What is UCHL1 Protein
The Ubiquitin Carboxy-terminal Hydrolase L1 (UCHL1), a protein encoded by the UCHL1 gene in humans, holds a significant position in the biomedical world due to its critical function in the neural system. UCHL1 contributes towards a range of functions and is associated with certain neurodegenerative diseases.
UCHL1, also recognized as Protein Gene Product 9.5 (PGP 9.5), was first discovered and characterized around the 1980s amid analyses to isolate proteins related to the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). Located on chromosome 4p14, the UCHL1 gene involves seven exons that encode this protein.
UCHL1 is a member of a gene family that comprises de-ubiquitinating enzymes — enzymes responsible for removing the ubiquitin molecule from proteins. The structure of the UCHL1 protein shows a unique fold in the form of the right-handed thumb-palm-fingers architecture. Its binding model with the ubiquitin C-terminus explains how specific residues of UCHL1 help facilitate the recognition and hydrolysis of their substrates.
Function of UCHL1 Protein
Primarily, UCHL1 is found in the neurons of the brain where it aids in maintaining the balance of the cell's protein metabolism. UCHL1's primary role involves trimming polymerized ubiquitin chains or recycling ubiquitin monomers by removing ubiquitin from the proteasome-bound, ubiquitinated proteins. The protein also has a secondary function related to the stabilization of mono-ubiquitin, ensuring a steady pool of ubiquitin for protein degradation. Thus, UCHL1 plays a central part in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Trouble arises when this delicate balance is disrupted.
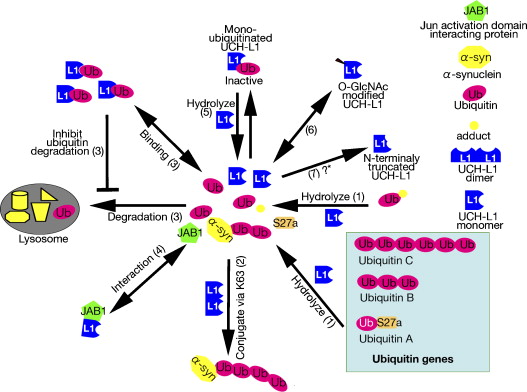
Fig1. The functions of UCH-L1 (Setsuie, R., & Wada, K. 2007)
UCHL1 Protein Related Signal Pathways
As a de-ubiquitinating enzyme, UCHL1 is a crucial regulator of several signaling pathways. It contributes to the ubiquitin-proteasome system that regulates cellular processes like DNA repair, cell cycle progression, and cellular differentiation. Furthermore, UCHL1 is involved in the NF-kB signaling pathway that oversees immune responses and inflammatory response. It also plays a role in the MAPK signaling pathway that controls cellular activities such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Thus, UCHL1's signaling capabilities are vital for the regular functioning of cells.
UCHL1 Protein Related Diseases
Malfunction or mutation of UCHL1 can lead to several neurodegenerative diseases. An abnormal UCHL1 gene leads to Familial Parkinson's disease, marked by a loss of motor control, tremors, rigidity, and more. UCHL1 has also been linked to Alzheimer's disease due to its interactions with hallmark proteins like Tau and beta-amyloid. Additionally, UCHL1 over-expression has been observed in several types of cancers, including lung, colorectal, and breast cancer, and it is considered a promising marker for malignant diseases.
UCHL1 Protein's Applications in Biomedicine
UCHL1's role in the framework of neurodegenerative disorders and cancer has brought it to the forefront of biomedical research. Its presence in bodily fluids makes it an excellent candidate for biomarkers to detect neurological conditions. Similarly, UCHL1's over-expression in many cancers has led to the exploration of its potential as a diagnostic and predictive biomarker in oncology.
Furthermore, the study of UCHL1 in neurobiology has been essential in generating potential treatments for neurological disorders. Efforts have been ongoing to develop UCHL1 inhibitors to control its over-activity observed in certain cancers and UCHL1-enhancing drugs for neurodegenerative conditions.
In conclusion, UCHL1 protein plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Its involvement in numerous signal pathways and disease realities confirms its biomedical significance. As researchers continue to unravel the functionalities and complexities of this protein, UCHL1 can potentially unfold as an instrumental component in combating some of the most debilitating diseases of our time.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UCHL1-1520H | Recombinant Human UCHL1 | Human | Human | N/A |
| UCHL1-2302H | Recombinant Human UCHL1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| UCHL1-20H | Recombinant Human UCHL1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| UCHL1-01HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human UCHL1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| UCHL1-49H | Recombinant Human UCHL1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| Uchl1-20M | Recombinant Mouse Uchl1, His tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Uchl1-611M | Active Recombinant Mouse Uchl1 Protein, His-tagged | Mouse | E.coli | His |
| Uchl1-17R | Recombinant Rat Uchl1 protein, His/S-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His/S |
| Uchl1-612R | Active Recombinant Rat Uchl1 Protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
Reference
- Setsuie, R., & Wada, K. (2007). The functions of UCH-L1 and its relation to neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochemistry International, 51(2-4), 105-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2007.05.007

