GABARAP
-
Official Full Name
GABA(A) receptor-associated protein -
Overview
Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors (GABA(A) receptors) are ligand-gated chloride channels that mediate inhibitory;neurotransmission. This gene encodes GABA(A) receptor-associated protein, which is highly positively charged in its;N-terminus and shares sequence similarity with light chain-3 of microtubule-associated proteins 1A and 1B. This;protein clusters neurotransmitter receptors by mediating interaction with the cytoskeleton. -
Synonyms
GABARAP;GABA(A) receptor-associated protein;gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein;ATG8A;MM46;GABARAP-a;FLJ25768;MGC120154;MGC120155
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- MBP
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is GABARAP protein?
GABARAP (GABA type A receptor-associated protein) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17p13. Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors [GABA(A) receptors] are ligand-gated chloride channels that mediate inhibitory neurotransmission. This gene encodes GABA(A) receptor-associated protein, which is highly positively charged in its N-terminus and shares sequence similarity with light chain-3 of microtubule-associated proteins 1A and 1B. This protein clusters neurotransmitter receptors by mediating interaction with the cytoskeleton. The GABARAP protein is consisted of 117 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 13.9 kDa.
What is the function of GABARAP protein?
GABARAP proteins are regulators of a class of small molecule G-protein-coupled receptors associated with GABA(gamma-aminobutyric acid). They play a variety of functions in the nervous system, including regulating neuronal excitability, participating in the transport and release of neurotransmitters, and regulating synaptic plasticity. In addition, GABARAP protein is also involved in the regulation of intracellular material transport, autophagy, metabolism and other processes, and is closely related to the occurrence and development of many diseases.
GABARAP Related Signaling Pathway
GABARAP proteins can bind and inhibit acetylcholine release, thereby regulating cholinergic synaptic signaling. GABARAP proteins can bind and inhibit glutamate release, thereby regulating glutamergic synaptic signaling. GABARAP proteins can bind and activate autophagy enzymes, thereby regulating the autophagy process. GABARAP protein can bind and activate caspase enzyme, thereby inducing cell apoptosis. The GABARAP protein binds to and regulates the structure and function of actin, thereby affecting the movement and morphology of cells.
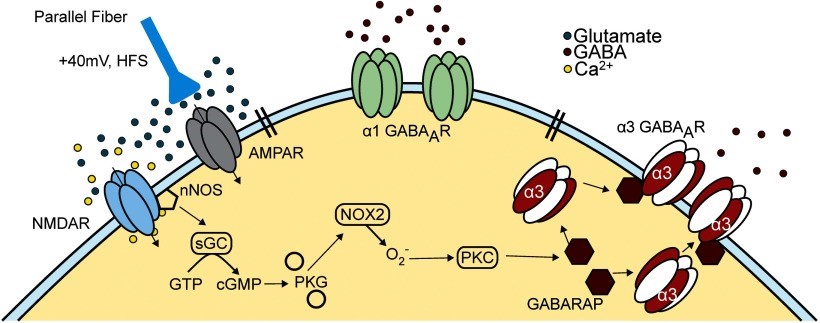
Fig1. Schematic summarizing the main signaling events and molecules that lead to the selective recruitment of α3-containing GABAARs into inhibitory synapses of cerebellar MLIs. (Erik A Larson, 2020)
GABARAP Related Diseases
Diseases associated with GABARAP include Pasteurella infection, Eisenmenger's syndrome, Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease. In these diseases, both the expression and function of GABARAP proteins may be affected, resulting in abnormal transport of intracellular substances, which affects the function and stability of nerve cells. For example, in Huntington's disease, the expression level of the GABARAP protein decreases, leading to the death of nerve cells and loss of motor function.
Bioapplications of GABARAP
The role of GABARAP protein in the nervous system is particularly important and has been implicated in a variety of neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders. Therefore, studying the structure and function of GABARAP protein, as well as developing drugs targeting GABARAP protein, is of great significance for understanding the pathogenesis of these diseases and developing new therapeutic approaches.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Ying Liu, 2021
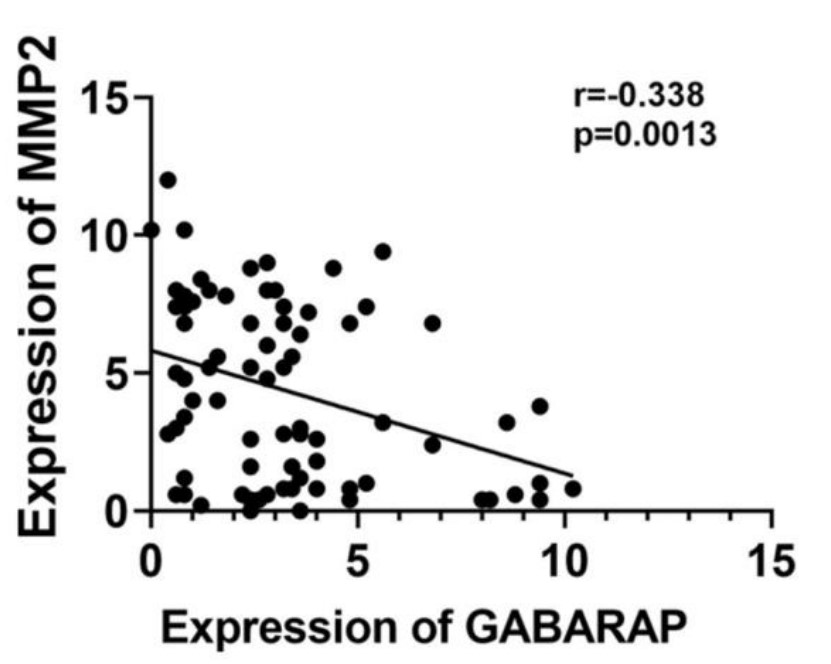
Few studies have focused on γ-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) in tumor progression. The researchers investigated the expression and importance of GABARAP in breast cancer. They analyzed the expression of GABARAP and its relationship with clinicopathological features and prognosis (TCGA). To explain the role and potential mechanism of GABARAP in regulating tumor development, they performed acquisition and loss of function experiments using cell lines and models of mouse xenotransplantation. GABARAP inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Notably, low levels of GABARAP induced the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Low levels of GABARAP increased p-AKT and p-mTOR levels, and a specific AKT pathway inhibitor reversed the downregulation of GABARAP-induced tumor progression. GABARAP negatively correlated with advanced clinicopathological features in clinical specimens, such as tumor size and TNM stage. Notably, patients with low GABARAP levels had a poor prognosis. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) revealed that GABARAP expression negatively correlated with matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 and MMP14.

Fig1. Western blotting analysis of GABARAP expression in 8 human breast cancer cell lines and non-transformed MCF-10A cells.
Case Study 2: Shin-ya Kawaguchi, 2007
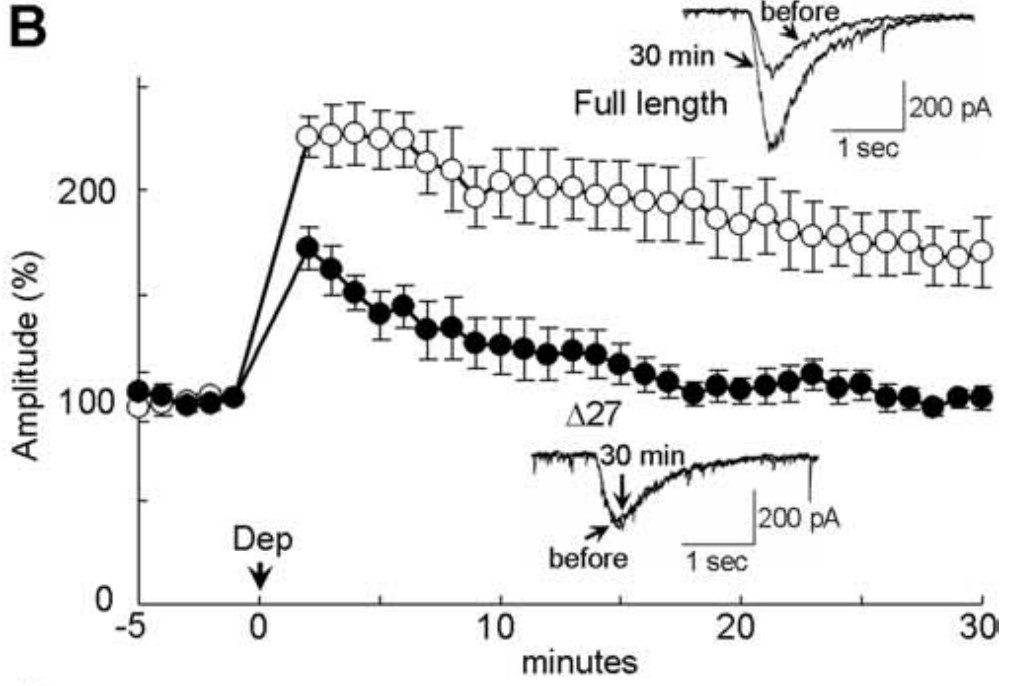
Fast inhibitory synaptic transmission is predominantly mediated by GABA(A) receptor (GABA(A)R) in the CNS. Although several types of neuronal activity-dependent plasticity at GABAergic synapses have been reported, the detailed mechanism is elusive. Here the researchers show that binding of structurally altered GABA(A)R-associated protein (GABARAP) to GABA(A)R gamma2 subunit and to tubulin is critical for long-term potentiation [called rebound potentiation (RP)] at inhibitory synapses on a cerebellar Purkinje neuron (PN). Either inhibition of GABARAP association with GABA(A)Rgamma2 or deletion of tubulin binding region of GABARAP impaired RP. Thus, precise regulation of GABA(A)Rgamma2-GABARAP-microtubule interaction is critical for RP. Furthermore, competitive inhibition of GABARAP binding to GABA(A)Rgamma2 after the RP establishment attenuated the potentiated response, suggesting that GABARAP is critical not only for the induction but also for the maintenance of RP. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis revealed that GABARAP underwent sustained structural alteration after brief depolarization of a PN depending on the activity of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), which is required for the RP induction. The susceptibility of GABARAP to undergo structural alteration was abolished by an amino acid replacement in GABARAP. Furthermore, RP was impaired by expression of the mutant GABARAP with the replacement.
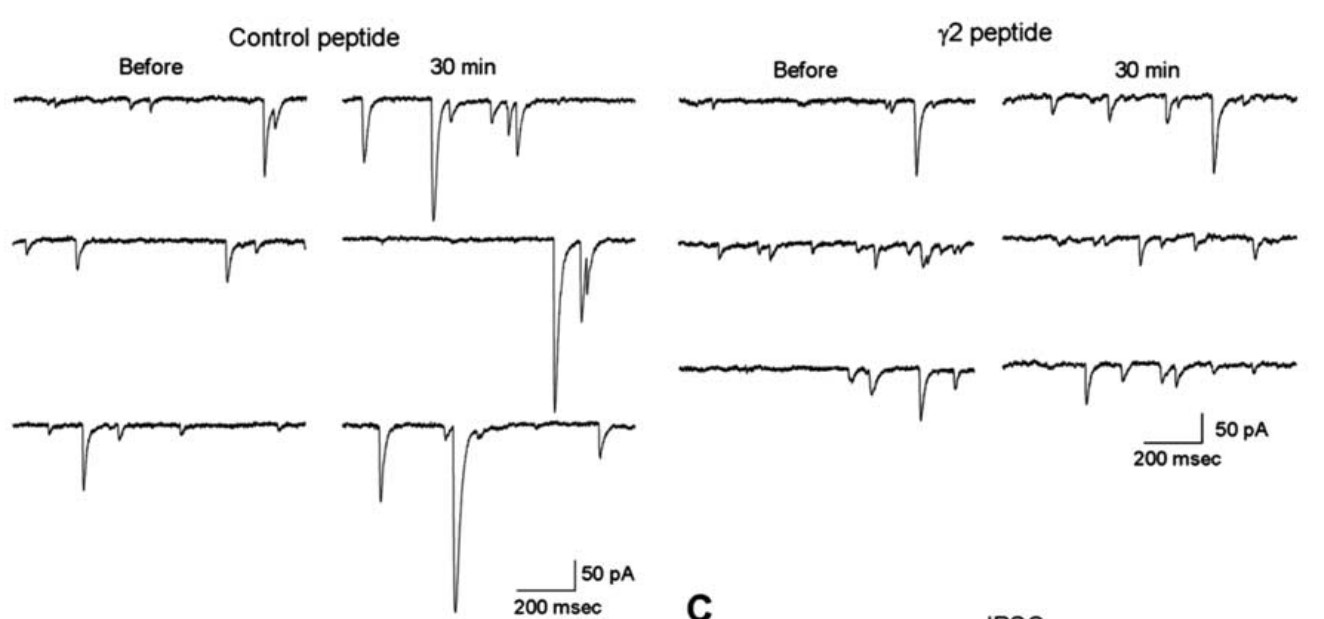
Fig3. Representative traces of mIPSCs before and 30 min after the conditioning depolarization in the presence of control peptide or γ2 peptide.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
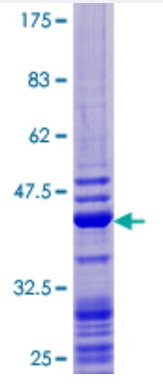
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GABARAP-4622H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
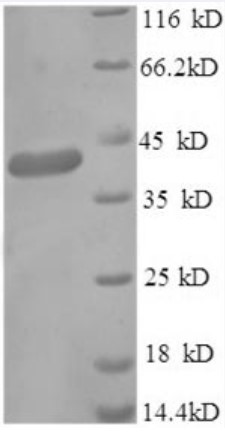
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GABARAP-5224H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
GABARAP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GABARAP participated on our site, such as Cellular responses to stress,FoxO signaling pathway,GABAergic synapse, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GABARAP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Macroautophagy | ATG9B,ULK1A,AMBRA1A,AMBRA1,ATG9A,ATG7,WDR45L,AMBRA1B,GABARAPL2,LC3 |
| Cellular responses to stress | KDM6B,AMBRA1,TERF2,PHC2,RBBP4,KIAA1967,HSPA13,HMGA1B,CDKN2A,HSBP1A |
| GABAergic synapse | GABRD,SLC38A1,GNGT2,GNB4,GABRB2,GABBR2,GAD1,GNAI1,GABRG1,GNG13 |
| Regulation of autophagy | ATG4D,ATG4C,IFNA8,INS1,BECN1,IFNA1,IFNA2,IFNA14,IFNG,IFNA21 |
| FoxO signaling pathway | BNIP4,G6PC3,PIK3R5,AGAP2,Fasl,SKP2,KLF2A,MAPK8,PIK3R3,PLK2 |
| Senescence and Autophagy | GABARAPL2,SLC39A1,IL24,UVRAG,ATG7,IGFBP7,FKBP8,SLC39A2,IGFBP5,SLC39A3 |
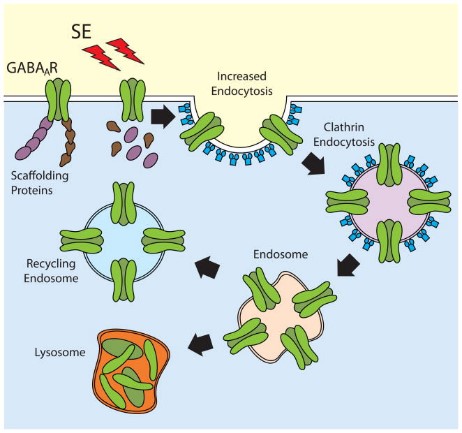
Fig1. Regulation of GABAA receptor trafficking during SE. (Marco I González, 2011)
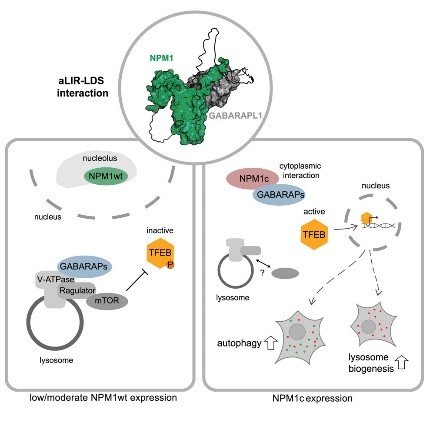
Fig2. NPM1/NPM1c bind to GABARAP proteins via an atypical module in their N-terminal regions. (Hannah Mende, 2023)
Protein Function
GABARAP has several biochemical functions, for example, GABA receptor binding,beta-tubulin binding,microtubule binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GABARAP itself. We selected most functions GABARAP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GABARAP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| microtubule binding | MTAP1B,CHP,PPP5C,KIF1C,KIF3C,KIF14,RAB11A,KIAA1128,MAPRE3B,FES |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | DIO2,DBT,IKBKG,KDM4A,UBE2J2,SMAD6,VCP,TRAF2,BCL10,LC3 |
| GABA receptor binding | PLCL1,PPP2CA,MAF1,GABARAPL1,GABRG1,JAKMIP1,AKAP5,TRAK1,GABARAPA,GABRA5 |
| protein binding | SPAG9,TOMM34,BRPF3,GPRIN2,RSPO1,SKP1,DDR2,AGRN,FGF21,VGLL4 |
| beta-tubulin binding | IFT74,RGS2,ARL8A,NDEL1,AKAP1,RANBP10,SNCA,GABARAPL1,PROL1,SLC6A2 |
Interacting Protein
GABARAP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GABARAP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GABARAP.
SQSTM1;CALR;NBR1;ATG7
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zsuzsanna, K; Patricia, P; et al. The stiff-person syndrome: a brief review and report of two cases. ORVOSI HETILAP 154:1984-1990(2013).
- Marcial, HS; Suga, K; et al. Molecular cloning and localization of GABA(A) receptor-associated protein in the rotifer Brachionus plicatilis. INTERNATIONAL REVIEW OF HYDROBIOLOGY 99:188-197(2014).



