What is ZEB1 Protein
The ZEB1 protein, also known as Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1, holds an impactful position in the field of molecular biology. This elaborate protein sequence, encoded by the ZEB1 gene, plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including cell differentiation, gene regulation and immune response, all the while contributing to a host of diseases.
The discovery of ZEB1 protein had led to a significant shift in our understanding of several significant biological processes, especially in the context of cancer biology. In the early 1990s, the ZEB1 gene was initially identified as a binding partner of the delta-crystallin enhancer, a sequence involved in lens differentiation in chickens.
Located on chromosome 10 at the position 10p11.22, the ZEB1 gene spans around 111.25 kilobases. It comprises over eight recognized variants producing different isoforms of the ZEB1 protein. The protein structure of ZEB1 includes a homeodomain flanked by two clusters of zinc fingers, hence the name. The N-terminal cluster contains four zinc fingers, while the C-terminal cluster contains three. These elements function as DNA-binding domains, enabling ZEB1 to control the transcription of other genes.
Function of ZEB1 protein
The primary function of the ZEB1 protein is transcriptional repressors, regulating the expression of specific genes involved in differentiation and development. By binding to E-box motifs in the DNA, it inhibits the transcription of various genes necessary for the epithelial phenotype. Additionally, the ZEB1 protein plays an integral role in the process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), critical in embryogenesis, tissue repair, and cancer progression.
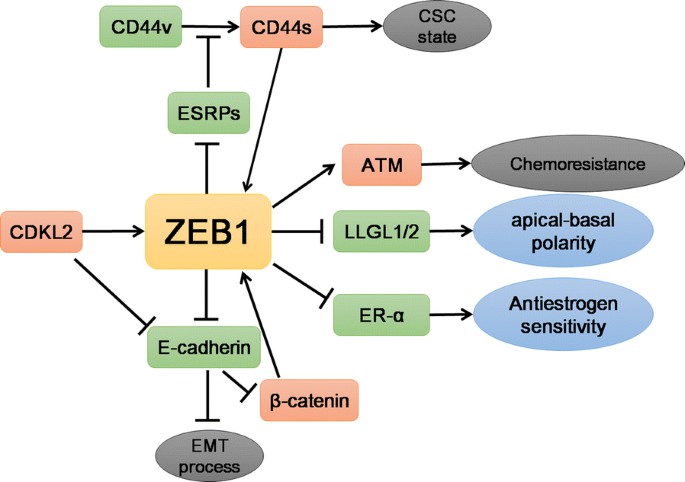
Fig1. The main targets of ZEB1 and the processes involved in breast cancers. (Hua-Tao Wu, et al. 2020)
To understand the functionality of ZEB1 comprehensively, it is imperative to assess its involvement in cellular signal pathways. A critical ZEB1 protein related signal pathway includes the TGF-beta signaling pathway, more specifically with the SMAD family of proteins. ZEB1 can interact with SMAD proteins to control gene expressions integral to EMT. Upon TGF-beta stimulation, the ZEB1/SMAD complex accumulates, suppressing epithelial gene expressions and promoting EMT.
ZEB1 protein related diseases
Further research into ZEB1 has unveiled its implications in several diseases, predominantly cancer. ZEB1 protein has been associated with a variety of cancers, including breast cancer, gastric cancer, and lung cancer. Its role in EMT is significant in tumor progression, as this process allows cancer cells to attain invasive properties, enabling metastasis. Moreover, ZEB1 protein stimulates cancer cell growth and inhibits apoptosis, contributing to tumor progression. In addition to cancer, ZEB1 mutations are also linked to several genetic disorders such as, posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy and late-onset Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy.
ZEB1 protein's applications in biomedical
In the field of biomedicine, the ZEB1 protein has been a central focus due to its implications in disease progression, particularly cancer. Because elevated ZEB1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in many cancers, it has become a significant biomarker for detecting cancer pathology. Moreover, the theoretical use of ZEB1 inhibitors, which would block the function of the ZEB1 protein and slow cancer progression, has opened new doors in cancer therapeutics.
However, the potential utility of the ZEB1 protein extends beyond disease detection and treatment. In stem cell research and regenerative medicine, the role of ZEB1 in EMT could be leveraged, as EMT is crucial for enabling cellular plasticity and Stemness. Understanding ZEB1 protein's role in these processes could aid in developing treatments for a multitude of diseases and injuries.
In conclusion, the ZEB1 protein is an intricate and multifaceted component of our biology. Its potent roles in gene regulation, disease progression, and EMT underline the potential for ZEB1 as a therapeutic target and biomedical tool in the future. However, research into the full potential and implications of ZEB1 is on-going, and it will require further studies to fully exploit its practical applications. While the road may be long and arduous, the potential rewards are vast, laying the foundations for improved diagnosis, treatment, and possible cures for many diseases.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZEB1-3796H | Recombinant Human ZEB1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| ZEB1-604H | Recombinant Human ZEB1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | N-His |
| ZEB1-10324M | Recombinant Mouse ZEB1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| ZEB1-6688C | Recombinant Chicken ZEB1 | Chicken | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Wu, HT., Zhong, HT., Li, GW. et al. Oncogenic functions of the EMT-related transcription factor ZEB1 in breast cancer. J Transl Med 18, 51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02240-z

