LIN28A
-
Official Full Name
lin-28 homolog A (C. elegans) -
Overview
Acts as a 'translational enhancer', driving specific mRNAs to polysomes and thus increasing the efficiency of protein synthesis. Its association with the translational machinery and target mRNAs results in an increased number of initiation events per molecule of mRNA and, indirectly, in stabilizing the mRNAs. Binds IGF2 mRNA, MYOD1 mRNA, ARBP/36B4 ribosomal protein mRNA and its own mRNA. Essential for skeletal muscle differentiation program through the translational up-regulation of IGF2 expression (By similarity). Acts as a suppressor of microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis by specifically binding the precursor let-7 (pre-let-7), a miRNA precursor. Acts by binding pre-let-7 and recruiting ZCCHC11/TUT4 uridylyltransferase, leading to the terminal uridylation of pre-let-7. Uridylated pre-let-7 miRNAs fail to be processed by Dicer and undergo degradation. Degradation of pre-let-7 in embryonic stem (ES) cells contributes to the maintenance of ES cells. In contrast, LIN28A down-regulation in neural stem cells by miR-125, allows the processing of pre-let-7. Specifically recognizes the 5'-GGAG-3' motif in the terminal loop of pre-let-7. Also recognizes and binds non pre-let-7 pre-miRNAs that contain the 5'-GGAG-3' motif in the terminal loop, leading to their terminal uridylation and subsequent degradation. -
Synonyms
LIN28A;lin-28 homolog A (C. elegans);CSDD1;LIN28;LIN-28;ZCCHC1;lin-28A;protein lin-28 homolog A;RNA-binding protein LIN-28;zinc finger, CCHC domain containing 1;zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Insect Cells
- E. coli
- His
- TAT
- Non
- Avi
- Flag
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- PDI
- GST
Background
What is LIN28A protein?
LIN28A gene (lectin, mannose binding 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 18 at locus 18q21. The LIN28A protein is consisted of 510 amino acids and LIN28A molecular weight is approximately 57.5 kDa.
What is the function of LIN28A protein?
The LIN28A protein is an RNA-binding protein originally discovered in Caenorhabditis elegans and plays a role in regulating the differentiation and proliferation of stem cells. In mammalian stem cells, LIN28A showed a similar function. Subsequent studies have found that LIN28A plays a role in regulating cell cycle and growth, tissue repair, and metabolism, particularly glucose metabolism. In addition, LIN28A affects the occurrence, development and prognosis of cancer by inhibiting miRNA differentiation and maturation and regulating the expression of some cell cycle related genes. LIN28A also plays an important role in tumor tolerance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. LIN28A is also believed to be an important pluripotent factor that reprograms translation and promotes cancer progression. LIN28A plays an important role in promoting somatic reprogramming and pluripotent state transition, and it inhibits the maturation of let-7 microRNA in the cytoplasm. LIN28A has also been implicated in the regulation of gene expression during embryonic development and tumorigenesis.
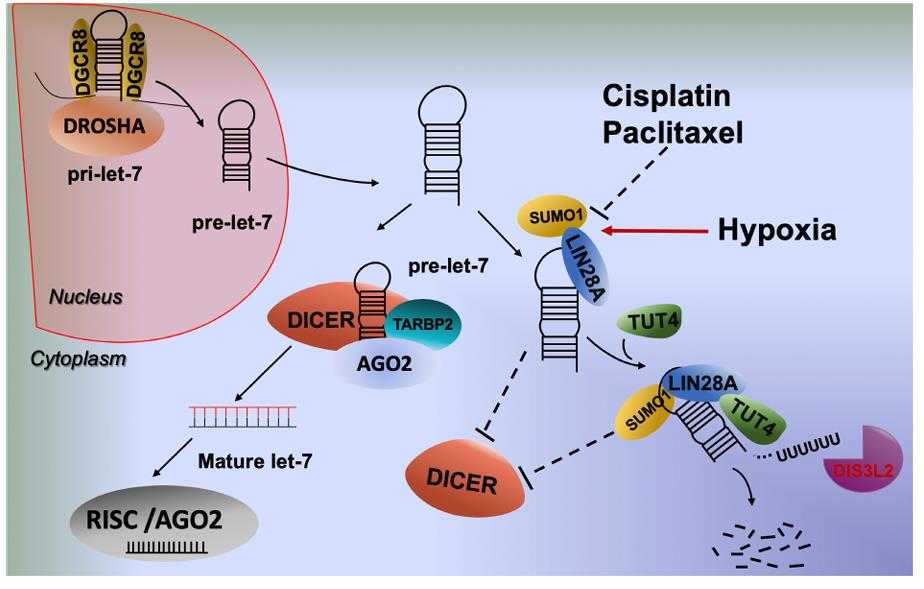
Fig1. The proposed model of SUMOylated LIN28A inhibiting let-7 maturation. (Jinzhuo Dou, 2020)
LIN28A Related Signaling Pathway
LIN28A prevents it from being processed by Drosha by binding to the primary let-7 (pri-let-7) and prevents Dicer processing by binding to the precursor let-7 (pre-let-7) while promoting its degradation. This mode of regulation affects the maturation of let-7 family miRNAs, which in turn affects the translation and stability of the mRNAs they target. LIN28A can up-regulate the expression of cell cycle related genes such as cyclin A and cyclin B, and promote the proliferation of stem cells. LIN28A can inhibit the activity of DUSP family phosphatases, thereby activating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway and maintaining the characteristics of pluripotent stem cells.
LIN28A Related Diseases
LIN28A protein is closely related to the development of a variety of diseases, and its abnormal expression plays a key role in tumors, liver diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. In the field of cancer, such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer and ovarian cancer, high expression of LIN28A is closely related to the proliferation of tumor stem cells, the occurrence and development of tumors, and poor prognosis. In liver diseases, LIN28A is associated with pathological processes such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis, and may be involved in the development of the disease by regulating the inflammatory response and fibrotic processes. In addition, the absence of LIN28A is associated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease, while its overexpression is associated with Rett syndrome, suggesting its importance in nervous system function. Although the direct link between LIN28A and cardiovascular disease and diabetes requires further investigation, its role in cell differentiation, growth, and metabolism may be relevant to the pathogenesis of these diseases.
Bioapplications of LIN28A
In cancer therapy, LIN28A inhibitors, specific nanoantibodies, and Lin28A-targeting deubiquitination enzymes may be viable therapeutic options. On the other hand, drugs that boost the expression of LIN28A may be used as regenerative treatments for neurodegenerative diseases. In addition, the potential of LIN28A in RNA-targeted therapy, including small interfering Rnas and RNA-protein interactions, is also considered promising for clinical applications.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Seungwon Jung, 2024
UPF1 and LIN28A are RNA-binding proteins involved in post-transcriptional regulation and stem cell differentiation. Most studies on UPF1 and LIN28A have focused on the molecular mechanisms of differentiated cells and stem cell differentiation, respectively. Researchers reveal that LIN28A directly interacts with UPF1 before UPF1-UPF2 complexing, thereby reducing UPF1 phosphorylation and inhibiting nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). they identify the interacting domains of UPF1 and LIN28A; moreover, they develop a peptide that impairs UPF1-LIN28A interaction and augments NMD efficiency. Transcriptome analysis of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) confirms that the levels of NMD targets are significantly regulated by both UPF1 and LIN28A. Inhibiting the UPF1-LIN28A interaction using a CPP-conjugated peptide promotes spontaneous differentiation by repressing the pluripotency of hPSCs during proliferation. Furthermore, the UPF1-LIN28A interaction specifically regulates transcripts involved in ectodermal differentiation.
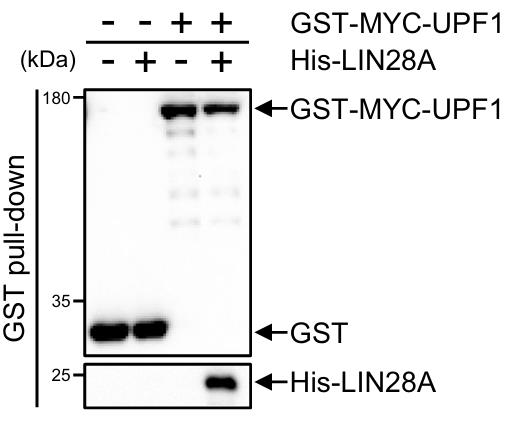
Fig1. WB was performed to detect GST pull-downed His-LIN28A with GST-MYC-UPF1.
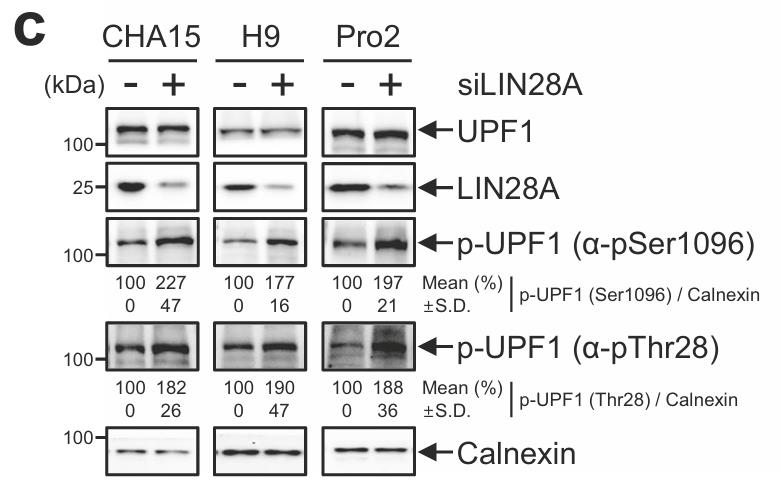
Fig2. hPSCs were transfected with siLIN28A or control siRNA.
Case Study 2: Panai Song, 2022
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a serious complication among patients with diabetes. Elucidating its pathogenesis is crucial for identifying novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets for DN. DN tissues were harvested for examining MALAT1, LIN28A and Nox4. Human kidney-2 (HK-2) cells were treated with high glucose (HG) for establishing a cell model of DN. Cell viability was examined by MTT assay. HG-induced cell apoptosis and secretion of TNF-α and IL-6 were analyzed by TUNEL and ELISA assays, respectively. RIP and RNA pull-down assays were applied to analyze the interaction between MALAT1, LIN28A and Nox4 in HK-2 and human embryonic kidney 293T (HEK-293T) cells. The results showed that MALAT1 directly interacted with LIN28A. Moreover, MALAT1 facilitated the interaction between LIN28A and Nox4 to increase Nox4 stability. Knockdown of MALAT1 alleviated renal tubular epithelial injury by suppressing LIN28A and the Nox4/AMPK/TOR signaling in DN.
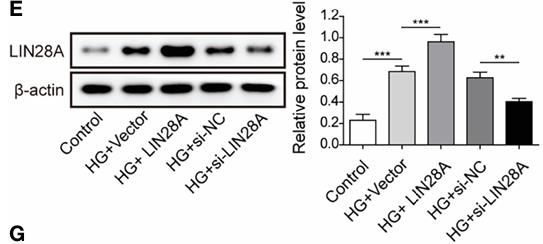
Fig3. LIN28A was detected using western blotting.
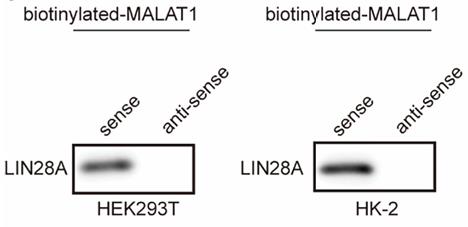
Fig4. LIN28A was pulled down by the MALAT1 sense probe.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LIN28A-1577H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LIN28A-1405HFL)
Involved Pathway
LIN28A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LIN28A participated on our site, such as Cardiac Progenitor Differentiation,Developmental Biology,Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LIN28A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cardiac Progenitor Differentiation | LIN28B,IRX4,SIRPA,TBX20,ROR2,T,NOG,SOX1,NKX2,NIPAL1 |
| Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells | NR5A1,HIF3A,NR6A1,PRDM14,POU5F3,TDGF1,SALL4,FOXD3 |
| Developmental Biology | PEBP1,COL9A3,PEA15A,CDH4,EPHB3A,MED9,EFNB2,FOXD3,DRAP1,HIF3A |
Protein Function
LIN28A has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA binding,mRNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LIN28A itself. We selected most functions LIN28A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LIN28A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA binding | HNRNPAB,TYMS,DHFR,IGF2BP1,PIWIL2,G3BP1,HSP26,NXF3,MRPL13,LUC7L3 |
| miRNA binding | AGO3,TRIM71,TARBP2,AGO4,AGO2,MEF2C,DICER1,PNPT1,SOX2,RBM4 |
| zinc ion binding | ZFP276,LHX9,TRIM48,TRIM16,ZNF184,TIMM10,Alb,ESRRA,ZNF638,ENPP2 |
| RNA binding | EIF3BA,RTCD1,IGF2BP3,AHCYL1,RPL29,THOC2,KHDC3,ADAD2,NHP2L1A,EIF4EA |
| DNA binding | FANCM,ASCL1,CTC1,HDGFRP2,ZFP451,C3orf37,NR0B2A,ARNTL1A,ZFP536,ZBED6 |
| translation initiation factor binding | EIF3C,ZFP259,EIF3B,DDX3X,POLR2G,CELF1,POLR2D,LARP1,ZNF259,RPS24 |
| protein binding | RPL36AL,KRT79,ATXN7L3,APBB1IP,TAF6L,KIAA1143,PTCH1,ATP6V0A2,IL1R1,SELP |
Interacting Protein
LIN28A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LIN28A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LIN28A.
ZCCHC11;pre-let-7a;ZDHHC17
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References




