GDF3
-
Official Full Name
growth differentiation factor 3 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family and the TGF-beta superfamily. This group of proteins is characterized by a polybasic proteolytic processing site which is cleaved to produce a mature protein containing seven conserved cysteine residues. The members of this family are regulators of cell growth and differentiation in both embryonic and adult tissues. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
GDF3;growth differentiation factor 3;KFS3;MCOP7;MCOPCB6;growth/differentiation factor 3;GDF-3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- E.coli
- CHO
- Human
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDF3-3659H | Recombinant Human GDF3 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 251-355 aa | |
| GDF3-02H |
Active Recombinant Human GDF3
|
E.coli | Human | Non |
|
|
| Gdf3-718M |
Active Recombinant Mouse Growth Differentiation Factor 3
|
E.coli | Mouse | Non | 253-366 a.a. |
|
| GDF3-246H | Recombinant Human GDF3 | CHO | Human | Non |
|
|
| GDF3-584H | Recombinant Human Growth Differentiation Factor 3 | Human | Human | His |
|
|
| GDF3-6287M | Recombinant Mouse GDF3 Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| GDF3-6764C | Recombinant Chicken GDF3 | Mammalian Cells | Chicken | His |
|
|
| GDF3-8587Z | Recombinant Zebrafish GDF3 | Mammalian Cells | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| GDF3-5969HCL | Recombinant Human GDF3 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| GDF3-048H | Active Recombinant Human GDF3 Protein | E.coli | Human | 251-364 a.a. |
|
|
| GDF3-271H | Recombinant Human GDF3 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ala251~Gly364 |
|
| Gdf3-272M | Recombinant Mouse Gdf3 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Mouse | His | Ala253~Gly366 |
|
| Gdf3-273R | Recombinant Rat Gdf3 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Rat | His | Ala253~Gly366 |
|
| GDF3-3520M | Recombinant Mouse GDF3 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| GDF3-3520M-B | Recombinant Mouse GDF3 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
||
| GDF3-3584H | Recombinant Human GDF3 Protein (Ala251-Gly364), His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ala251-Gly364 |
|
| GDF3-4825H | Recombinant Human GDF3 Protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST |
|
|
| GDF3-5238HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GDF3 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 364 amino acids |
|
Background
What is GDF3 protein?
GDF3 gene (growth differentiation factor 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p13. This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein plays a role ocular and skeletal development. The GDF3 protein is consisted of 364 amino acids and GDF3 molecular weight is approximately 41.4 kDa.
What is the function of GDF3 protein?
The GDF3 protein is a protein belonging to the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) superfamily. GDF3 plays an important role in early embryonic development, bone and retinal development. Including: involved in the regulation of cell fate and cell pluripotency, involved in the regulation of bone and cartilage growth and maturation. During embryogenesis, GDF3 influences the formation of provisceral endoderm and mesoderm by controlling the establishment of pre - and post-identity. As a member of TGF-β superfamily, GDF3 activates SMAD family transcription factors by binding to corresponding receptors, thereby regulating gene expression. GDF3 is involved in regulating the homeostasis and energy balance of adipose tissue under nutrient overload.
GDF3 Related Signaling Pathway
By binding to TGF-β receptor, GDF3 activates SAMad-dependent signaling pathway, affecting cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. In some cases, GDF3 can inhibit BMP signaling pathways and affect cell fate decisions. GDF3 is specifically expressed in embryonic stem cells and is involved in the regulation of self-renewal and pluripotency maintenance of stem cells. Studies have shown that GDF3 at high doses activates the Nodal signaling pathway, an important signaling pathway associated with early embryonic pattern formation. GDF3 may influence cell behavior through a non-mad dependent pathway, such as activating other signaling pathways such as MAPK.
GDF3 Related Diseases
Klippel-Feil syndrome is a disease characterized by abnormal fusion of the vertebrae in the neck and affects many parts of the body. At least four mutations in the GDF3 gene have been found to cause this syndrome, and these mutations may reduce levels of functional proteins. The GDF3 protein is also involved in the development of the eye, particularly the retina. Mutations in the GDF3 gene are associated with certain eye diseases, such as retinal dysplasia. GDF3 may play a role in regulating the host's response to infection, for example in a model of sepsis, where GDF3 administration improves survival in mice. In addition, it is associated with cardiomyopathy and some tumors.
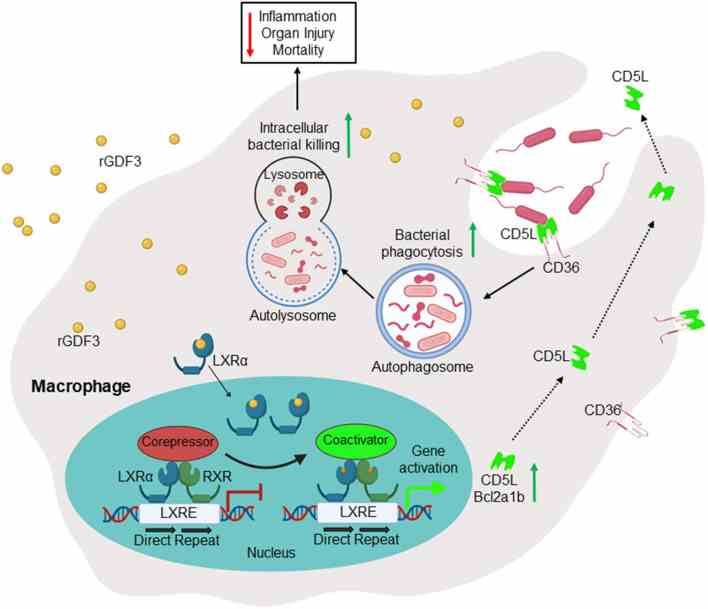
Fig1. Scheme depicting that administration of GDF3 into septic mice improves survival via enhancing macrophage phagocytosis. (Peng Wang, 2021)
Bioapplications of GDF3
GDF3 has been identified as a biomarker of adverse fibrosis remodeling after myocardial infarction and is helpful in understanding the process of cardiac fibrosis scar formation after myocardial infarction. As an inhibitor of the BMP (bone morphogenetic proteins) family, the regulatory effects of GDF3 have potential applications in drug development, especially in the treatment of diseases associated with BMP signaling pathways. Due to GDF3's role in bone and cartilage development, it may be used in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to promote tissue repair and regeneration. The role of GDF3 in early embryonic development makes it an important molecule to study the mechanism of embryonic development, which helps to reveal the molecular mechanism of embryo formation and organ development.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mi-Hee Han, 2016
Growth and differentiation factor 3 (GDF3), a mammalian-specific transforming growth factor β ligand, and OCT4, one of key stem cell transcription factors, are expressed in testicular germ cell tumors (TGCTs) as well as pluripotent stem cells. To understand the molecular mechanism by which OCT4 and GDF3 function in tumorigenesis as well as stemness, researchers investigated the transcriptional regulation of GDF3 mediated by OCT4 in human embryonic carcinoma (EC) NCCIT cells, which are pluripotent stem cells of TGCTs. GDF3 and OCT4 was highly expressed in undifferentiated NCCIT cells and then significantly decreased upon retinoic acid-induced differentiation in a time-dependent manner. Moreover, GDF3 expression was reduced by short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of OCT4 and increased by OCT4 overexpression, suggesting that GDF3 and OCT4 have a functional relationship in pluripotent stem cells. A promoter-reporter assay revealed that the GDF3 promoter (-1721-Luc) activity was significantly activated by OCT4 in a dose-dependent manner.
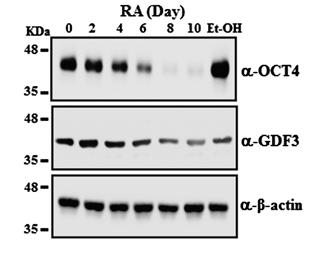
Fig1. GDF3 and OCT4 protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting.
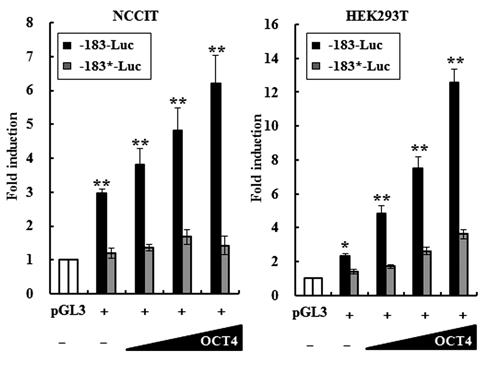
Fig2. The GDF3 minimal promoter (−183-Luc) is activated by OCT4 in a dose-dependent manner in NCCIT and HEK293T cells.
Case Study 2: Qiang Li, 2012
The aim of this study is to investigate whether GDF3 is related to the progression of human breast cancer and the effects of GDF3 on breast cancer cells. Breast cancer cells were treated with different concentrations of recombinant human GDF3 protein. Soft agar assay was performed to explore the effects of GDF3 on colony formation. Different anti-tumor drugs dealt with MCF-7 cells stably expressing GDF3. The results showed that GDF3 proteins could inhibit the proliferation of MCF-7 and T47D cells. Knockdown of GDF3 resulted in the promotion of colony formation and enhanced the ability of anchorage-independent cell growth in soft agar. Furthermore, overexpression of GDF2 could promote the apoptosis induced by Taxol.
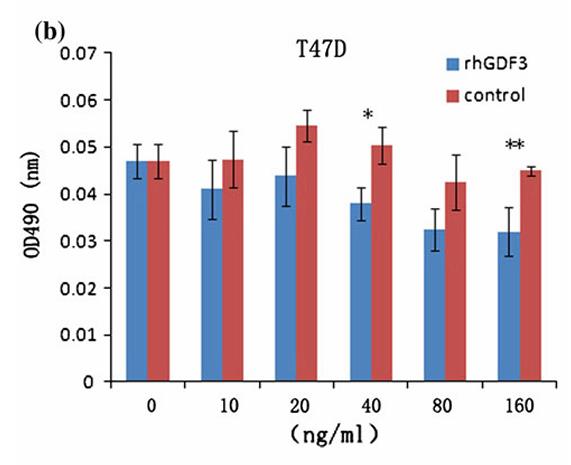
Fig3. GDF3 inhibited the growth of breast cancer cells. T47D cells were treated with different concentration rhGDF3 protein.
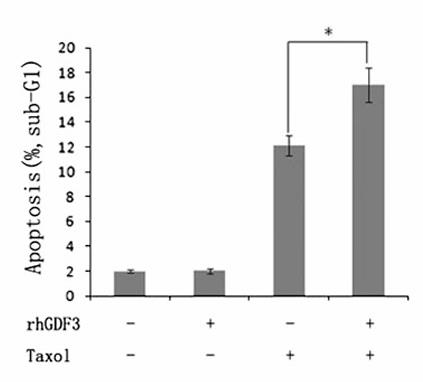
Fig4. The combination of Taxol and rhGDF3 proteins could increase the percents of sub-G1 phase cells.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GDF3-271H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GDF3-4825H)
Involved Pathway
GDF3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GDF3 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GDF3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
GDF3 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,growth factor activity,protein kinase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GDF3 itself. We selected most functions GDF3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GDF3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| growth factor activity | PDGFD,GSDF,VEGFC,GDF6,HBEGFB,LEP,BDNF,FGF22,AMELX,TGFB3 |
| protein kinase binding | CDK5RAP3,BAD,GSK3B,SPDYA,NEFH,LAT,GHR,MLKL,FAM83B,PRKCZ |
| cytokine activity | INHBAA,IL18,OSM,GDF10,IFNA12,TNFSF10,IL1B,IL22,IL9,IL6 |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor binding | MSTNB,GDF15,BMP5,LRG1,BMP8B,LFT2,INHBAA,INHA,SPAW,TGFB1A |
Interacting Protein
GDF3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GDF3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GDF3.
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Adewumi, O; Aflatoonian, B; et al. Characterization of human embryonic stem cell lines by the International Stem Cell Initiative. NATURE BIOTECHNOLOGY 25:803-816(2007).



