PDGF Receptor
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for PDGF Receptor Research
At Creative BioMart, we are dedicated to offering a wide range of products associated with the PDGF receptor, each chosen with care. Our selection includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, and cell and tissue lysates, providing researchers with the necessary tools to advance their studies effectively. Moreover, we understand that every research project is unique, and therefore, we offer customizable services to ensure that you receive the most suitable product tailored to your specific needs.
In addition to our extensive product portfolio, we are committed to providing an abundance of information about the PDGF receptor. Our resources cover various essential aspects, including pathways involved, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other pertinent topics. By offering these comprehensive resources, we aim to serve as a valuable reference, empowering researchers to deepen their understanding of the PDGF receptor and its critical role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDGFRA-1612H | Recombinant Human PDGFRA, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| PDGFRA-825HAF647 | Recombinant Human PDGFRA Protein, DDDDK-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | Human | HEK293 | DDDDK |
| Pdgfra-51RAF555 | Recombinant Rat Pdgfra Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | Fc |
| PDGFRB-2187H | Active Recombinant Human PDGFRB protein(Met1-Lys531), His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | C-His |
| Pdgfrb-8786RF | Recombinant Rat Pdgfrb Protein, His-tagged, FITC conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | His |
| PDGFRB-1208RAF647 | Recombinant Monkey PDGFRB Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | Monkey | HEK293 | Fc |
| PDGFRL-2899H | Recombinant Human PDGFRL protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
About PDGF Receptor
The PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) receptor is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. It consists of two main isoforms: PDGFR-α (alpha) and PDGFR-β (beta). Both isoforms have similar structures and share some overlapping functions, but they also have distinct roles in various biological processes.
Function
The PDGF receptor plays a crucial role in cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. Upon binding to its ligands, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, or PDGF-DD, the receptor undergoes dimerization and autophosphorylation, activating its intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. This activation initiates downstream signaling pathways, including the Ras-MAPK, PI3K-Akt, and PLCγ pathways, which regulate cellular processes such as cell survival, migration, and proliferation.
The PDGF receptor is involved in various physiological and pathological processes. During embryonic development, it contributes to organogenesis and tissue morphogenesis. In adulthood, it plays a role in tissue repair, wound healing, and maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Aberrant activation or dysregulation of PDGF receptors can lead to pathological conditions, including cancer, fibrosis, and vascular disorders.
Structure
The PDGF receptor is a transmembrane protein with an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a single transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain that possesses tyrosine kinase activity. The extracellular domain consists of five immunoglobulin-like domains and is responsible for ligand binding. The intracellular domain contains the tyrosine kinase region, which becomes activated upon ligand binding and autophosphorylation.
Expression Pattern
The expression pattern of PDGF receptors varies depending on the isoform and the tissue or cell type. PDGFR-α is predominantly expressed on mesenchymal cells, including fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, pericytes, and certain types of glial cells. It is also found in specific cell populations during embryonic development.
PDGFR-β is expressed on cells of mesenchymal and hematopoietic origin, such as fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, pericytes, osteoblasts, and certain types of immune cells, including macrophages and mast cells. PDGFR-β is also expressed in certain cell populations during embryonic development, particularly in the developing vascular system.
The expression of PDGF receptors can be regulated by various factors, including growth factors, cytokines, and extracellular matrix components. The precise expression pattern and regulation of PDGF receptors in different tissues and cell types contribute to their diverse functions in various physiological and pathological contexts.
In summary, the PDGF receptor is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a critical role in cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation. It consists of two main isoforms, PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β, with distinct expression patterns and functions. Understanding the structure, function, and expression pattern of PDGF receptors is important for elucidating their roles in normal development, tissue homeostasis, and disease processes.
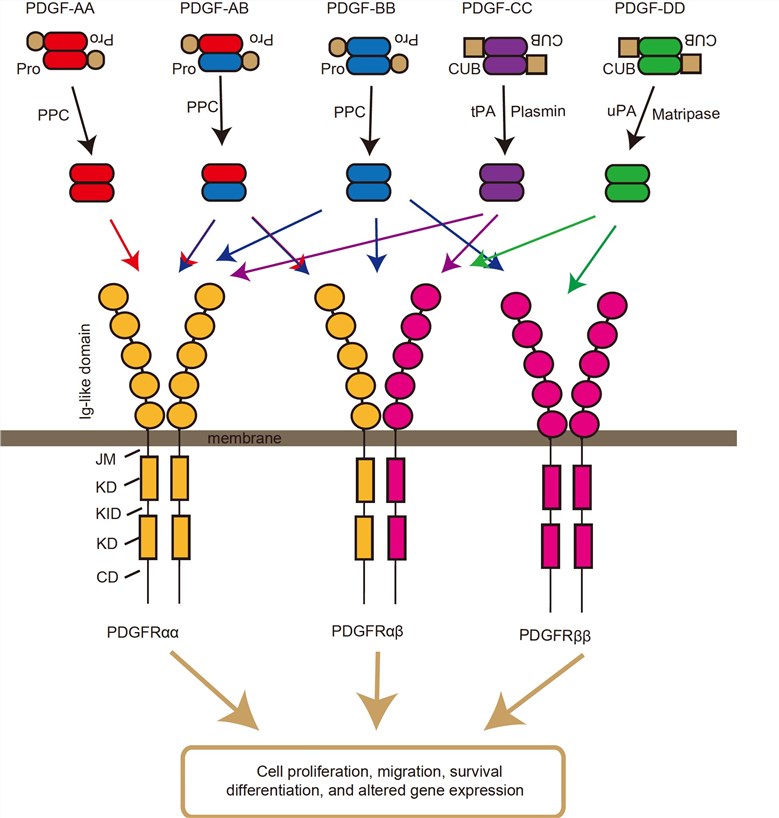 Fig.1 The signaling pathway of PDGF and PDGFR. (Wang M M, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 The signaling pathway of PDGF and PDGFR. (Wang M M, et al., 2019)
Physiological Functions of PDGF Receptor
The activation of PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) receptors initiates a complex network of signaling pathways that regulate various cellular processes. Here are some key signaling pathways and regulators associated with PDGF receptor signaling:
Signaling Pathways of PDGF Receptor
- Ras-MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) Pathway: Upon PDGF receptor activation, the receptor recruits and activates the small GTPase Ras. This leads to the activation of a cascade of protein kinases, including Raf, MEK (MAPK/ERK kinase), and ERK (Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase). Ultimately, the Ras-MAPK pathway regulates gene expression, cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation.
- PI3K-Akt (Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Akt) Pathway: PDGF receptor activation also leads to the recruitment and activation of PI3K. This results in the generation of phosphoinositide lipids, which in turn activate the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Akt regulates various downstream targets involved in cell survival, growth, and metabolism.
- PLCγ (Phospholipase C-gamma) Pathway: PDGF receptor activation triggers the activation of PLCγ, which cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into inositol trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). IP3 induces the release of calcium from intracellular stores, while DAG activates protein kinase C (PKC). These events regulate diverse cellular processes, including proliferation, migration, and cytoskeletal rearrangement.
Regulators of PDGF Receptor
- STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) Pathway: PDGF receptor activation can also lead to the activation of STAT proteins. STATs are transcription factors that, upon phosphorylation, translocate to the nucleus and regulate the expression of target genes. STAT signaling is involved in cell proliferation, survival, and immune responses.
- SHP-2 (Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 2): SHP-2 is a phosphatase that interacts with PDGF receptors and acts as a positive regulator of PDGF receptor signaling. It promotes the activation of downstream signaling pathways such as Ras-MAPK and PI3K-Akt, thereby enhancing cellular responses to PDGF stimulation.
- Grb2 (Growth Factor Receptor-Bound Protein 2): Grb2 is an adaptor protein that links the activated PDGF receptor to the Ras-MAPK pathway. It binds to phosphorylated tyrosine residues on the receptor, recruiting and activating the guanine nucleotide exchange factor SOS (Son of Sevenless), which facilitates Ras activation.
- Cbl (Casitas B-Lineage Lymphoma): Cbl is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that negatively regulates PDGF receptor signaling. It promotes receptor internalization and degradation, attenuating downstream signaling events. Cbl also interacts with other signaling molecules, such as the adapter protein Crk, to modulate cellular responses.
These are just a few examples of the signaling pathways and regulators involved in PDGF receptor signaling. The activation and modulation of these pathways contribute to the regulation of cell growth, survival, proliferation, migration, and other cellular responses to PDGF stimulation. The precise signaling outcomes depend on the context and cell type, as well as the interplay between different signaling pathways and regulators.
Aberrant activation of PDGF receptors and dysregulated signaling have been implicated in several diseases, including cancer, fibrosis, and vascular disorders. Mutations or overexpression of PDGF receptors can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and contribute to the development and progression of various cancers. Therefore, PDGF receptors have become attractive targets for therapeutic interventions, and several drugs targeting PDGF receptors have been developed for the treatment of certain cancers and fibrotic diseases.
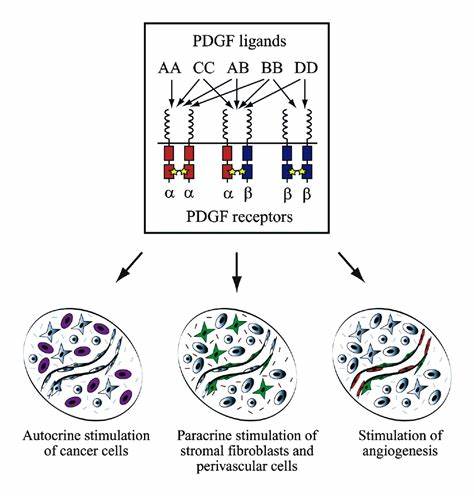 Fig.2 The PDGF system is involved in multiple tumor-associated processes. (Pietras K, et al., 2003)
Fig.2 The PDGF system is involved in multiple tumor-associated processes. (Pietras K, et al., 2003)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Pietras K, Sjöblom T, Rubin K, et al. PDGF receptors as cancer drug targets[J]. Cancer Cell, 2003, 3(5): 439-443.
- Zou X, Tang X Y, Qu Z Y, et al. Targeting the PDGF/PDGFR signaling pathway for cancer therapy: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 202: 539-557.
- Wang M M, Qin X H, Lizhi M I. The structural and functional studies of the PDGF receptors[J].SCIENTIA SINICA Vitae, 2019, 49(6):683-697. DOI:10.1360/N052018-00242.

