CXC Chemokines
Related Symbol Search List
- CXCL1
- Cxcl10
- CXCL11
- CXCL12
- CXCL13
- CXCL14
- CXCL16
- CXCL17
- Cxcl2
- CXCL3
- CXCL5
- CXCL6
- IL-8
- CXCL8
- CXCL9
- PF4
- CXCL7
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CXC Chemokines Research
Creative BioMart is your premier destination for all of your research needs surrounding CXC chemokines. Our vast selection of meticulously curated products and tailored services are designed to guide your exploration into the world of CXC chemokines and their critical roles in a variety of physiological processes.
- Among our product offerings, you will discover high-quality recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more.
- Furthermore, we provide an extensive database of resources on CXC chemokines, including essential information on associated pathways, protein functions, protein interactions, relevant literature, and current research trends.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL1-11715H | Recombinant Human CXCL1, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Cxcl2-200M | Recombinant Mouse Cxcl2 protein, His&SUMO-tagged | Human | E.coli | His&SUMO |
| CXCL8-3703H | Recombinant Human CXCL8 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CXCL9-11728H | Recombinant Human CXCL9, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CXCL10-08H | Recombinant Human CXCL10 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| CXCL11-65S | Active Recombinant Swine Chemokine (C-X-C motif) Ligand 11 | Pig | Yeast | N/A |
| Cxcl12-11719M | Recombinant mouse Cxcl12, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| Cxcl13-79R | Recombinant Rat Cxcl13 Protein, His-GST-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His/GST |
| CXCL14-11720H | Recombinant Human CXCL14, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CXCL16-11721H | Recombinant Human CXCL16, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PF4-1654H | Recombinant Human PF4, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About CXC Chemokines
CXC chemokines are a subgroup of chemokines, which are small secreted proteins involved in immune cell migration and various physiological processes. The name "CXC" refers to the presence of a pair of cysteine residues separated by another amino acid (represented as 'X') in the amino acid sequence of these chemokines. CXC chemokines are characterized by their ability to bind to CXC chemokine receptors, a subset of G protein-coupled receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells and other cell types.
CXC chemokines are produced by various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and epithelial cells, in response to inflammatory stimuli, infection, or tissue damage. They act as chemoattractants, guiding immune cells to specific locations within the body. Additionally, CXC chemokines play important roles in regulating immune cell activation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and tissue repair.
The CXC chemokine family is diverse and encompasses multiple members, each with its own unique functions and receptor specificities. Some well-known CXC chemokines include interleukin-8 (CXCL8), which is a potent chemoattractant for neutrophils, and interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10 (CXCL10), which is involved in the recruitment of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
The receptors for CXC chemokines are primarily expressed on leukocytes, including neutrophils, monocytes, T cells, and dendritic cells. Upon binding to their respective receptors, CXC chemokines initiate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate cell migration, activation, survival, and other immune responses.
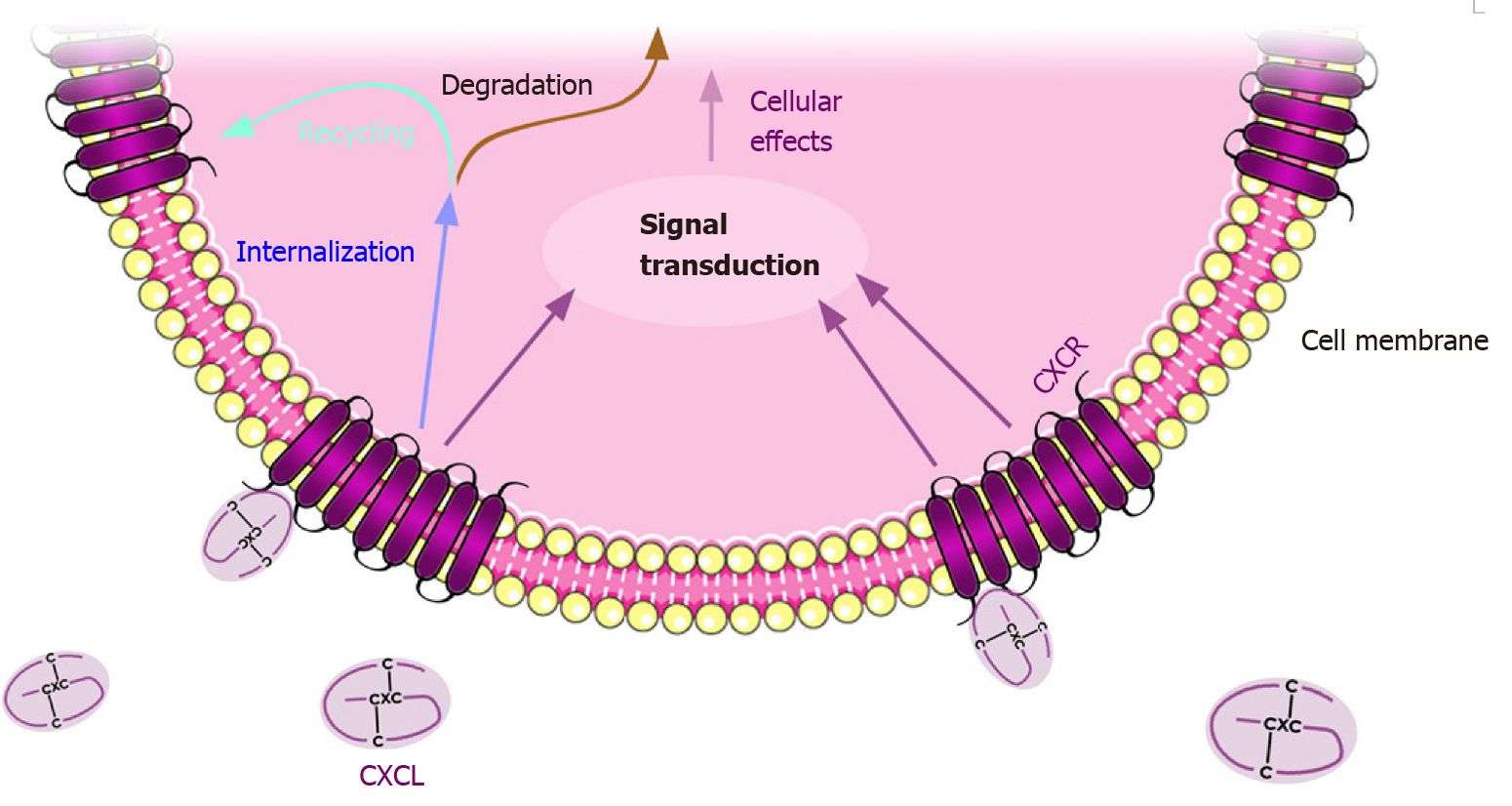 Fig.1 CXCL and CXCR regulatory mechanisms. CXCL binding to the CXCR located at the cellular membrane, internalizing and transducing the signal into the nucleus. CXCR internalization is usually followed by degradation or recycling to the plasma membrane. (Cabrero-de Las Heras S, et al., 2018)
Fig.1 CXCL and CXCR regulatory mechanisms. CXCL binding to the CXCR located at the cellular membrane, internalizing and transducing the signal into the nucleus. CXCR internalization is usually followed by degradation or recycling to the plasma membrane. (Cabrero-de Las Heras S, et al., 2018)
The functions of CXC chemokines and their receptors are crucial for the proper functioning of the immune system. They are involved in immune cell trafficking, allowing immune cells to be recruited to sites of infection, inflammation, or tissue injury. Moreover, CXC chemokines contribute to the coordination and regulation of immune responses by facilitating cell-cell communication and the formation of immune cell clusters.
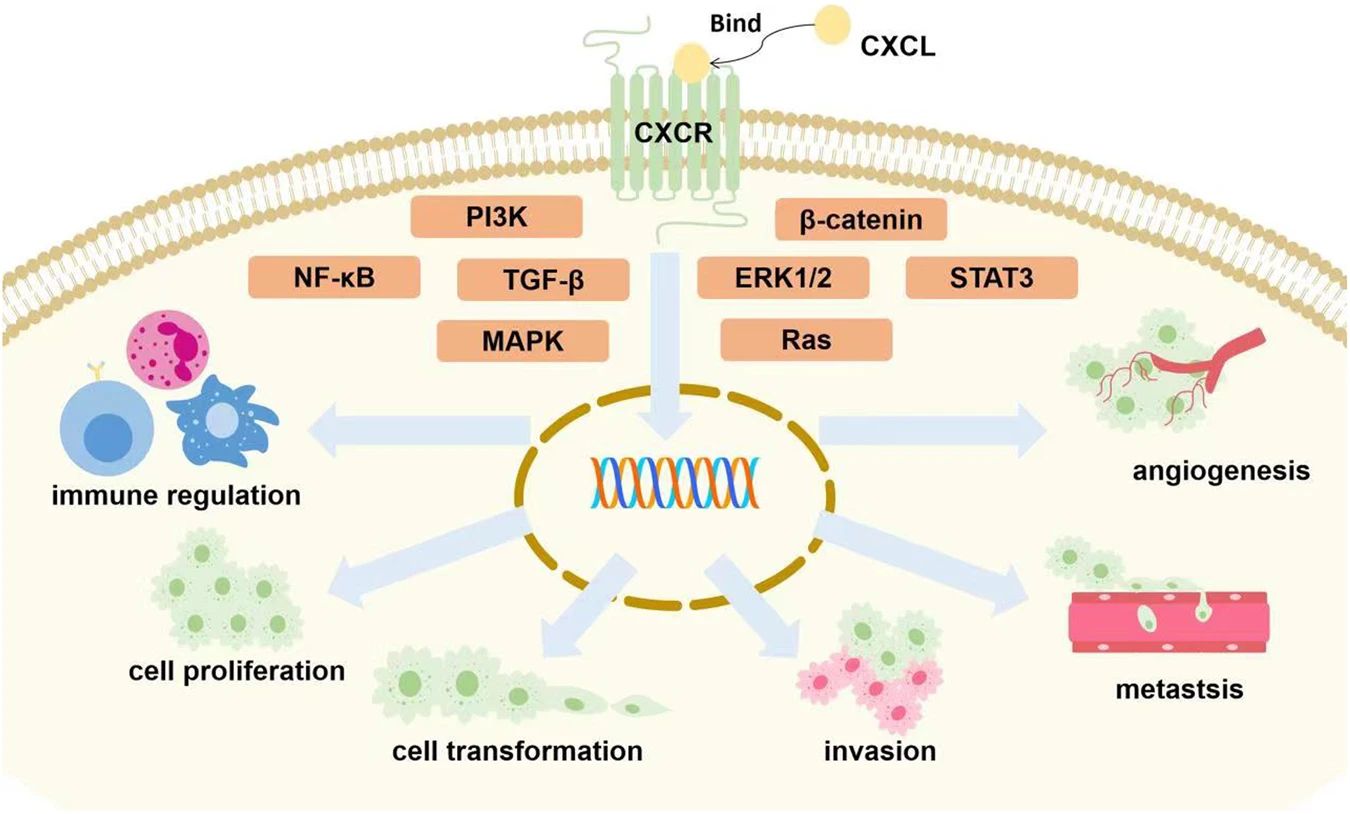 Fig.2 Majority of CXCL chemokines binding to corresponding receptors are involved in tumor growth via the activation of different signaling pathways (STAT3, NF-κB, Ras, MAPK, PI3K, TGF-β, β-catenin, ERK1/2). It eventually affects proliferation, invasion, migration and transformation of cancer cells, immune control, and tumor angiogenesis. (Zhou C, et al., 2023)
Fig.2 Majority of CXCL chemokines binding to corresponding receptors are involved in tumor growth via the activation of different signaling pathways (STAT3, NF-κB, Ras, MAPK, PI3K, TGF-β, β-catenin, ERK1/2). It eventually affects proliferation, invasion, migration and transformation of cancer cells, immune control, and tumor angiogenesis. (Zhou C, et al., 2023)
Research on CXC Chemokines
Research on CXC chemokines has been extensive and has provided valuable insights into their functions, mechanisms of action, and their roles in various physiological and pathological conditions. Here are some notable areas of research on CXC chemokines:
- Chemotaxis and Cell Migration: CXC chemokines are well-known for their ability to induce chemotaxis and direct the migration of immune cells. Numerous studies have investigated the specific chemotactic effects of different CXC chemokines on different cell types, elucidating the receptor-ligand interactions and intracellular signaling pathways involved in cell migration.
- Inflammatory Responses: CXC chemokines are key players in inflammatory processes. Research has focused on understanding their roles in orchestrating immune cell recruitment to inflamed tissues, the regulation of inflammatory cytokine production, and the modulation of leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions during inflammation.
- Immune Cell Activation and Differentiation: CXC chemokines can influence the activation and differentiation of various immune cell types. Studies have investigated how CXC chemokines affect T cell activation, polarization of T helper cell subsets (e.g., Th1, Th2, Th17), and the recruitment and function of dendritic cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
- Infectious Diseases: Research has explored the involvement of CXC chemokines in infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and parasites. For example, studies have investigated the role of CXC chemokines in the recruitment and activation of immune cells during bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis and pneumonia, as well as viral infections, including HIV and influenza.
- Cancer and Metastasis: CXC chemokines and their receptors have been implicated in tumor development, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Research has focused on understanding how CXC chemokines contribute to tumor progression, immune cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment, and the migration and dissemination of cancer cells to distant sites.
- Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Dysregulation of CXC chemokines has been associated with various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Studies have explored the roles of specific CXC chemokines and their receptors in mediating disease pathogenesis, immune cell recruitment, and tissue damage.
- Therapeutic Potential: Given the involvement of CXC chemokines in various diseases, research has also focused on exploring their therapeutic potential. This includes the development of chemokine receptor antagonists, neutralizing antibodies, and small molecules targeting CXC chemokine receptors as potential therapeutic interventions for inflammatory disorders, cancer, and other conditions.
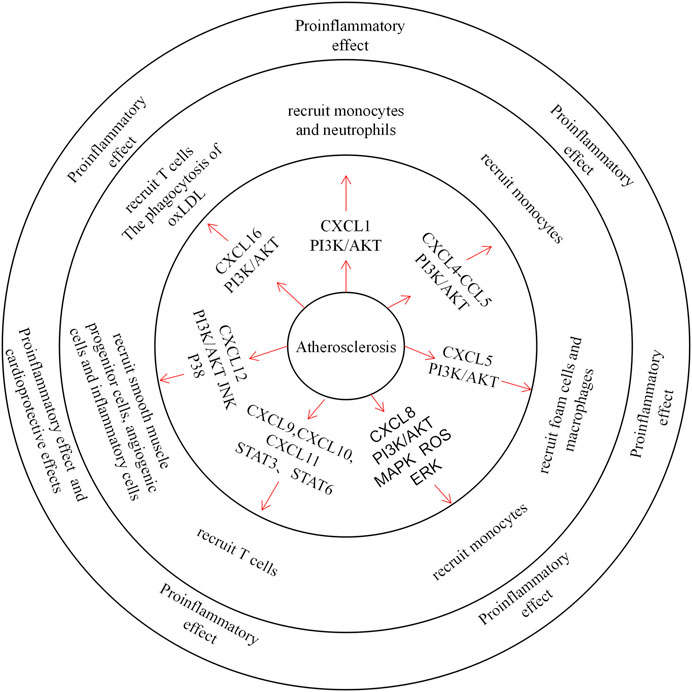 Fig.3 The role of CXC Chemokines in atherosclerosis. (Lu X, et al., 2022)
Fig.3 The role of CXC Chemokines in atherosclerosis. (Lu X, et al., 2022)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Wu T, Yang W, Sun A, Wei Z, Lin Q. The Role of CXC Chemokines in Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2022;15(1):167.
- Lu X, Wang Z, Ye D, et al. The Role of CXC Chemokines in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2022;12:765768.
- Zhou C, Gao Y, Ding P, Wu T, Ji G. The role of CXCL family members in different diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):212.
- Chen X, Chen R, Jin R, Huang Z. The role of CXCL chemokine family in the development and progression of gastric cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020;13(3):484-492.
- Cabrero-de Las Heras S, Martínez-Balibrea E. CXC family of chemokines as prognostic or predictive biomarkers and possible drug targets in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(42):4738-4749.

