PDE4DIP
-
Official Full Name
phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene serves to anchor phosphodiesterase 4D to the Golgi/centrosome region of the cell. Defects in this gene may be a cause of myeloproliferative disorder (MBD) associated with eosinophilia. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. -
Synonyms
PDE4DIP;phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein;cardiomyopathy associated 2 , CMYA2;myomegalin;KIAA0454;KIAA0477;MMGL;Cardiomyopathy associated protein 2;CMYA2;OTTHUMP00000015720;OTTHUMP00000015721;OTTHUMP00000015722;OTTHUMP00000015723;OTTHUMP00000015724;OTTHUMP00000015725;OTTHUMP00000015726;OTTHUMP00000015727;OTTHUMP00000230044;OTTHUMP00000230074;OTTHUMP00000230075;OTTHUMP00000230076;OTTHUMP000002300
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDE4DIP-1602H | Recombinant Human PDE4DIP, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 1-310aa | |
| PDE4DIP-12557M | Recombinant Mouse PDE4DIP Protein | Mammalian Cells | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PDE4DIP-4333R | Recombinant Rat PDE4DIP Protein | Mammalian Cells | Rat | His |
|
|
| PDE4DIP-77H | Recombinant Human PDE4DIP protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 188aa(including fusion tag) |
|
| PDE4DIP-3349HCL | Recombinant Human PDE4DIP 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PDE4DIP-2566H | Recombinant Human PDE4DIP Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Met1-Ile177 |
|
| PDE4DIP-3993R | Recombinant Rat PDE4DIP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PDE4DIP-3993R-B | Recombinant Rat PDE4DIP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| PDE4DIP-6586M | Recombinant Mouse PDE4DIP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | Avi&Fc&His |
|
|
| PDE4DIP-6586M-B | Recombinant Mouse PDE4DIP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PDE4DIP protein?
PDE4DIP (phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. PDE4DIP is a protein that interacts with Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), an enzyme that controls the level of cAMP, a crucial second messenger in cellular signaling pathways. PDE4DIP is involved in various cellular processes, including the regulation of cardiac contractility, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi trafficking, Golgi/centrosome organization, and microtubule assembly. PDE4DIP is a centrosome/Golgi protein that is associated with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. PDE4DIP protein is consisted of 2346 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 265.1 kDa.
What is the function of PDE4DIP protein?
PDE4DIP interacts with Phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), an enzyme that controls the level of cAMP, a crucial second messenger in cellular signaling pathways. PDE4DIP has been reported to play a role in the regulation of cardiac contractility by affecting the phosphorylation of cMyBPC. PDE4DIP localizes to the centrosome and Golgi apparatus and binds directly to AKAP9, EB1/EB3, and FAM161A to form a functional complex. It affects endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi trafficking, Golgi/centrosome organization, and microtubule assembly. Related to PDE4DIP are GO annotations that include binding and enzyme binding, indicating its role in molecular functions within the cell.
PDE4DIP Related Signaling Pathway
There is a functional association between PDE4DIP and the neurofibrin 1(NF1) and RAS protein families. In colorectal cancer (CRC), PDE4DIP plays an important role in the growth of KRAS mutant CRC by promoting PKCε-mediated degradation of NF1. PDE4DIP is essential for the complete activation of the carcinogenic RAS/ERK/AKT signaling pathway. It maintains the activation state of RAS signaling pathway by inhibiting the expression of RasGAP neurofibrin (NF1). PDE4DIP induces structural activation of PKCε by promoting the reaggregation of PLCγ/PKCε into the Golgi apparatus, which triggers the degradation of NF1 and reactivates the RAS/ERK pathway. cAMP influences cell response to various stimuli through the regulation of anchoring proteins such as PDE4DIP.
PDE4DIP Related Diseases
The up-regulated expression of PDE4DIP in colorectal cancer is associated with poor prognosis in patients. It promotes growth and chemical resistance in colorectal cancer by modulating the NF1/RAS signaling axis. PDE4DIP is associated with cardiac function and the cAMP signaling pathway. Impaired PDE4DIP function due to inherited genetic mutations or acquired injuries has been associated with arrhythmia, heart failure, and pathological cardiac remodeling. The expression of PDE4DIP is associated with immune cell infiltration and immune-related genes. Mutations in the PDE4DIP gene have been found in non-small cell lung cancer, particularly in cases with pia meningeal metastasis. PDE4 is considered to be an important target for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders such as depression and memory and cognitive disorders.
Bioapplications of PDE4DIP
PDE4DIP has been linked to a variety of diseases, including some types of cancer. The recombinant PDE4DIP protein can be used in high-throughput screening experiments to identify small molecule drugs that can modulate its activity and thus develop new therapeutic approaches. PDE4DIP recombinant proteins can be used in immunological research, such as when studying how the immune system recognizes and responds to PDE4DIP-related diseases. Abnormal expression of PDE4DIP is associated with a variety of diseases, so recombinant PDE4DIP protein or its antibodies can be used as biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring of diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rulu Pan, 2023
Phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein (PDE4DIP) is a centrosome/Golgi protein associated with cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. PDE4DIP is commonly mutated in human cancers, and its alteration in mice leads to a predisposition to intestinal cancer. However, the biological function of PDE4DIP in human cancer remains obscure. Here, the researchers report for the first time the oncogenic role of PDE4DIP in colorectal cancer (CRC) growth and adaptive MEK inhibitor (MEKi) resistance. They show that the expression of PDE4DIP is upregulated in CRC tissues and associated with the clinical characteristics and poor prognosis of CRC patients. Knockdown of PDE4DIP impairs the growth of KRAS-mutant CRC cells by inhibiting the core RAS signaling pathway. PDE4DIP plays an essential role in the full activation of oncogenic RAS/ERK signaling by suppressing the expression of the RAS GTPase-activating protein (RasGAP) neurofibromin (NF1). Mechanistically, PDE4DIP promotes the recruitment of PLCγ/PKCε to the Golgi apparatus, leading to constitutive activation of PKCε, which triggers the degradation of NF1. Upregulation of PDE4DIP results in adaptive MEKi resistance in KRAS-mutant CRC by reactivating the RAS/ERK pathway.
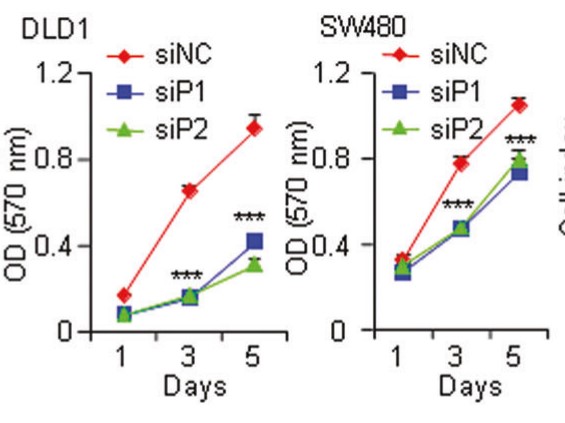
Fig1. MTT assay in control and PDE4DIP-silenced DLD1 and SW480 cells.
 attenuated PDE4DIP-promoted phosphorylation.jpg)
Fig2. Western blot showing that the RAS inhibitor FTS (salirasib) attenuated PDE4DIP-promoted ERK/AKT phosphorylation.
Case Study 2: Habib Bouguenina, 2017
Control of microtubule dynamics underlies several fundamental processes such as cell polarity, cell division, and cell motility. To gain insights into the mechanisms that control microtubule dynamics during cell motility, the researchers investigated the interactome of the microtubule plus-end-binding protein end-binding 1 (EB1). Via molecular mapping and cross-linking mass spectrometry they identified and characterized a large complex associating a specific isoform of myomegalin termed "SMYLE" (an isoform of PDE4DIP), the PKA scaffolding protein AKAP9, and the pericentrosomal protein CDK5RAP2. SMYLE was associated through an evolutionarily conserved N-terminal domain with AKAP9, which in turn was anchored at the centrosome via CDK5RAP2. SMYLE connected the pericentrosomal complex to the microtubule-nucleating complex (γ-TuRC) via Galectin-3-binding protein. SMYLE associated with nascent centrosomal microtubules to promote microtubule assembly and acetylation. Disruption of SMYLE interaction with EB1 or AKAP9 prevented microtubule nucleation and their stabilization at the leading edge of migrating cells. In addition, SMYLE depletion led to defective astral microtubules and abnormal orientation of the mitotic spindle and triggered G1 cell-cycle arrest, which might be due to defective centrosome integrity.
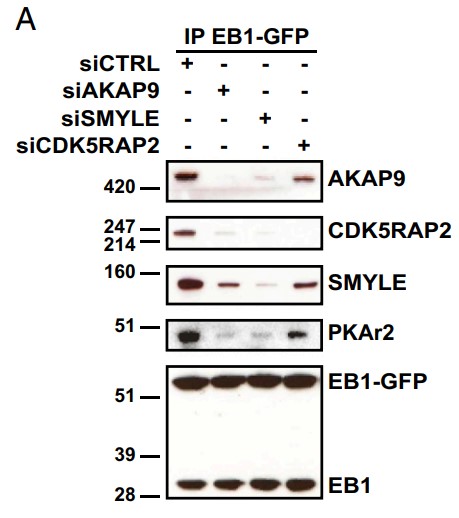
Fig3. AKAP9 and SMYLE mediate CDK5RAP2 binding to EB1.
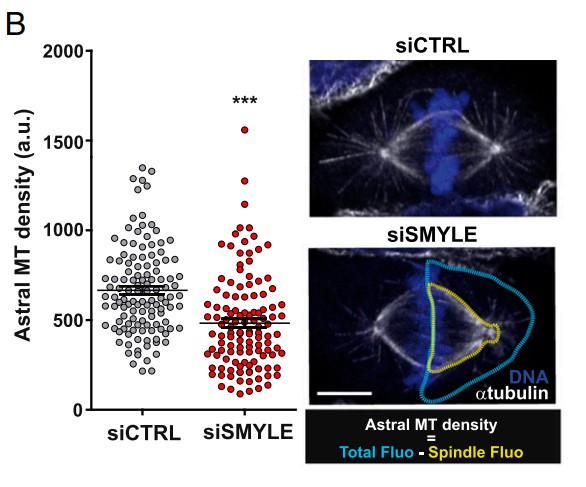
Fig4. Effect of SMYLE on HeLa cell astral MT density.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PDE4DIP-2566H)
Involved Pathway
PDE4DIP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PDE4DIP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PDE4DIP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
PDE4DIP has several biochemical functions, for example, enzyme binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PDE4DIP itself. We selected most functions PDE4DIP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PDE4DIP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| enzyme binding | XRCC1,GOT2,CYP3A4,UGT1A3,GSTM3,BACE1,CYP1A2,RPS2,HDAC10,PEX7 |
| protein binding | SYT17,MOBP,NCOA3,LTC4S,MRPL51,SF3A3,2610109H07Rik,FAM167A,CCDC25,RBM25 |
Interacting Protein
PDE4DIP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PDE4DIP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PDE4DIP.
MIF4GD;PRPF31;SDCBP;NAA10;LMO4;GOLGA8F;UTP14C
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



