What is RAC1 Protein
The highly conserved RAC1 protein, encoded by the "Ras-Related C3 Botulinum Toxin Substrate 1" (RAC1) gene, is a member of the Rho family of GTPases. It was initially discovered in the late 1980s while scientists were working on identifying genes similar to RAS. It has since emerged as a major player in several vital biological processes.
RAC1 protein has genes at locus 7p22.1 and constitutes seven exons that span over 31.6 kilobases. The genomic DNA flanking the start codon lacks classic TATA or CAAT boxes, but exhibits multiple transcription initiation sites. RAC1 protein is assembled from 192 amino acids, consisting of 6 helices and 6 beta strands, arranged to form the typical small GTPase fold. The structure includes a six-strand beta sheet surrounded by five alpha helices, creating a deep nucleotide-binding pocket.
Function of RAC1 protein
The function of the RAC1 protein is intriguing due to its diversity and centrality in essential cell processes. It regulates various intracellular mechanisms, such as control of cell growth, cytoskeletal rearrangements that lead to cell morphogenesis, as well as the cell cycle progression and gene expression. Other functions include the mobility and polarity of cells during migration, and the Latin name "Ras-Related C3" confirms its involvement in signal transduction pathways, especially those related to cell division and growth.
RAC1 protein related signal pathway
RAC1 modulates numerous signal transduction pathways, positioning it at the center of many biological processes. Owing to its role as molecular switches, RAC1 cycles between an inactive GDP-bound state and an active GTP-bound state, regulating significant receptor-mediated signaling pathways. It interacts with several effector proteins, for instance, p21-activated kinases, leading to the activation of Jun N-terminal Kinase and stimulating cell proliferation. RAC-GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors) activate RAC1 by facilitating the exchange of GDP for GTP. Once activated, RAC1 binds to an extensive range of effector proteins to generate downstream signals regulating actin cytoskeleton, gene expression, cell cycle, and antioxidative response.
RAC1 protein related diseases
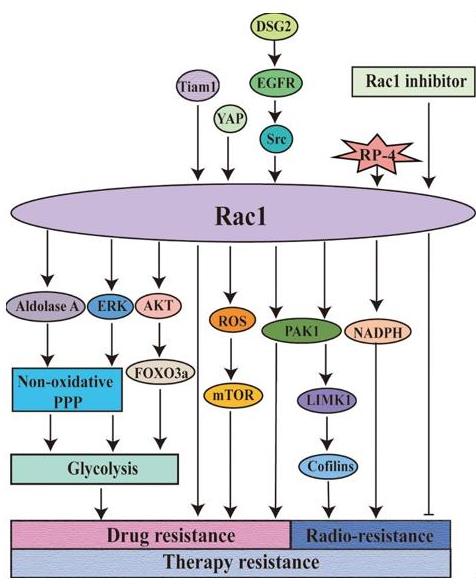
Fig1. Rac1 is involved in the regulation of resistance to tumor therapy (Jiaxin Liang, et al. 2021)
Considering its wide-ranging involvement, alterations in RAC1 protein function can result in numerous diseases. In many cancers, the RAC1 gene mutation or overexpression is connected to poorer survival rates and cancer progression. Genomic sequencing studies have identified RAC1 as a frequently mutated gene in melanoma, signifying its importance in tumorigenesis. Additionally, the RAC1 protein has been implicated in neurodegenerative conditions. For instance, RAC1 activity decreases in Alzheimer's disease, affecting the neurons' shape and function. Furthermore, aberrations in the RAC1 pathway are found to aid the spread of viral and bacterial infections.
RAC1 protein's applications in biomedical
Biomedical applications of RAC1 protein are gaining prominence due to its critical role in disease pathologies. Monitory of RAC1 activity can serve as a promising biomarker for disease diagnosis and treatment response. Small molecules inhibiting RAC1 activation are under consideration for therapeutic prospects. Particular attention is being paid to potential drugs for cancer, where chemotherapy resistance is a recurring problem. Also, given its involvement in cell migration, targeting RAC1 might help in treating pathological conditions related to abnormal cell movement like metastasizing tumors.
In neurology, therapeutic approaches aim to modulate RAC1 activity to normal levels. In Alzheimer's disease, an upregulation of RAC1 activity could counteract the characteristic neuronal changes; thus, they could alleviate or even arrest disease progression. The same principle might also apply to neurodevelopmental disorders linked to RAC1 mutations, like intellectual disability.
To conclude, the RAC1 protein is an essential component of cellular functions and signal transduction pathways, influencing several diseases' pathophysiology, mainly cancer and neurological disorders. Ongoing investigations into RAC1's role and modulation offer great potential for developing targeted therapies, making this small GTPase a compelling interest in the field of biomedical research. However, understanding the RAC1 protein's multiple nuances also demands a cautious approach due to its fundamental role in healthy cell functioning. Therefore, future research and clinical trials should be meticulously designed to harness the therapeutic potential of RAC1 without causing undue harm.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAC1-2147H | Recombinant Human RAC1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| RAC1-2213H | Recombinant Human RAC1 protein, GST-tagged | Human | Insect Cells | GST |
| RAC1-445H | Recombinant Human RAC1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| RAC1-1105HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human RAC1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| RAC1-1845H | Recombinant Human RAC1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| RAC1-7379M | Recombinant Mouse RAC1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Rac1-5344M | Recombinant Mouse Rac1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Jiaxin Liang, Linda Oyang, Shan Rao, et al. Rac1, A Potential Target for Tumor Therapy. Front. Oncol., 17 May 2021. Sec. Cancer Molecular Targets and Therapeutics. Volume 11 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.674426

