FTL
-
Official Full Name
ferritin, light polypeptide -
Overview
This gene encodes the light subunit of the ferritin protein. Ferritin is the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is composed of 24 subunits of the heavy and light ferritin chains. Variation in ferritin subunit composition may affect the rates of iron uptake and release in different tissues. A major function of ferritin is the storage of iron in a soluble and nontoxic state. Defects in this light chain ferritin gene are associated with several neurodegenerative diseases and hyperferritinemia-cataract syndrome. This gene has multiple pseudogenes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
FTL;ferritin, light polypeptide;LFTD;NBIA3;ferritin light chain;ferritin L-chain;ferritin L subunit;ferritin light polypeptide-like 3
Recombinant Proteins
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Human
- Chicken
- Cattle
- Horse
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Liver
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Human Liver
- His
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is FTL protein?
FTL (ferritin light chain) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19q13. This gene encodes the light subunit of the ferritin protein. Ferritin is the major intracellular iron storage protein in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It is composed of 24 subunits of the heavy and light ferritin chains. The FTL protein is consisted of 175 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 20.0 kDa.
What is the function of FTL protein?
The FTL protein, also known as the ferritin light chain, is mainly involved in iron storage and regulation of intracellular iron ion balance, and together with another protein, FTH (ferritin heavy chain), it forms the ferritin complex, which can increase iron levels through autophagy degradation, a process associated with iron death (a mode of cell death). FTL can form stable complexes with free iron, store excess iron ions, and release iron ions when iron levels in the cell are too low to maintain iron ion balance.
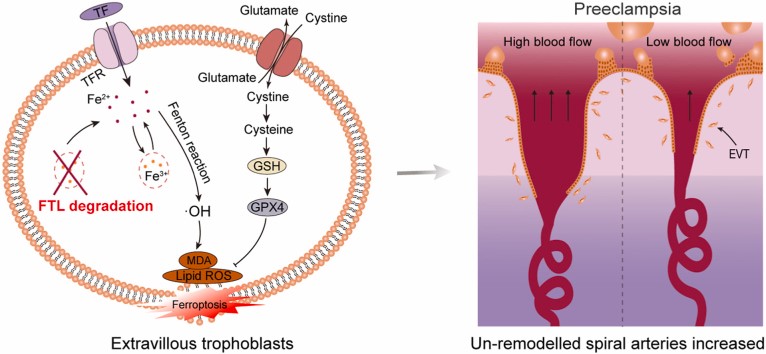
Fig1. FTL reduction during pregnancy triggered ferroptosis and then caused defective uterine spiral artery remodelling, thereby leading to PE. (Xiaofeng Yang, 2022)
FTL Related Signaling Pathway
FTL protein is positively correlated with inflammatory response and IL2/STAT5 signaling pathway. FTL protein is also associated with JAK1-STAT1 signaling pathway. This pathway plays a key role in regulating the immune response of cells and iron death, a mode of cell death. In particular, IFN-γ released by CD8+ T cells induces iron death in tumor cells by activating the JAK1-STAT1 signaling pathway, a process in which the expression of SLC7A11 and SLC3A2 is transcriptionally regulated.
FTL Related Diseases
In brain tissue, the ferritin complex is primarily composed of FTH, but abnormalities in FTL may also be associated with hereditary Neuroferritinopathy (NF), a neurodegenerative disease associated with the accumulation of iron in the brain. FTL protein plays a key role in maintaining iron ion balance in cells, and its abnormality may lead to iron overload. The abnormality of FTL protein may also be associated with other diseases, such as hereditary anemia and neurodegenerative diseases.
Bioapplications of FTL
By regulating the function of FTL protein, it is possible to treat iron metabolic disorders such as iron overload or iron deficiency. For example, using the properties of the FTL protein to regulate iron levels in the body may help treat certain types of anemia. At the same time, the development of drugs that can regulate the expression or activity of FTL proteins may help treat diseases related to iron metabolism.
Case Study
Case study 1: Junhui Liu, 2020
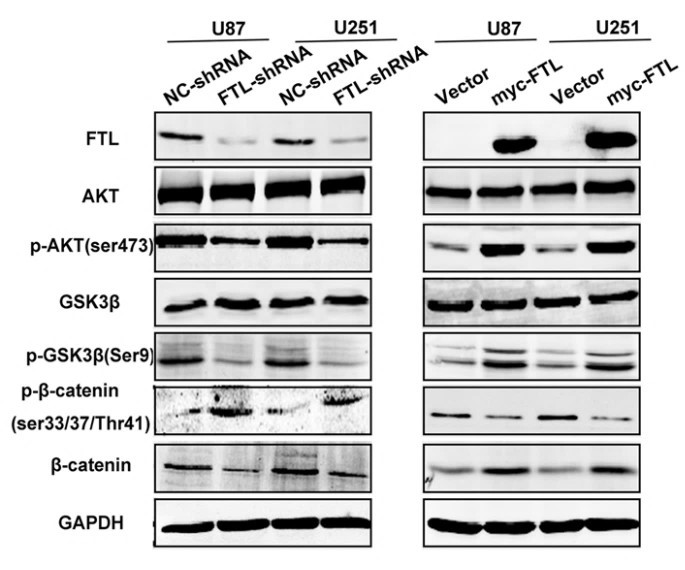
Hypoxia, a fundamental characteristic of glioma, is considered to promote tumor malignancy by inducing process of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT). Ferritin Light Chain (FTL) is one of the iron metabolism regulators and is overexpressed in glioma. However, relationship between hypoxia and FTL expression and its role in regulating EMT remains unclear.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC), western blot and public datasets were used to evaluate FTL level in glioma. Wound healing, transwell assays, CCK8, annexin V staining assay were used to measure migration, invasion, proliferation and apoptosis of glioma cells in vitro. Interaction between HIF1A and FTL was assessed by luciferase reporter and Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays. FTL expression was enriched in high grade glioma (HGG) and its expression significantly associated with IDH1/2 wildtype and unfavorable prognosis of glioma patients. FTL expression positively correlated with HIF1A in glioma tissues and obviously increased in U87 and U251 cells under hypoxia in a time-dependent manner. Moreover, this study found downregulation FTL decreased the survival rate and increased the apoptosis of glioma cells treated with temozolomide (TMZ).
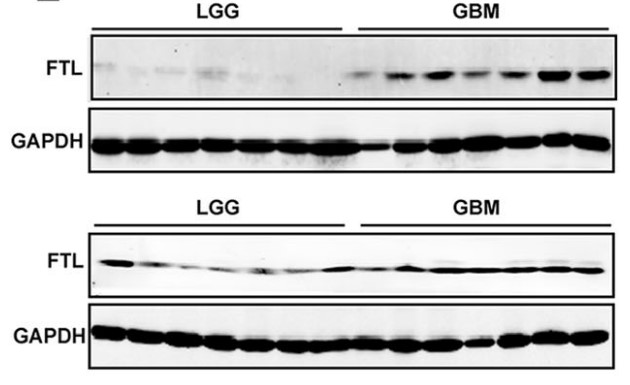
Fig1. Western blot was performed to compared FTL expression in LGG and GBM.
Case study 2: Tingfeng Wu, 2016
Accumulating evidence suggests that iron-associated proteins contribute to tumor initiation and development. Ferritin light chain (FTL), a key protein in iron metabolism, is associated with the survival of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) patients; however, the molecular mechanisms underlying this association remain largely unclear.
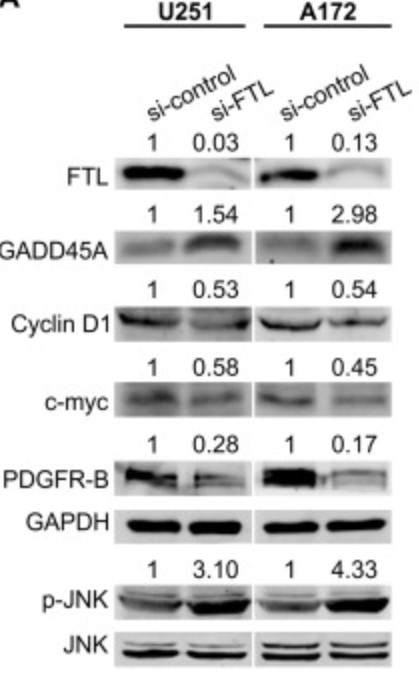
By using quantitative real-time RT-PCR, the researchers found that expression of FTL was higher in patients with GBM than in those with low-grade glioma. Immunofluorescence showed that FTL was mainly localized in the nucleus of GBM cells and was closely associated with mitotic spindles. Knockdown of FTL resulted in inhibition of cell growth and activation of the GADD45A/JNK pathway in GBM cells. FTL was found to localize with GADD45A in GBM cells, and a coimmunoprecipitation experiment showed that the two proteins physically interacted. Taken together, these results demonstrate a novel mechanism by which FTL regulates the growth of GBM cells via the GADD45/JNK pathway.
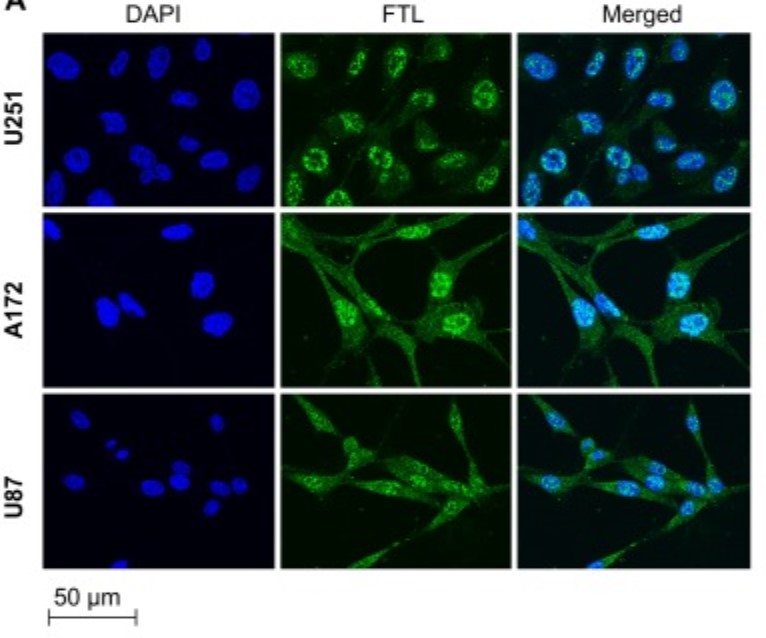
Fig3. Subcellular localization of ferritin light chain in glioblastoma multiforme cell lines during cell cycle phases.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
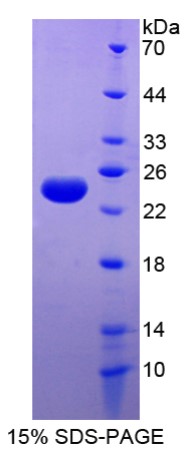
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FTL-8235H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
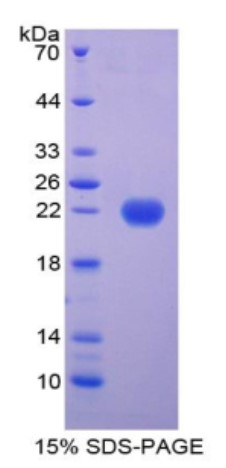
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FTL-8233C) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
FTL involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FTL participated on our site, such as Mineral absorption, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FTL were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Mineral absorption | SLC8A1,ATP1B2,TF,ATP1A4,ATP7A,SLC26A3,STEAP1,MT2A,TRPM6,FTH1 |
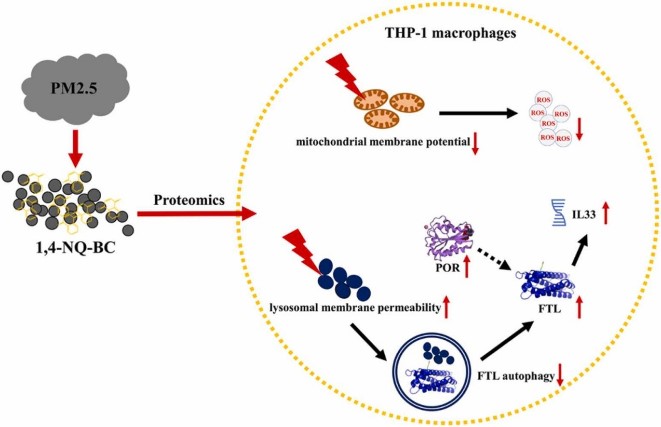
Fig1. 1,4 NQ-BC is a form of simulating the aging of BC in nature, which is more realistic. 1,4 NQ-BC prevented the removal of FTL by inhibiting autophagy. 1,4 NQ-BC increased IL-33 level by POR/FTL/IL-33 axis. (Yuan Cui, 2023)
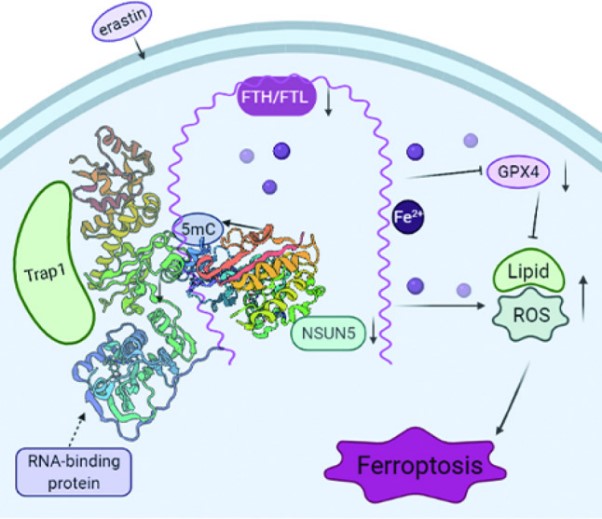
Fig2. Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms of NSUN5-FTH1/FTL. (Jie Liu, 2022)
Protein Function
FTL has several biochemical functions, for example, ferric iron binding,identical protein binding,iron ion binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FTL itself. We selected most functions FTL had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FTL. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ferric iron binding | FTH1,FTHL17,TH,FXN,Trf,MIOX,ACP5,FTH1B,FTH1A,TF |
| identical protein binding | TOPBP1,NELL2,GNPNAT1,NQO1,CEP72,VPS41,PRKD1,YWHAZ,C1QTNF9,MPST |
| iron ion binding | CYP4Z1,FAXDC2,NOS1,FDX1,NDOR1,CYP4V7,SCD,NOS2B,PAH,TMEM195 |
| protein binding | FCN3,IGFN1,RBBP6,CYP4F2,AIRE,MPPE1,GTF3C6,NGF,STIM2,MEIS1 |
Interacting Protein
FTL has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FTL here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FTL.
FTH1;SDCBP
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Jeon, JO; Kim, S; et al. Designed Nanocage Displaying Ligand-Specific Peptide Bunches for High Affinity and Biological Activity. ACS NANO 7:7462-7471(2013).
- Mahawar, M; Rabadi, SM; et al. Identification of a Live Attenuated Vaccine Candidate for Tularemia Prophylaxis. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).


