GDF6
-
Official Full Name
growth differentiation factor 6 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family and the TGF-beta superfamily of secreted signaling molecules. It is required for normal formation of some bones and joints in the limbs, skull, and axial skeleton. Mutations in this gene result in colobomata, which are congenital abnormalities in ocular development, and in Klippel-Feil syndrome (KFS), which is a congenital disorder of spinal segmentation. -
Synonyms
GDF6;growth differentiation factor 6;growth/differentiation factor 6;BMP13;GDF-6;Klippel-Feil syndrome;Klip-Feil malformation;Klippel-Feil malformation;growth/differentiation factor 16;KFM;KFS;KFS1;KFSL;SGM1;CDMP2;MCOP4;SCDO4;MCOPCB6;MGC
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Non
- His
- Avi
- Fc
Background
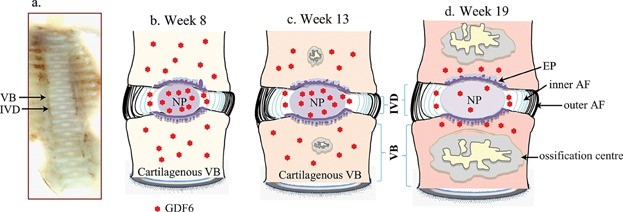
Fig1. A schematic diagram, based on the template image of human fetal spine sectioned in sagittal plane (a), shows the organization of the vertebral column and associated GDF6 expression at week 8 (b), week 13 (c) and week 19 (d) of gestational ages. (Aiqun Wei, 2016)
What is GDF6 protein?
GDF6 (growth differentiation factor 6) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8q22. This gene encodes a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family and the TGF-beta superfamily of secreted signaling molecules. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. This protein is required for normal formation of some bones and joints in the limbs, skull, and axial skeleton. The GDF6 protein is consisted of 455 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 50.7 kDa.
What is the function of GDF6 protein?
GDF6 mainly plays a role in embryonic development, tissue repair and maintenance of adult tissue homeostasis. It is involved in the formation and maintenance of bone, muscle and nervous system, and plays a key role in regulating the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells. In the nervous system, GDF6 has a positive effect on neuroprotection and neuronal regeneration, and may be involved in the pathological processes of neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, GDF6 also showed potential functions in regulating inflammatory response and inhibiting tumor development.
GDF6 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathway of GDF6 is mainly involved in a MAD-dependent pathway in which ligand binding leads to receptor activation, which in turn leads to phosphorylation of Smad proteins. These phosphorylated Smad proteins then form complexes with co-mediators Smad, such as Smad4, and migrate into the nucleus to regulate transcription of target genes. In addition, GDF6 can also activate Smad independent pathways, including MAPK (e.g. ERK, JNK, p38), PI3K/Akt, and Wnt signaling pathways, which may have different roles in different types of cells. Through these signaling cascades, GDF6 is involved in regulating a variety of biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and tissue regeneration and repair.
GDF6 Related Diseases
Gdf-6-related diseases involve a variety of pathological states, including muscle dysplasia, bone disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain types of cancer. For example, GDF-6's role in muscle atrophy and muscle regeneration suggests a link to muscle dysplasia and motor neurone disease. Furthermore, the increased expression of GDF-6 in osteoarthritis suggests that it may be involved in the process of destruction and repair of articular cartilage. There is also research suggesting that GDF-6 may play a role in neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease. In the field of oncology, changes in the expression of GDF-6 have also been found to be associated with the development of breast cancer, prostate cancer and other cancers.
Bioapplications of GDF6
Existing applications lie primarily in the fields of regenerative medicine and tissue engineering, where GDF6 is being studied for the treatment of arthritis and cartilage damage due to its potential to promote cartilage formation and repair. In addition, GDF6 is also of interest in the field of neurobiology because it may be involved in neuroprotection and nerve regeneration processes. Although therapeutic applications for GDF6 are still in the research and development phase, preliminary studies show that its potential therapeutic value for certain diseases, such as muscular dystrophy and other degenerative diseases, is being explored.
Case Study
Case study 1: Bojiang Shen, 2009
Bone morphogenetic protein-13 (BMP-13) plays an important role in skeletal development. In the light of a recent report that mutations in the BMP-13 gene are associated with spine vertebral fusion in Klippel-Feil syndrome, the researchers hypothesized that BMP-13 signaling is crucial for regulating embryonic endochondral ossification. In this study, they found that BMP-13 inhibited the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (BM MSCs) in vitro. The endogenous BMP-13 gene expression in MSCs was examined under expansion conditions. The MSCs were then induced to differentiate into osteoblasts in osteo-inductive medium containing exogenous BMP-13. Gene expression was analysed by real-time PCR. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression and activity, proteoglycan (PG) synthesis and matrix mineralization were assessed by cytological staining or ALP assay. Results showed that endogenous BMP-13 mRNA expression was higher than BMP-2 or -7 during MSC growth. BMP-13 supplementation strongly inhibited matrix mineralization and ALP activity of osteogenic differentiated MSCs, yet increased PG synthesis under the same conditions.
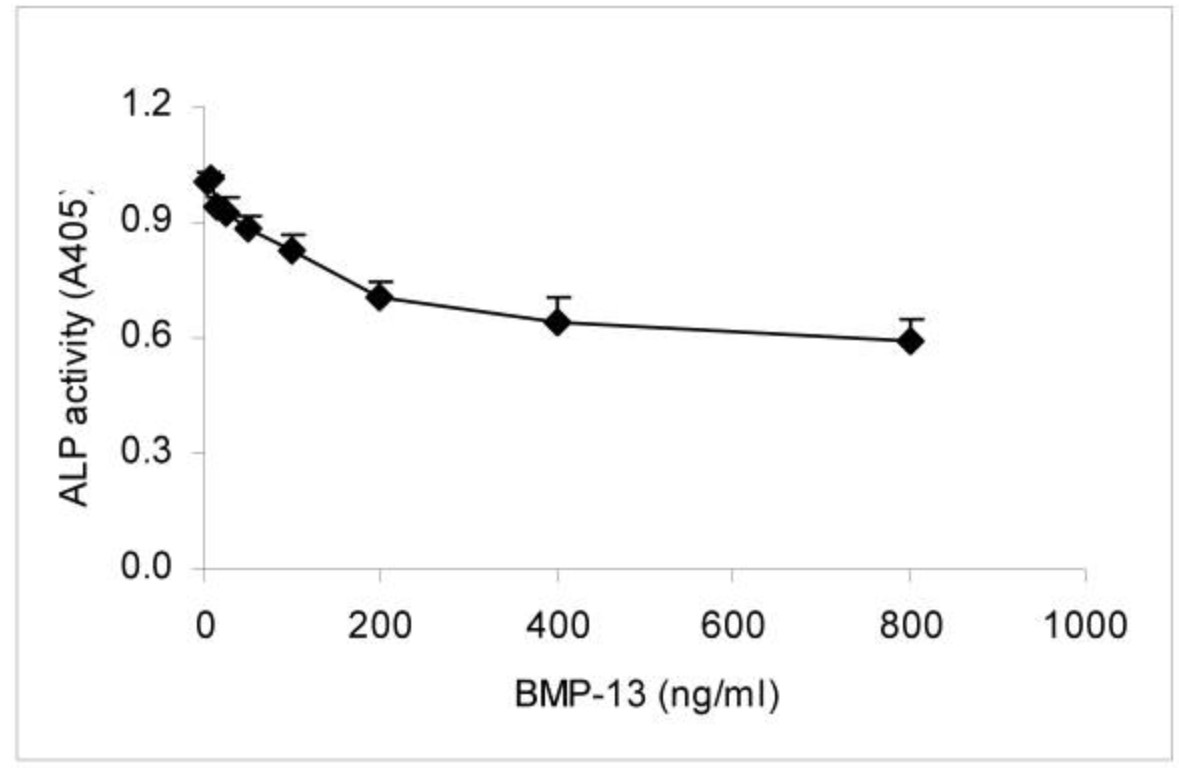
Fig1. ALP activity was measured in MSCs after 14 days differentiation in osteo-inductive medium with or without BMP-13 (3-800 ng/ml).
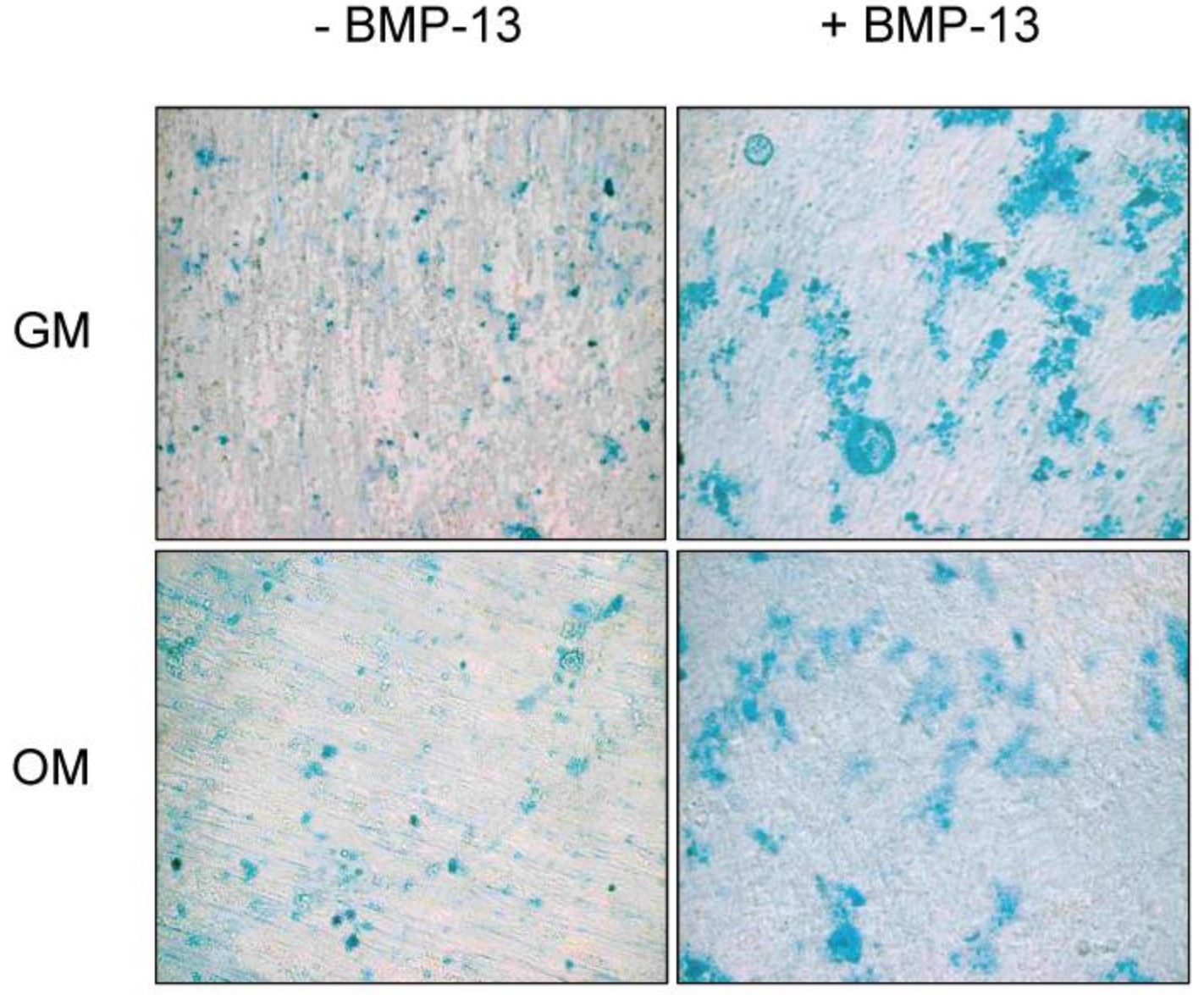
Case study 2: Fuchun Zhou, 2020
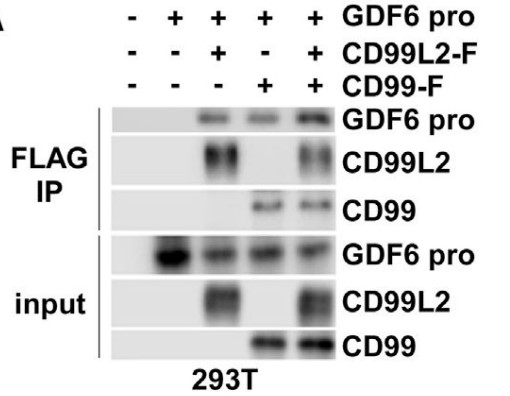
The researchers report here that the autocrine signaling mediated by growth and differentiation factor 6 (GDF6), a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family of cytokines, maintains Ewing sarcoma growth by preventing Src hyperactivation. Surprisingly, Ewing sarcoma depends on the prodomain, not the BMP domain, of GDF6. They demonstrate that the GDF6 prodomain is a ligand for CD99, a transmembrane protein that has been widely used as a marker of Ewing sarcoma. The binding of the GDF6 prodomain to the CD99 extracellular domain results in recruitment of CSK (C-terminal Src kinase) to the YQKKK motif in the intracellular domain of CD99, inhibiting Src activity. GDF6 silencing causes hyperactivation of Src and p21-dependent growth arrest. They demonstrate that two GDF6 prodomain mutants linked to Klippel-Feil syndrome are hyperactive in CD99-Src signaling. These results reveal a cytokine signaling pathway that regulates the CSK-Src axis and cancer cell proliferation and suggest the gain-of-function activity for disease-causing GDF6 mutants.
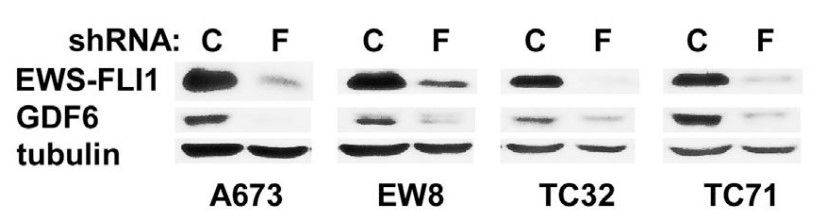
Fig3. EWS-FLI1 silencing results in reduced GDF6 protein expression in Ewing sarcoma.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
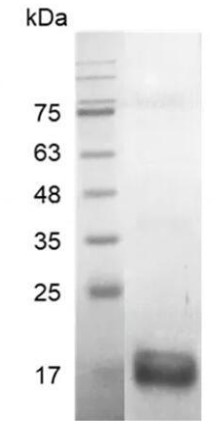
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GDF6-188H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
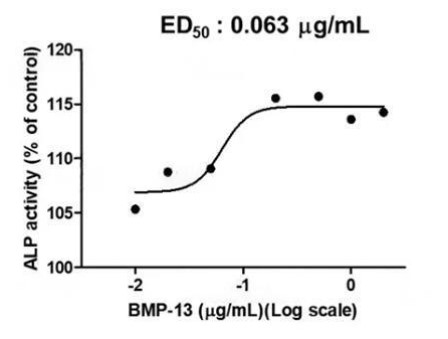
Fig2. Activity Data. (GDF6-188H)
Involved Pathway
GDF6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GDF6 participated on our site, such as TGF-beta signaling pathway,Hippo signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GDF6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hippo signaling pathway | GDF7,BTRC,NKD1,LEF1,ID1,PPP2R2A,CRB1,Fzd4,DLG1,BMP6 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | PPP2R1A,RPS6KB1,NBL1,NOG3,AMHR2,ROCK1,BMP2B,ACVR2AA,SMAD1,TNF |
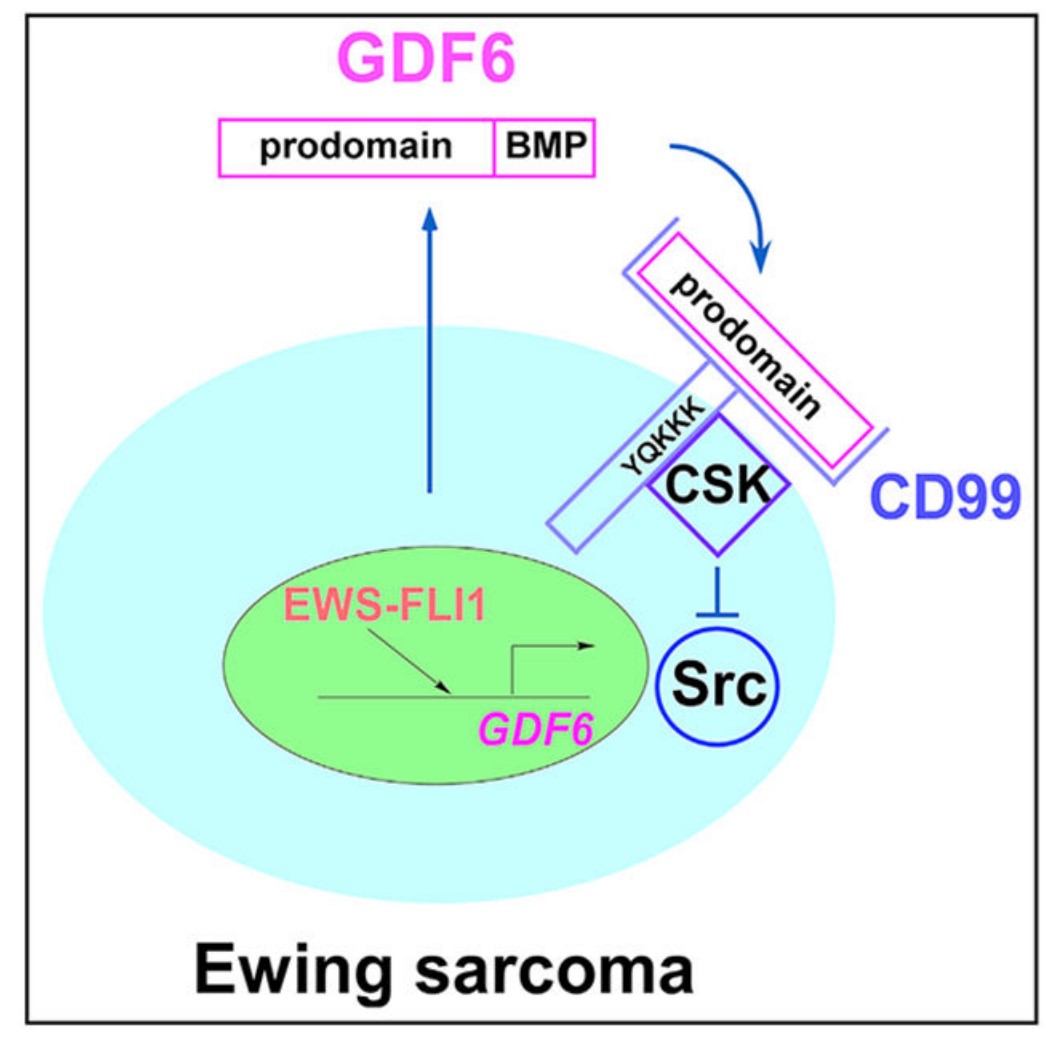
Fig1. Ewing sarcoma is driven by the EWS-ETS fusion oncoprotein, but little is known about the extracellular signaling regulating this cancer. (Fuchun Zhou, 2020)
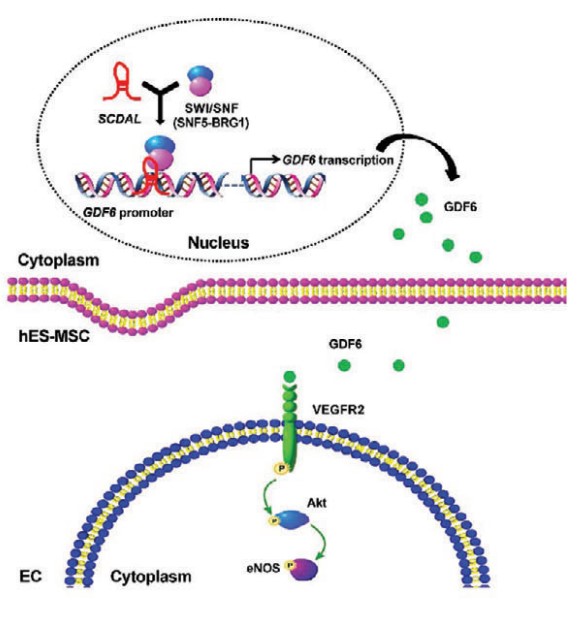
Fig2. Schematic model of SCDAL-regulated GDF6 function in mediating angiogenesis. (Rongrong Wu, 2021)
Protein Function
GDF6 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,growth factor activity,protein homodimerization activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GDF6 itself. We selected most functions GDF6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GDF6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein homodimerization activity | GSTM3,GRHPR,C6orf108,YARS2,G6PDX,ACHE,ASNS,UGT1A7,OXCT1,ABCD3 |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor binding | BMP10,TGFB2,BMP2,BMP5,GDF6B,LEFTY1,INHBB,TGFBR3,SPAW,LEFTY2 |
| cytokine activity | Flt3l,INHA,CCL38A.4,TNFRSF11B,TNFSF14,IFNA16,WNT2,NDR2,BMP4,NRG1 |
| growth factor activity | NENF,OSGIN1,PSPN,ANGPTL3,Il2,MSTN,TDGF1,Fgf15,PDGFAA,TGFB1A |
Interacting Protein
GDF6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GDF6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GDF6.
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wendroth, SM; Mentrikoski, MJ; et al. GATA3 expression in morphologic subtypes of breast carcinoma: a comparison with gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 and mammaglobin. ANNALS OF DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY 19:6-9(2015).
- Esser, JS; Rahner, S; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Endothelial Cells Is Activated by BMPER to Promote Angiogenesis. ARTERIOSCLEROSIS THROMBOSIS AND VASCULAR BIOLOGY 35:358-367(2015).



