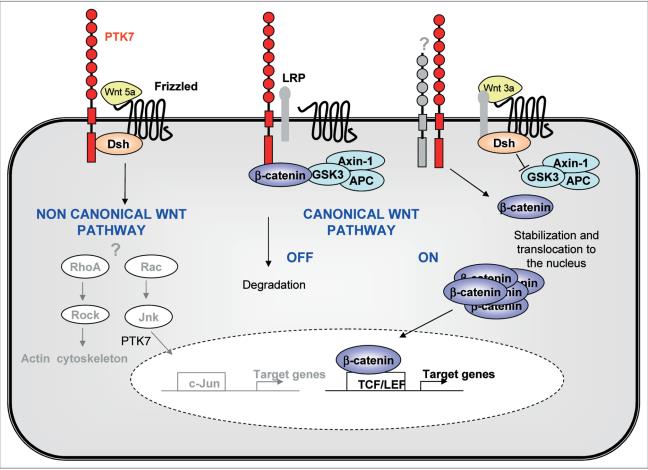
Fig1. Multiple modes of action of PTK7 in Wnt signaling. (Anne-Catherine Lhoumeau, et al. 2011)
PTK7 Protein Related Diseases
Given the critical role of PTK7 in key cellular processes, it is unsurprising that abnormalities in PTK7 can result in a myriad of conditions. It has been strongly linked to the progression of various types of cancer, including colorectal, gastric, and lung cancer. Overexpression of PTK7 protein in these cancers has been associated with advanced disease stages, poor patient prognosis, and increased metastasis.
Apart from cancer, alterations in PTK7 protein are also known to contribute to congenital disorders like neural tube defects. Studies have highlighted how mutations in PTK7 resulted in disrupted cell movements, contributing to neural tube defects in mice.
PTK7 Protein's Applications in Biomedicine
Thanks to the understanding of the PTK7 protein's role in disease pathology, medical science has been making advancements to leverage this knowledge. The overexpression of PTK7 in different cancer types has been exploited for targeting cancer cells using PTK7 as an antigen for antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). This has significantly expanded the scope of targeted cancer treatment.
Moreover, the ability of PTK7 to regulate cell adhesion and migration has also been investigated for its potential to manage the process of wound healing and tissue repair. The identification of specific PTK7 inhibitors may provide therapeutic opportunities to manage poor wound healing and chronic ulcers.
In summary, PTK7 protein holds promise as a key player in modulating primary cellular functions, impacting disease progression, and offering therapeutic targets for numerous conditions, particularly cancers. Leveraging its potentials can revolutionize the management of these conditions, making it a fascinating candidate for further research.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTK7-0637H | Recombinant Human PTK7 protein, His-Avi-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | HEK293 | His-Avi |
| PTK7-1752H | Recombinant Human PTK7 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| PTK7-01H | Active Recombinant Human PTK7 Protein, Fc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| PTK7-2109H | Recombinant Human PTK7 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| PTK7-13660M | Recombinant Mouse PTK7 Protein, His and Myc tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His and Myc |
| PTK7-7266M | Recombinant Mouse PTK7 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Ptk7-5229M | Recombinant Mouse Ptk7 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Anne-Catherine Lhoumeau, Francesca Puppo, Thomas Prébet, Laurent Kodjabachian & Jean-Paul Borg (2011) PTK7: A cell polarity receptor with multiple facets, Cell Cycle, 10:8, 1233-1236, DOI: 10.4161/cc.10.8.15368

