CXCL14
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14 -
Overview
This gene belongs to the cytokine gene family which encode secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally related to the CXC (Cys-X-Cys) subfamily of cytokines. Members of this subfamily are characterized by two cysteines separated by a single amino acid. This cytokine displays chemotactic activity for monocytes but not for lymphocytes, dendritic cells, neutrophils or macrophages. It has been implicated that this cytokine is involved in the homeostasis of monocyte-derived macrophages rather than in inflammation. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
CXCL14;chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 14;KEC;KS1;BMAC;BRAK;NJAC;MIP2G;MIP-2g;SCYB14;C-X-C motif chemokine 14;bolekine;MIP-2 gamma;chemokine BRAK;breast and kidney;tumor-suppressing chemokine;small-inducible cytokine B14;CXC chemokine in breast and kidney;small inducible cytokine subfamily B (Cys-X-Cys), member 14 (BRAK)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- GST
- His
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
Background
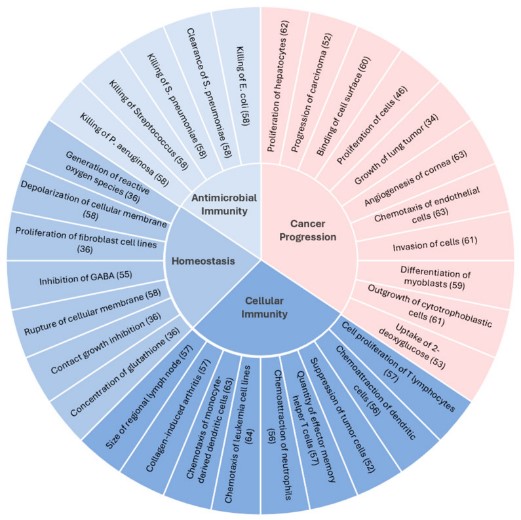
Fig1. Classification of CXCL14 gene-to-functions. (Nicholas S Giacobbi, 2024)
What is CXCL14 protein?
CXCL14 (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5q31. This gene belongs to the cytokine gene family which encode secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally related to the CXC (Cys-X-Cys) subfamily of cytokines. Members of this subfamily are characterized by two cysteines separated by a single amino acid. This cytokine displays chemotactic activity for monocytes but not for lymphocytes, dendritic cells, neutrophils or macrophages. The CXCL14 protein is consisted of 111 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 13.1 kDa.
What is the function of CXCL14 protein?
CXCL14 attracts immune cells and is involved in immune surveillance and inflammation. CXCL14 is thought to inhibit angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is crucial for tumor growth and metastasis. In some cases, CXCL14 may be involved in tissue repair and regeneration processes. By binding to CXCR4, CXCL14 inhibits the entry of HIV into cells, making it a potential therapeutic target in HIV/AIDS research.
CXCL14 Related Signaling Pathway
The CXCL14 protein, also known as breast and kidney expression chemokine (BRAK), is a member of the CXC chemokine family. It is involved in several signaling pathways, mainly involved in the regulation of inflammatory immune response and tumor-related biological processes. Specifically, CXCL14 has chemotactic effects on monocytes, but does not affect B cells and T cells. In addition, CXCL14 is involved in the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway, and the S100A6/CXCL14 signaling pathway has been found to be a potential target for renal clear cell carcinoma therapy.
CXCL14 Related Diseases
CXCL14 plays an important role in autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and its overexpression may exacerbate inflammatory responses and abnormal activation of the immune system. The expression of CXCL14 is associated with a variety of tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. CXCL14 also plays an important role in chronic inflammatory diseases such as inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis). It may also play a role in diseases such as atherosclerosis.
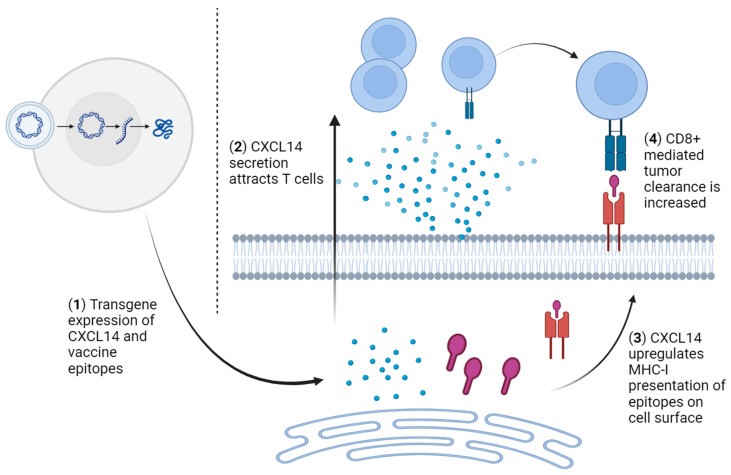
Fig2. Schematic strategy for activating antitumor CD8+ T-cell responses using CXCL14 combined with therapeutic HPV vaccines. (Nicholas S Giacobbi, 2024)
Bioapplications of CXCL14
Because CXCL14 expression levels vary significantly in specific types of cancer (e.g., breast cancer, kidney cancer) and other diseases (e.g., cardiovascular disease), it is being investigated as a potential biomarker for diagnosis, prognostic assessment, and monitoring of therapeutic effects.
Case Study
Case study 1: Tsung-Ming Chang, 2023
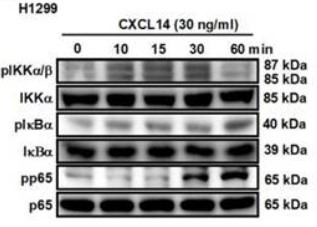
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor with metastatic potential. Chemokine ligand 14 (CXCL14) has been reported to be associated with different cancer cell migration and invasion. However, few studies have explored the function of CXCL14 and its specific receptor in lung cancer metastasis. This study aims to determine the mechanism of CXCL14-promoted cancer metastasis. The expression of CXCL14, atypical chemokine receptor 2 (ACKR2), and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers was evaluated by the public database of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), Western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). Migration and wound healing assays were used to observe the motility of cancer cells. overexpression of CXCL14 and ACKR2 was observed in lung cancer datasets, human lung tumor sections, and lung cancer cells. Furthermore, the migration of CXCL14-promoted lung cancer cells was determined in vitro and in vivo. In particular, ACKR2 knockdown abolished CXCL14-induced cancer cell motility. Additionally, ACKR2 was involved in CXCL14-triggered phospholipase Cβ3 (PLCβ3), protein kinase Cα (PKCα), and proto-oncogene c-Src signaling pathway and subsequently upregulated nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) transcription activity leading to EMT and migration of lung cancer cells.
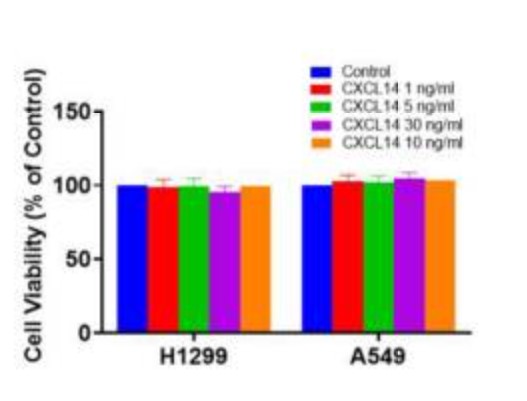
Fig1. H1299 and A549 cells were treated with CXCL14 (1-30 ng/ml) for 24 h, cell viability was evaluated using a CCK-8 assay.
Case study 2: Anupam Kumar, 2022
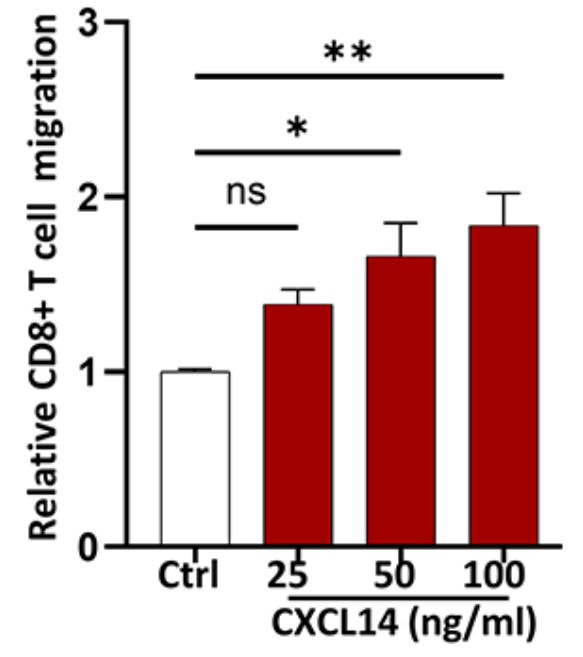
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment present in the majority of diffuse glioma limits therapeutic response to immunotherapy. As the determinants of the glioma-associated immune response are relatively poorly understood, the study of glioma with more robust tumor-associated immune responses may be particularly useful to identify novel immunomodulatory factors that can promote T-cell effector function in glioma. The researchers used multiplex immune-profiling, proteomic profiling, and gene expression analysis to define the tumor-associated immune response in two molecular subtypes of glioma and identify factors that may modulate this response. They then used patient-derived glioma cultures and an immunocompetent murine model for malignant glioma to analyze the ability of tumor-intrinsic factors to promote a CD8+ T-cell response. As compared with isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-mutant astrocytoma, MAPK-activated pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA) harbored increased numbers of activated cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and Iba1+ microglia/macrophages, increased MHC class I expression, enrichment of genes associated with antigen presentation and processing, and increased tumor cell secretion of the chemokine CXCL14. CXCL14 promoted activated CD8+ T-cell chemotaxis in vitro.
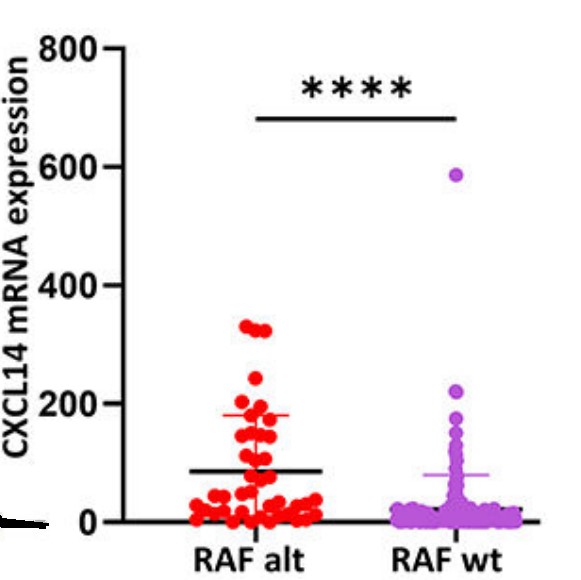
Fig3. Increased expression of CXCL14 in RAF altered astrocytoma (n=38) versus RAF wildtype astrocytoma (n=164) in a cohort of pediatric low-grade and high-grade astrocytoma.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CXCL14-2281H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Cxcl14-7163M) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
CXCL14 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CXCL14 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CXCL14 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | INHBA,CCL3L1,IL19,IL8L2,CCL7,EGFRA,CCR10,TNFSF9,IL6R,GM-CSF |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | GRK5,Ccl21c,RAC2,CCL21,XCR1,CCR5,RAP1A,BCAR1,CXCR6,NFKBIB |
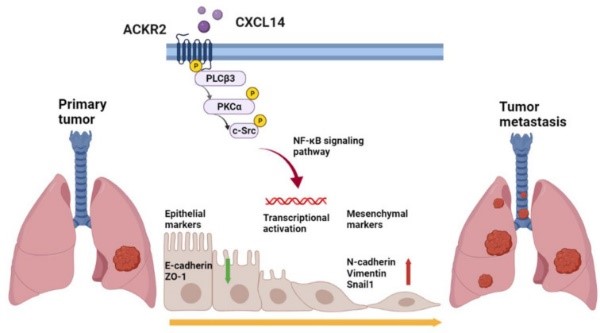
Fig1. Schematic mechanism of CXCL14 promotes tumor metastasis in lung cancer. (Tsung-Ming Chang, 2023)
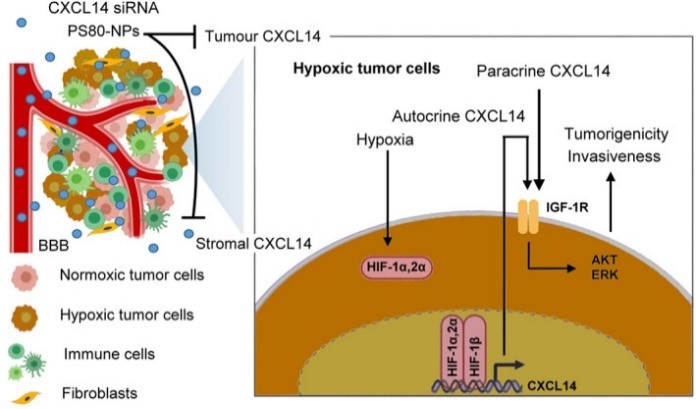
Fig2. Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanisms and therapeutic impact of hypoxic tumor microenvironment (HTM)-regulated CXC chemokine ligand 14 (CXCL14) in glioblastoma progression. (Sung-Tai Wei, 2023)
Protein Function
CXCL14 has several biochemical functions, for example, chemokine activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CXCL14 itself. We selected most functions CXCL14 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CXCL14. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chemokine activity | CCL21,CCL24,CXL34B.11,CCL17,C5,CCL34B.1,CCL26,CCL13,CCL11,CCL1 |
| protein binding | PIP4K2B,BLOC1S4,TGFBR3,ZAK,CASQ2,PSMA2,IL11,SRSF1,XAB2,SIRT4 |
Interacting Protein
CXCL14 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CXCL14 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CXCL14.
TRIM23;TEX11;CXCR4;REL;nadA;q81t38_bacan
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Suzuki, H; Itoh, M; et al. CXCL14-like immunoreactivity in growth hormone-containing cells of urodele pituitaries. REGULATORY PEPTIDES 174:53-57(2012).
- Lietz, R; Bayer, W; et al. Codelivery of the Chemokine CCL3 by an Adenovirus-Based Vaccine Improves Protection from Retrovirus Infection. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY 86:1706-1716(2012).



