What is UBA1 Protein
The UBA1 protein, formally known as Ubiquitin-like Modifier Activating Enzyme 1, operates at the intricate intersection of cellular regulation. Also recognized by synonyms such as UBE1 or UBE1A, this protein is a crucial member of the ubiquitin-activating enzyme family. Its classification places it within the E1 enzyme category, signifying its role as the initiator of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
UBA1 Protein Structural Characteristics
Structurally, UBA1 boasts an intricate architecture that facilitates its biological functions. Comprising approximately 1050 amino acids, this protein exhibits a modular organization, with distinct domains responsible for specific interactions. Recent advances in research have shed light on the dynamic nature of UBA1, unraveling its participation in diverse cellular processes.
UBA1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
UBA1 orchestrates a molecular ballet within cells, primarily revolving around the activation of ubiquitin. Its fundamental role lies in catalyzing the adenylation and subsequent conjugation of ubiquitin to target proteins, marking them for degradation by the proteasome. This process is integral to cellular homeostasis, ensuring the removal of damaged or surplus proteins.
At a molecular level, UBA1 engages in a two-step enzymatic process. Initially, it adenylates ubiquitin, forming a high-energy thioester bond. Subsequently, this activated ubiquitin is transferred to a cysteine residue on the enzyme itself. This activation primes ubiquitin for subsequent attachment to target proteins, thereby modulating their fate within the cell.
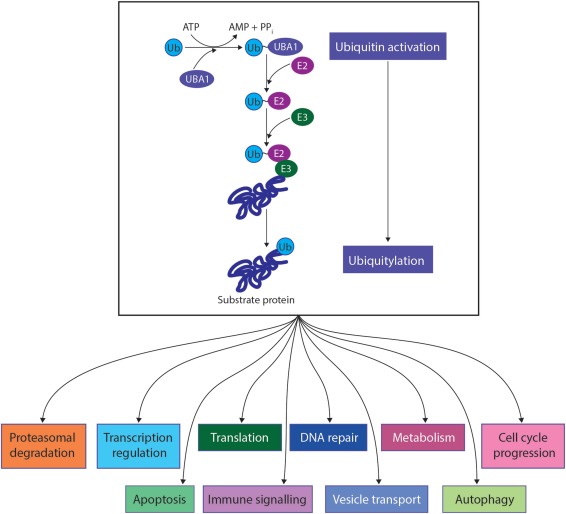
Figure 1. UBA1 biological functions. (Lambert-Smith I A, et al., 2020)
UBA1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway associated with UBA1 is intricately connected to cellular responses. As a pivotal player in ubiquitin-mediated signaling, UBA1 influences processes such as DNA repair, immune response, and cell cycle progression. The activation of ubiquitin by UBA1 initiates a cascade of events, culminating in the degradation of specific proteins or the modulation of signaling cascades.
Elucidating the UBA1-related signal pathway provides insights into the broader cellular context in which this protein operates, offering potential targets for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating specific cellular responses.
UBA1 Related Diseases
Disruptions in UBA1 function have been implicated in various diseases, underscoring its significance in maintaining cellular health. Mutations in the UBA1 gene have been linked to neurodegenerative disorders, highlighting the critical role of this protein in neuronal function. Additionally, aberrant UBA1 activity has been observed in certain cancers, emphasizing its involvement in the regulation of cell growth and proliferation.
Understanding these disease associations opens avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions, aiming to restore normal UBA1 function and mitigate pathological consequences.
UBA1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of UBA1 have positioned it as a valuable tool in biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, the detection of UBA1 levels can serve as a biomarker for certain diseases, providing a non-invasive means of assessing cellular health. Furthermore, the intricate involvement of UBA1 in immune responses opens avenues for vaccine development, leveraging its role in antigen presentation.
In the realm of therapeutics, UBA1 is a promising target for drug development. Small molecules that selectively modulate UBA1 activity hold the potential to fine-tune cellular processes, offering a novel approach to treating diseases associated with aberrant ubiquitin signaling.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBA1-105H | Active Recombinant Human UBA1 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| UBA1-832H | Recombinant Human UBA1, GST-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | GST |
| UBA1-7333H | Recombinant Human UBA1, His & GST tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His/GST |
| UBA1-476H | Recombinant Human UBA1, GST-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | Flag |
| UBA1-641H | Active Recombinant Human UBA1 Protein, GST-tagged, Active | Human | Insect Cell | GST |
| UBA1-337H | Recombinant Human UBA1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | Insect Cells | His |
| UBA1-58H | Recombinant Human Ubiquitin-like Modifier Activating Enzyme 1 | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | N/A |
| UBA1-264H | Recombinant Human UBA1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293 | C-Myc/DDK |
| UBA1-212H | Recombinant Human UBA1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| Uba1-6764M | Recombinant Mouse Uba1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Lambert-Smith I A, et al. The pivotal role of ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 (UBA1) in neuronal health and neurodegeneration. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2020, 123: 105746.

