What is TNC Protein
Tenascin-C (TNC), a complex glycoprotein integral to the extracellular matrix, stands as a molecular cornerstone with far-reaching implications in biological processes.
What is TNC Protein?
TNC, a modular glycoprotein, encapsulates the essence of extracellular matrix dynamics. Comprising epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats and fibronectin type III (FNIII) domains, TNC's structural complexity underscores its functional significance. Its expression, while subdued in adult tissues under normal conditions, becomes pronounced during embryonic development, hinting at a critical role in morphogenesis.
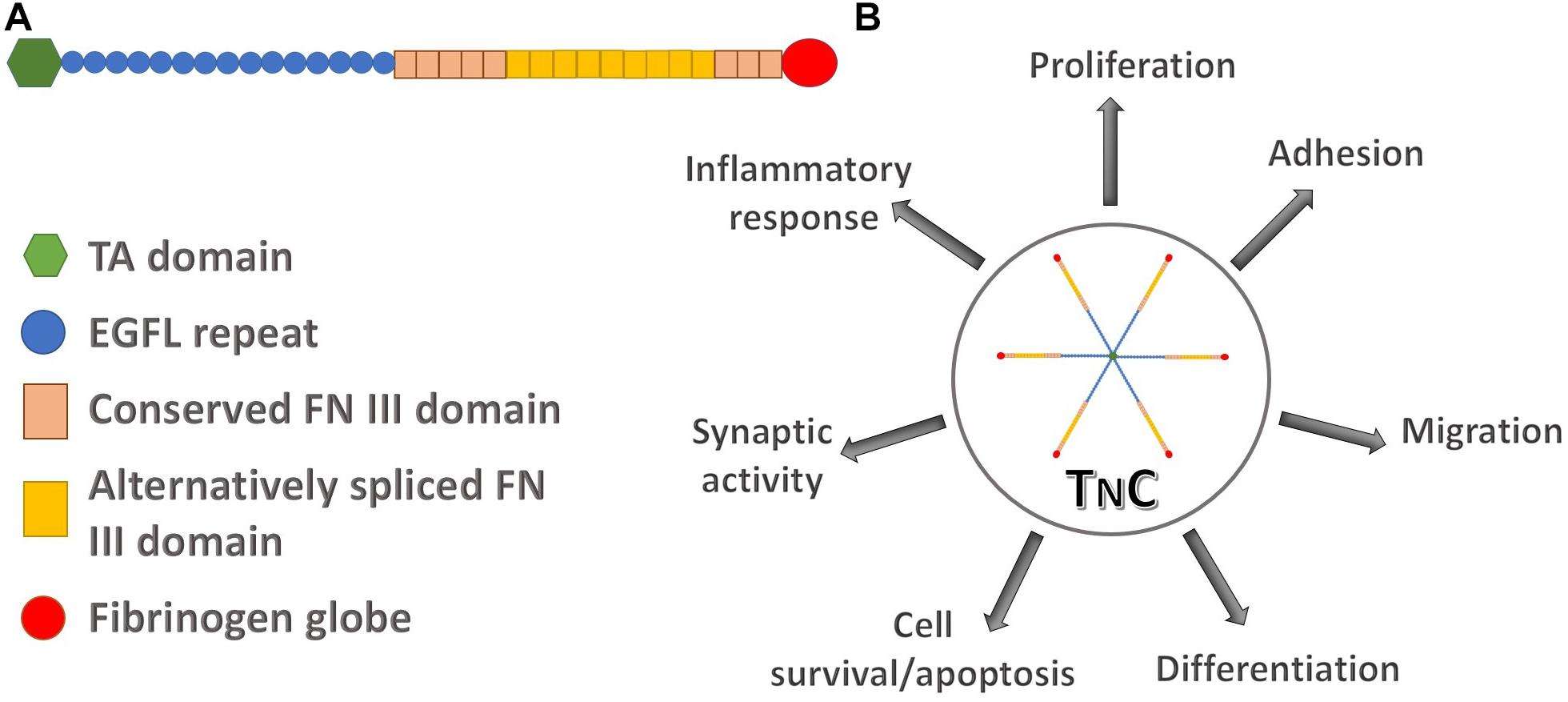
Figure 1. The structure of human tenascin C and its involvement in different regulatory pathways. (Tucić, M., et al. 2021)
The Function of TNC Protein
- Cell Adhesion and Migration
At the heart of TNC's functionality lies its prowess in cell adhesion and migration. TNC acts as a substrate facilitating cellular attachment and orchestrates cellular movements in critical processes such as tissue repair and regeneration. Its interaction with cell surface receptors manifests in the modulation of various cell types, ranging from neural cells to immune and endothelial cells.
- Tissue Development and Remodeling
Embryonic development witnesses a surge in TNC expression, contributing significantly to tissue development and remodeling. By influencing cell differentiation and the assembly of extracellular matrix components, TNC emerges as a key player in sculpting the architecture of developing tissues and organs.
- Regulation of Inflammation
TNC's role in immune responses and inflammation is noteworthy. It serves as a dynamic modulator, impacting the activation and function of immune cells. Dysregulation of TNC expression can exacerbate inflammation, potentially influencing the trajectory of diseases.
TNC-Related Diseases
- Cancer
TNC's association with cancer underscores its significance in disease pathology. Elevated TNC levels in the tumor microenvironment provide a conducive milieu for cancer cell survival, invasion, and metastasis. Its modulatory role in the interaction between cancer cells and the extracellular matrix amplifies its impact on tumor progression.
- Neurological Disorders
Implications of TNC in neurological disorders add another layer to its biological relevance. Playing a role in axon guidance during development, aberrant TNC expression surfaces in conditions like multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and spinal cord injury, offering avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions.
- Cardiovascular Diseases
TNC's involvement in cardiovascular diseases, particularly in tissue repair and remodeling post-injury, positions it as a potential player in conditions such as myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis. Deciphering its exact role in these scenarios holds promise for innovative therapeutic strategies.
TNC Related Signaling Pathways
- Wnt Signaling
TNC's entanglement with the Wnt signaling pathway unveils its participation in fundamental cellular processes. Interactions between TNC and Wnt signaling components intricately influence cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue homeostasis, contributing to both physiological and pathological conditions.
- Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) Signaling
The interplay between TNC and the TGF-β signaling pathway assumes significance in tissue development, repair, and fibrosis. TNC's capacity to modulate TGF-β activity adds a layer of complexity to cellular responses, offering potential insights into the pathogenesis of fibrotic diseases.
- Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) Signaling
TNC's regulation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling emerges as a crucial determinant of cell adhesion and migration. The interplay between TNC and FAK signaling pathways intricately governs cellular processes, including migration, invasion, and tissue remodeling.
Applications of TNC in Biomedical Research
- Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
TNC's unique properties position it as a promising candidate in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Scaffolds and substrates coated with TNC demonstrate efficacy in promoting cell adhesion, migration, and tissue regeneration, presenting themselves as valuable tools for therapeutic interventions in tissue repair.
- Cancer Therapeutics
The prospect of targeting TNC in cancer therapy opens new avenues. Strategies aimed at inhibiting TNC expression or disrupting its interactions with cancer cells hold promise in impeding tumor progression and metastasis. TNC-targeted therapies represent a burgeoning field in cancer research.
- Neurological Interventions
Manipulating TNC levels in the nervous system holds potential for therapeutic interventions in neurological disorders. Understanding TNC's precise role in conditions such as spinal cord injury or neurodegenerative diseases is imperative for the development of targeted treatment approaches.
The multifaceted nature of the Tenascin-C protein makes it a captivating subject of study in the realm of molecular biology and medicine. From its fundamental role in cell adhesion and migration to its implication in diseases ranging from cancer to neurological disorders, TNC continues to reveal its complexity. Moreover, the involvement of TNC in various signaling pathways underscores its importance as a potential therapeutic target. As researchers continue to unravel the intricacies of TNC, its applications in biomedical fields, such as tissue engineering and cancer therapeutics, hold promise for the development of innovative and targeted treatments for a wide array of conditions.
Recommended Products for TNC Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNC-31215TH | Human | Recombinant Human TNC | Wheat Germ | N/A |
| TNC-301211H | Human | Recombinant Human TNC protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST |
| TNC-33H | Human | Recombinant Human TNC protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| TNC-995HFL | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human TNC Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| TNC-34H | Human | Recombinant Human TNC protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| TNC-1082H | Human | Recombinant Human TNC Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| TNC-4224H | Human | Recombinant Human TNC Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Tnc-2326M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Tnc protein, His&Myc-tagged | Insect Cell | His&Myc |
| Tnc-2052R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Tnc protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| TNC-256R | Rabbit | Recombinant Rabbit Cardiac Troponin C | E.coli | N/A |
Reference
- Tucić, M., et al. The Extracellular Matrix Glycoprotein Tenascin C and Adult Neurogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021, 9: 674199.

