Active Recombinant Human RAD51
| Cat.No. : | RAD51-1121H |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Properly controlled recombination between homologous DNA molecules (Homologous Recombination -HR) is essential for the maintenance of genome stability and for the prevention of tumorigenesis. Rad51 is a mammalian homologue of yeast RAD51 and bacterial RecA and, like its counterparts, plays a central role in HR. Rad51 coats ssDNA to form a nucleoprotein filament that invades and pairs with a homologous region in duplex DNA. It can then activate strand exchange to generate a crossover between the juxtaposed DNA molecules. In addition to Rad51, these steps require the coordinated action of a number of other homologous-recombination proteins, including the RP-A protein, which binds single-stranded DNA, Rad52, which can bind DNA ends, anneal complementary single-stranded DNA molecules and enhance the specificity of RAD51, and a number of Rad51 paralogs. The tumour-suppressor proteins BRCA1 and BRCA2 colocalize with RAD51 in DNA-damage-induced nulear foci. BRCA2 has been shown to interact directly with RAD51 and thus plays a direct role in repair by HR, through control of the availability and function of the central mediator, Rad51. Recombinant RAD51 was expressed in a strain of E.coli and purified by an affinity column in combination with FPLC chromatography. |
| Form : | Liquid. Supplied in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 100 mM KCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT and 20% glycerol. |
| Purity : | ≥95% by SDS-PAGE. |
| Application : | RAD51 has been applied in DNA and protein-protein interaction assays. |
| Activity : | 20 ng are sufficient for a DNA-protein assay and 100 ng are sufficient for a protein-protein interaction assay. |
| Usage : | For in vitro use only. |
| Storage : | Quality guaranteed for 12 months store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Gene Name | RAD51 RAD51 homolog (RecA homolog, E. coli) (S. cerevisiae) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | RAD51; RAD51 homolog (RecA homolog, E. coli) (S. cerevisiae); RECA; BRCC5; HRAD51; RAD51A; HsRad51; HsT16930; RAD51 homolog protein; RecA-like protein; RAD51D; recombination protein A; RecA, E. coli, homolog of DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1; BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex, subunit 5; RAD51L3; hRAD51; RAD51 (S. cerevisiae) homolog (E coli RecA homolog) |
| Gene ID | 5888 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_002875 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_002866 |
| MIM | 179617 |
| UniProt ID | Q06609 |
| Chromosome Location | 15q15 |
| Pathway | Homologous recombination; Pancreatic cancer; Pathways in cancer |
| Function | ATP binding; damaged DNA binding; double-stranded DNA binding; identical protein binding; nucleoside-triphosphatase activity; nucleotide binding; protein C-terminus binding; single-stranded DNA binding; single-stranded DNA-dependent ATPase activity |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| RAD1-02H | Recombinant Human RAD51 (G151D) Mutation Protein | +Inquiry |
| RAD51-6728C | Recombinant Chicken RAD51 | +Inquiry |
| RAD51-101H | Recombinant Huamn RAD51 Protein | +Inquiry |
| RAD51-02H | Recombinant Human RAD51 Protein, isoform 2 | +Inquiry |
| RAD51-29581TH | Recombinant Human RAD51 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| RAD51-286HKCL | Human RAD51 Knockdown Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| RAD51-2556HCL | Recombinant Human RAD51 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Efficient Zygotic Genome Editing via RAD51-Enhanced Interhomolog Repair
Journal: bioRxiv Data: 2018/8/6
Authors: Wilde Jonathan J., Aida Tomomi, Feng Guoping
Article Snippet:PrePrint: For experiments using wildtype recombinant proteins, the following proteins were used: RAD51 (Creative BioMart RAD51-134H), USP1/WDR48 (Creative BioMart USP1&WDR48-1067H), BCCIP (Origene TP303061), XRCC1 (TP304952), XRCC4 (Origene TP312684), DMC1 (Origene TP318311).For experiments using wildtype recombinant proteins, the following proteins were used: RAD51 (Creative BioMart RAD51-134H), USP1/WDR48 (Creative BioMart USP1&WDR48-1067H), BCCIP (Origene TP303061), XRCC1 (TP304952), XRCC4 (Origene TP312684), DMC1 (Origene TP318311).. For experiments using mutant RAD51, custom RAD51 preparations were produced by Creative BioMart according to their standard protocol for producing the wildtype RAD51 used in all other experiments.. DNA sequences used for cloning the mutant forms of Rad51 are described in Supplementary Table 2 .DNA sequences used for cloning the mutant forms of Rad51 are described in Supplementary Table 2 .
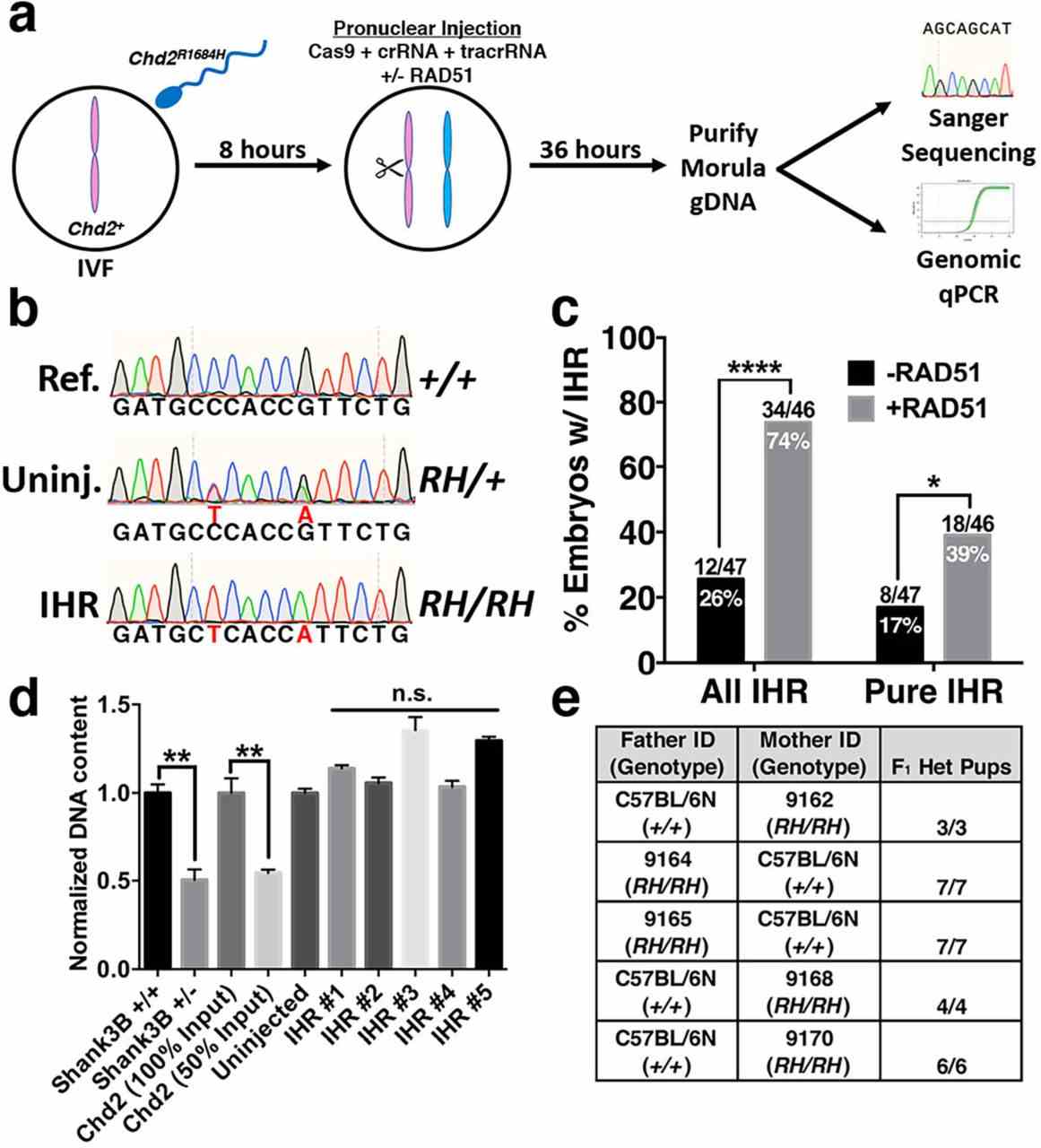
a, Schematic of strategy for testing
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All RAD51 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All RAD51 Products
Required fields are marked with *



