Bax
-
Official Full Name
BCL2-associated X protein -
Overview
This gene encodes a polypeptide hormone precursor that undergoes extensive, tissue-specific, post-translational processing via cleavage by subtilisin-like enzymes known as prohormone convertases. There are eight potential cleavage sites within the polypeptide precursor and, depending on tissue type and the available convertases, processing may yield as many as ten biologically active peptides involved in diverse cellular functions. The encoded protein is synthesized mainly in corticotroph cells of the anterior pituitary where four cleavage sites are used; adrenocorticotrophin, essential for normal steroidogenesis and the maintenance of normal adrenal weight, and lipotropin beta are the major end products. In other tissues, including the hypothalamus, placenta, and epithelium, all cleavage sites may be used, giving rise to peptides with roles in pain and energy homeostasis, melanocyte stimulation, and immune modulation. These include several distinct melanotropins, lipotropins, and endorphins that are contained within the adrenocorticotrophin and beta-lipotropin peptides. Mutations in this gene have been associated with early onset obesity, adrenal insufficiency, and red hair pigmentation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. -
Synonyms
BAX;bcl2-L-4;BCL2L4;Bcl2-L-4;BCL2-associated X protein;Bcl-2-associated X protein;Apoptosis regulator BAX;apoptosis regulator BAX;Bcl-2-like protein 4;bcl-2-like protein 4;OTTHUMP00000218291;OTTHUMP00000218292;OTTHUMP00000218293;OTTHUMP00000218294;OTTHUMP00000218295;OTTHUMP00000218296
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Pig
- Bovine
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Protein Conjugation
- Human Cells
- His
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is BAX Protein?
BAX gene (BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the BCL2 protein family. BCL2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. This protein forms a heterodimer with BCL2, and functions as an apoptotic activator. This protein is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The BAX protein is consisted of 192 amino acids and BAX molecular weight is approximately 21.2 kDa.
What is the Function of BAX Protein?
The BAX protein is usually present as a monomer in the cytoplasm, but upon receiving the apoptotic signal, it transfers to the mitochondria and oligomerizes there, forming pores and resulting in increased permeability of the mitochondrial outer membrane. Activation of the BAX protein involves significant changes in its molecular structure. In the unactivated state, the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of BAX have self-inhibitory properties, maintaining their latent state in the cytoplasm. However, when cells receive apoptotic signals such as the BH3-only protein, BAX undergoes conformational changes that cause the release of its C-terminal helix (α9) and BH3 helix, which promotes its transfer to the mitochondria and oligomerization. In addition, BAX activity is tightly regulated by other members of the BCL-2 family within the cell.
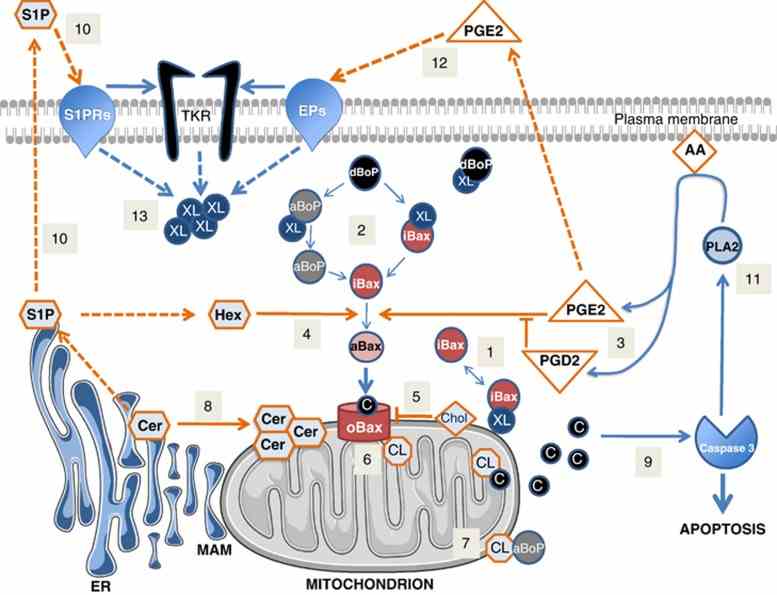
Fig1. Activation of Bax during apoptosis is controlled by lipids at multiple levels. (V Mignard, 2014)
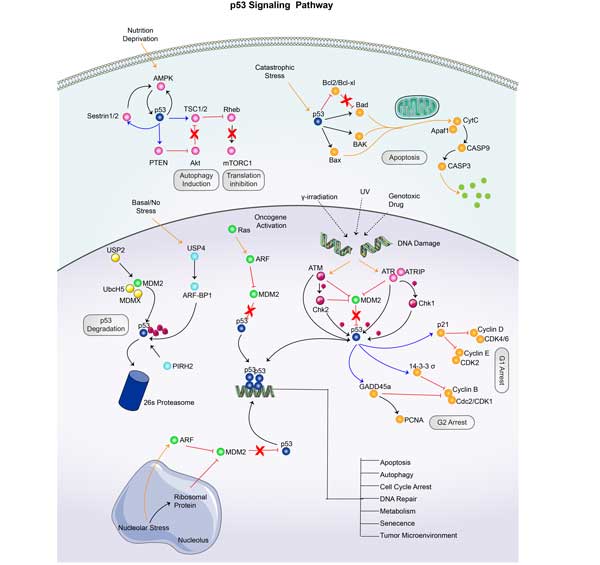
BAX Related Signaling Pathway
As a proapoptotic protein in the Bcl-2 family, BAX interacts with anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL to control mitochondrial permeability and thereby regulate apoptosis. The accumulation of BAX on the mitochondrial membrane leads to the increase of membrane permeability and the release of cytochrome C, which then binds with APAF-1 to activate Caspase-9 and initiate the caspase cascade, leading to apoptosis. BAX undergoes conformational change and activation under the stimulation of apoptosis signal, and forms oligomers on mitochondria together with Bak protein, resulting in mitochondrial membrane permeation. The serine 184 site of BAX protein can be phosphorylated by different kinases, such as AKT and PKCζ, which affect its pro-apoptotic activity.
BAX Related Diseases
BAX, as a pro-apoptotic protein, plays an important role in tumor development, and its expression level is associated with the survival and death of tumor cells. Abnormal functioning of BAX may affect the normal regulation of the immune system, leading to the development of autoimmune diseases. In neurodegenerative diseases, abnormal activation of BAX may lead to the loss of neurons, which can affect the development of the disease. BAX plays a role in mitochondria-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and its dysfunction may be related to the pathogenesis of heart failure. The regulatory mechanism and drug discovery of BAX are the focus of current research, aiming to develop small molecule apoptosis regulators targeting BAX and provide new strategies for the treatment of related diseases.
Bioapplications of BAX
The dysfunction of BAX is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. Small molecule apoptosis regulators targeting BAX provide a new strategy for cancer therapy and contribute to the development of the next generation of apoptosis regulators. The role of BAX in neurodegenerative diseases is the focus of current research, and by studying BAX antibodies, its relationship with nerve cell death can be explored, providing new perspectives for the treatment of related diseases. BAX is an important target for directly targeted drug discovery, and research has focused on identifying functional and potentially drug-binding sites on BAX, as well as developing small molecule compounds capable of regulating BAX activity. In the treatment of hemophilia, clinical trials of BAX 335 gene therapy have shown its potential in boosting FIX activity and improving symptoms in patients, despite some immune response challenges.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mieko Matsuyama, 2023
The scientists identified a series of small molecule cell protectors (CSMs) capable of inhibiting the Bax protein through cell-based high-throughput screening methods. Optimized for medicinal chemistry, they developed a compound called M109S that is not only able to be absorbed orally, but also effectively penetrates the blood-brain and retinal barriers. In a mouse model of eye disease, M109S showed protective effects on retinal cells. M109S blocks conformational change and transfer to mitochondria by directly binding to Bax protein. In addition, M109S also inhibited apoptosis induced by ABT-737, staurosporine, etoposide and obatoclax. M109S can also reduce the maximum rate of mitochondrial oxygen consumption and the production of reactive oxygen species, while promoting the glycolysis process. These regulatory effects on cell metabolism may be one of the mechanisms by which M109S exerts its cellular protective effect. Overall, M109S is a novel small molecule capable of protecting cells from mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathways in cell cultures and animal models.
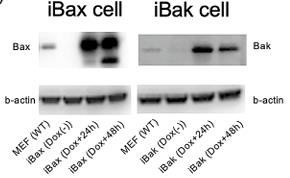
Fig1. Western blot analysis of the expression levels of Bax or Bak in wild-type (Wt) MEFs, iBax, and iBak cells.
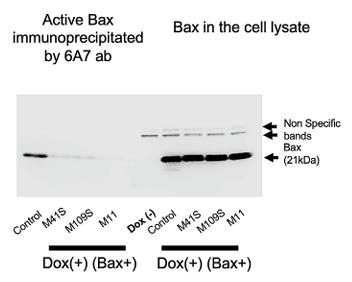
Fig2. CSMs suppressed the conformation change of Bax.
Case Study 2: Lillian Ferkany, 2023
According to their structure and function, Bcl-2 family proteins are classified as BH3-only proteins, pro-survival proteins or pro-apoptotic proteins, which interact with Bax through the BH3 domain to produce excitatory or inhibitory effects on the apoptosis process. All BH3 domains are alpha helices composed of 5 to 7 conserved hydrophobic residues labeled H0 to H5. This study tested the hypothesis that the VDAC2 subtype contains a functional BH3 domain capable of binding to the recombinant Bax protein in a manner similar to the BH3 domain of Bim. Bax was found to bind to VDAC2 using fluorescently labeled peptides. In this interaction, a conserved aspartic acid is essential for binding, and when the aspartic acid in this position is replaced by arginine, the affinity of Bax is reduced by 2.6 times. A proline at the H0 position also promotes Bax binding to VDAC2. Replacing leucine at H2 with a smaller hydrophobic alanine significantly reduced KD values, suggesting that leucine at H2, together with large aromatic residues (tyrosine) at H1, phenylalanine at H4, and phenylalanine at H5, contribute to the lower Bax affinity for VDAC2.
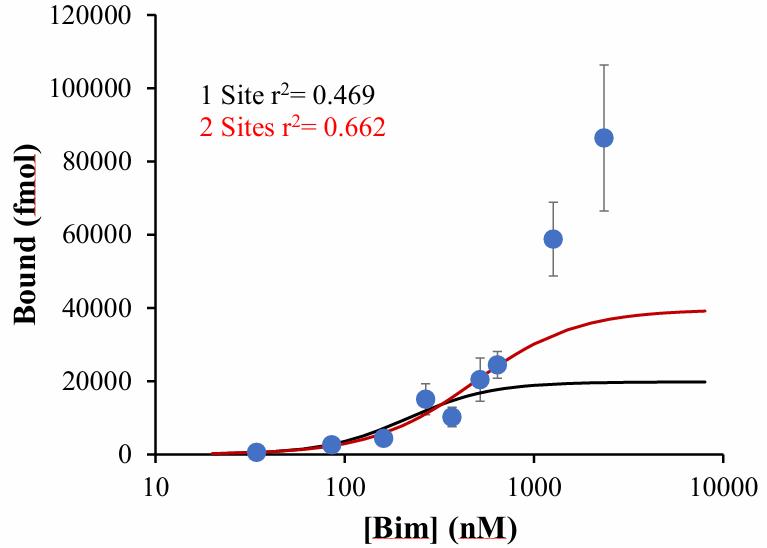
Fig3. Recombinant Bax binding to wild type Bim peptide.
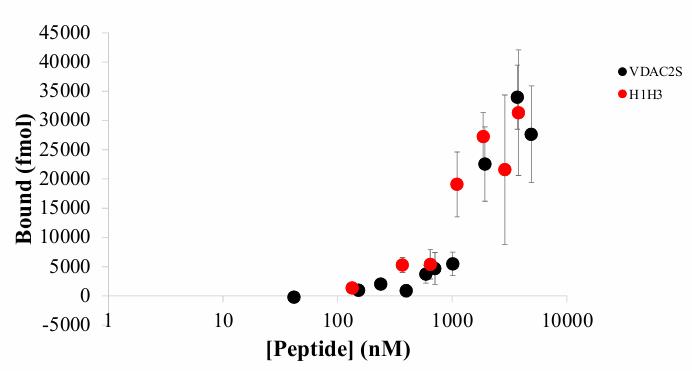
Fig4. Overlay of binding curves for VDAC2S and H1H3 mutant peptide.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BAX-26650TH)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (BAX-094H)
Involved Pathway
Bax involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Bax participated on our site, such as Sphingolipid signaling pathway,p signaling pathway,Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Bax were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Apoptosis | CASP2,FASLG,IL1RAP,NFKBIA,DIABLOB,PRKAR2B,BCL2L1,Casp3,SATB1,BOK |
| Tuberculosis | cgr2b,CD14,SPHK2,EP300,PIK3C3,ITGAX,CARD9,TGFB3,MAPK10,FCGR2B |
| Viral carcinogenesis | TBPL1,DLG1,HIST1H2BH,ATF4,PIK3R2,ACTN3,TRAF3,ATP6V0D2,RBL2,PMAIP1 |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | IL1A,PIK3CA,SREBF1,MAPK8,TNF,NDUFA12,UQCRB,INS1,NDUFA6,IL6R |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | FYN,NSMAF,S1PR4,RELA,LASS5,TNF,PPP2R5D,CERS2,SPTLC2,MAPK9 |
| Prion diseases | PRKACG,NCAM2,Hc,MAPK1,FYN,C8G,C9,HSPA1A,NCAM1,IL1A |
| p signaling pathway | CYCSB,TP53I3,PTEN,CD82B,CASP8,MDM2,IGF1,GADD45BA,MDM4,CCND1 |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | HSPA2,UBE2E2,MBTPS1,UBE2D2,UBE4B,SEC61AL2,ERN1,SEC24C,SEC61A1,DNAJB2 |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | PIK3CG,SHC2,ZFP110,CAMK2A,ABL1,MAPKAPK2,HRAS,PSEN1,CALM1,PRDM4 |
Protein Function
Bax has several biochemical functions, for example, BH3 domain binding,channel activity,chaperone binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Bax itself. We selected most functions Bax had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Bax. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| channel activity | P2RX6,PANX1B,TRPA1,BAXB,BCL2,GJA8,PANX2,APNL,CHRNB1,MAL |
| lipid binding | APOA4B.1,PITPNM3,APOL4,DNM1L,UNC119,PAQR5A,S1PR2,Fert2,PAQR7B,APOL2 |
| identical protein binding | C1QTNF6,ECI1,KLHL7,COL1A2,PDGFB,TNPO3,TP73,PRPS2,WRNIP1,TRIM39 |
| protein complex binding | CDKN1B,ATM,NOG,RANBP2,CDK5RAP1,TXN2,CRHR1,DRD1,PRKACA,FBLN1 |
| heat shock protein binding | DLST,PPID,DNAJA2,HDAC2,TPR,HSPA6,BAK1,PACRG,SSUH2RS1,FKBP4 |
| chaperone binding | CXorf41,DNAJA2,TSACC,DNAJA3B,Alb,DNAJA3A,TIMM9,GRPEL1,HLA-B,DNAJB1 |
| BH3 domain binding | BCL2,MCL1,BCL2L1 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | ADORA2A,CRLF1,NOTCH4,KATNB1,ITGB1B,DDIT3,POLA1,BHLHE40,TXLNG,EPAS1 |
| protein binding | TLE2,COPG,ZMAT2,USP28,HAGH,TUBA4A,SNX32,GNAI2,MAP2K4,RHOT1 |
Interacting Protein
Bax has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Bax here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Bax.
Bax Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Beers, K; Ferguson, J; et al. Comparison of the RAPID-B-(R) flow cytometer and the BAX((R)) system for the detection of non-0157 shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in beef products. FOOD CONTROL 50:72-75(2015).
- Gurzu, S; Kadar, Z; et al. Gastric cancer in young vs old Romanian patients: immunoprofile with emphasis on maspin and mena protein reactivity. APMIS 123:223-233(2015).