CaM Kinases
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About CaM Kinases
Calmodulin-dependent kinases (CaM kinases) represent a group of serine/threonine protein kinases that are activated by the calcium-bound form of the protein calmodulin. The family of CaM kinases includes several members, such as CaMKI, CaMKII, CaMKIII, and CaMKIV. These kinases share a conserved catalytic domain and contain regulatory domains that are responsible for their calcium/calmodulin-dependent activation.
Ca2+/CaM-stimulated protein kinases are classified according to their substrate specificity. One group is the multifunctional CaM kinases (CaMKK, CaMKI, CaMKII, and CaMKIV), which each have multiple downstream targets, and the other group is the substrate-specific CaM kinases (CaMKIII, phosphorylase kinase (PhK), and myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK)), which have only one known downstream target.
These kinases play crucial roles in calcium-dependent signaling pathways and are involved in various cellular processes, including neuronal function, muscle contraction, gene expression, and cell survival. Understanding the nuances of CaM kinases is essential for unraveling their diverse roles in cellular physiology and their potential implications in diseases.
Mechanism of Action of CaM Kinases
The activation of CaM kinases involves complex regulatory mechanisms. CaMKK and CaMKIV localize both to the nucleus and to the cytoplasm, whereas CaMKI is only cytosolic. Upon an increase in intracellular calcium concentration, calmodulin binds to calcium ions and undergoes a conformational change. The calcium-calmodulin complex then associates with the regulatory domain of CaM kinases, leading to their activation. The activated CaM kinases phosphorylate downstream targets, including proteins involved in transcriptional regulation, ion channel activity, synaptic plasticity, and cell survival.
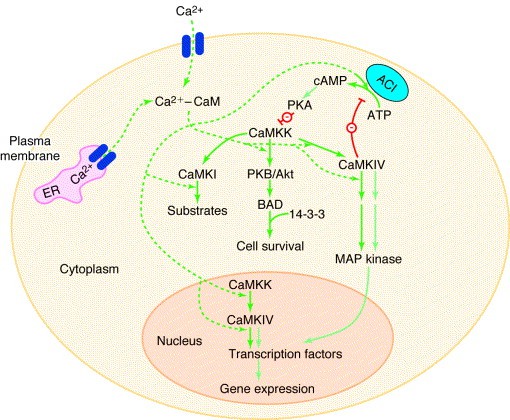 Fig.1 The Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascade. (Thomas R Soderling, 1999)
Fig.1 The Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascade. (Thomas R Soderling, 1999)
Functions of CaM Kinases
CaM kinases play diverse roles in cellular signaling and are involved in various physiological and pathological processes. Here are some examples of their functions:
- Neuronal Function and Synaptic Plasticity
CaM kinases, particularly CaMKII, are critical for neuronal function and synaptic plasticity. They regulate the activity of ion channels and neurotransmitter receptors, modulate synaptic strength, and contribute to the formation and maintenance of long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). CaM kinases also participate in neuronal development, dendritic growth, and axonal guidance.
- Muscle Contraction and Calcium Homeostasis
CaM kinases are involved in regulating muscle contraction and calcium homeostasis. They phosphorylate and modulate the activity of proteins involved in excitation-contraction coupling and calcium handling in muscle cells. CaM kinases also play a role in regulating smooth muscle contraction, cardiac function, and skeletal muscle development.
- Gene Expression and Transcriptional Regulation
CaM kinases participate in the regulation of gene expression and transcriptional processes. They phosphorylate and modulate the activity of transcription factors, co-activators, and chromatin remodeling proteins, influencing the transcription of specific genes. CaM kinases are involved in neuronal gene expression, synaptic plasticity-associated gene regulation, and cellular responses to calcium signaling.
- Cell Survival and Apoptosis
CaM kinases contribute to cell survival and apoptosis regulation. They phosphorylate and regulate the activity of proteins involved in cell survival pathways, including the Bcl-2 family members, cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB), and transcription factors involved in anti-apoptotic gene expression. Dysregulation of CaM kinase signaling can impact cell survival and contribute to various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and cancer.
Available Resources for CaM Kinases
Understanding the specific functions and regulation of CaM kinases is crucial for unraveling the complexities of calcium-dependent signaling pathways and their implications in cellular processes. At Creative BioMart, we offer a comprehensive range of research tools and services to support studies related to CaM kinases, including recombinant proteins, antibodies, and custom assay development. The following CaM kinases are displayed, click to view all related molecules/targets and research reagents. Please feel free to contact us with any questions or requests.
References:
- Soderling, Thomas R. "The Ca2+–calmodulin-dependent protein kinase cascade." Trends in biochemical sciences 24.6 (1999): 232-236.
- Swulius MT, Waxham MN. Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65(17):2637-2657.

