TGF-beta Family Modulator
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for TGF-beta Family Modulator Research
At Creative BioMart, we are pleased to offer a wide range of products associated with the TGF-beta family modulator. Our extensive selection includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, and cell and tissue lysates, enabling researchers to access the necessary tools to advance their studies. Additionally, our customizable services are specifically designed to address your unique requirements, ensuring you receive the most suitable product for your specific needs.
In conjunction with our comprehensive product portfolio, we provide an abundance of information on the TGF-beta family modulator. Our resources encompass various aspects, including involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources serve as invaluable references, empowering researchers to deepen their understanding of the TGF-beta family modulator and its significant role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMAD1-2799H | Recombinant Human SMAD1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| SMAD5-2800H | Recombinant Human SMAD5, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About TGF-beta Family Modulator
The TGF-beta (Transforming Growth Factor-beta) family modulators are a group of proteins that regulate the activity and signaling of TGF-beta ligands within the TGF-beta superfamily. These modulators can enhance or inhibit TGF-beta signaling, fine-tuning the cellular responses to TGF-beta ligands. Here's an introduction to TGF-beta family modulators:
Activators/Enhancers
- TGF-beta family activators/enhancers are proteins that promote the activation or signaling of TGF-beta ligands.
- One example is the TGF-beta Binding Protein-Like (TBPL) family, which includes proteins like fibrillins and latent TGF-beta binding proteins (LTBPs). These proteins interact with TGF-beta ligands and facilitate their activation or release from latent complexes.
- Another example is the R-Spondin (RSPO) family, which enhances TGF-beta signaling by binding to the E3 ubiquitin ligases that target TGF-beta receptors for degradation, thereby stabilizing the receptors and prolonging their signaling activity.
Inhibitors/Suppressors
- TGF-beta family inhibitors/suppressors are proteins that negatively regulate TGF-beta signaling, preventing excessive or aberrant TGF-beta pathway activation.
- One prominent group of inhibitors is the Smad7 protein, which directly interacts with TGF-beta receptors and prevents the phosphorylation and activation of downstream Smad proteins, thereby suppressing TGF-beta signaling.
- Other examples include inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), such as Smad6 and Smad7, which competitively bind to type I receptors and prevent the activation of downstream signaling pathways.
- Additional inhibitors include extracellular proteins like follistatin and gremlin, which bind to TGF-beta ligands and prevent their interaction with receptors.
Co-receptors/Co-factors
- TGF-beta family co-receptors/co-factors are proteins that interact with TGF-beta ligands and receptors, modulating the binding and signaling of TGF-beta ligands.
- One example is the betaglycan (also known as TGF-beta type III receptor), which acts as a co-receptor for various TGF-beta ligands, enhancing their binding to type II receptors and promoting TGF-beta signaling.
- Other co-receptors/co-factors, like endoglin and Cripto-1, also modulate TGF-beta signaling by interacting with TGF-beta ligands or receptors.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Components
- The extracellular matrix, which surrounds cells, can also modulate TGF-beta signaling.
- Components of the ECM, such as heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) and integrins, can interact with TGF-beta ligands, receptors, and modulators, influencing the availability, presentation, and activation of TGF-beta ligands.
TGF-beta family modulators are crucial for controlling the intensity, duration, and specificity of TGF-beta signaling. They fine-tune the cellular responses to TGF-beta ligands and play essential roles in various biological processes, including development, tissue homeostasis, immune response, and disease pathogenesis. Dysregulation of TGF-beta modulators can disrupt normal TGF-beta signaling, contributing to various diseases, such as cancer, fibrosis, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases.
Studying the functions and mechanisms of TGF-beta family modulators provides insights into the intricate regulation of TGF-beta signaling and offers potential targets for therapeutic interventions in diseases associated with dysregulated TGF-beta signaling.
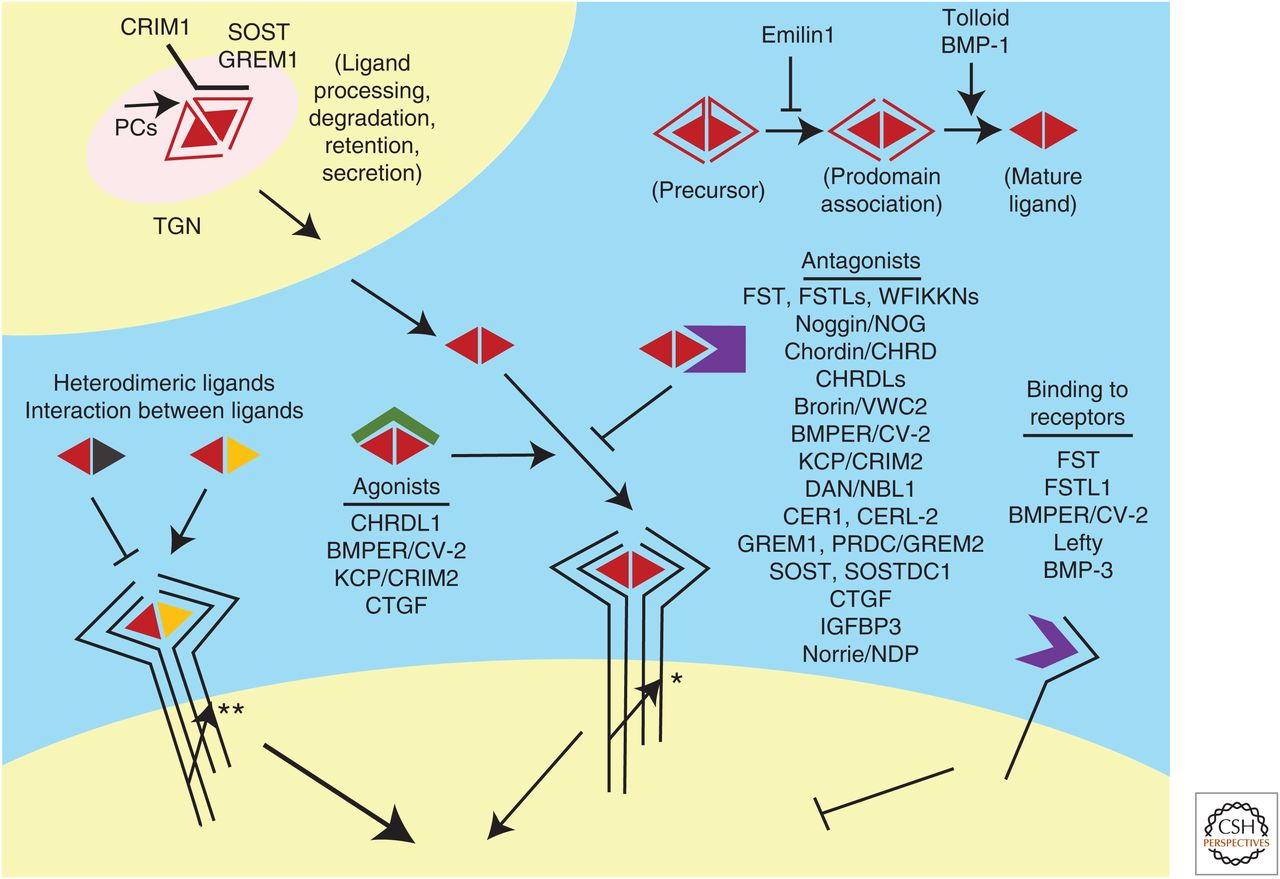 Fig.1 Regulation of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family signals by extracellular agonists and antagonists. (Chang C, 2016)
Fig.1 Regulation of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) family signals by extracellular agonists and antagonists. (Chang C, 2016)
TGF-beta Family Regulators in Various Biological Processes
The TGF-beta family regulators play diverse roles in numerous biological processes. These regulators control the activity and signaling of TGF-beta ligands within the TGF-beta superfamily, thereby influencing various cellular and physiological processes. Here are some examples of TGF-beta family regulators and their roles in different biological processes:
Development and Morphogenesis
TGF-beta family regulators are essential for embryonic development and tissue morphogenesis.
- Nodal, a member of the TGF-beta superfamily, acts as a morphogen during embryonic patterning and axis formation.
- Chordin and Noggin are secreted proteins that bind to TGF-beta superfamily ligands and inhibit their signaling. They play critical roles in neural tube development and dorsal-ventral patterning of the embryo.
- Lefty proteins, including Lefty1 and Lefty2, are antagonists of Nodal signaling and are involved in left-right axis specification during embryonic development.
Cell Proliferation and Differentiation
TGF-beta family regulators are involved in regulating cell proliferation and differentiation processes.
- Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) are a subgroup of the TGF-beta superfamily that play key roles in promoting osteogenesis and bone development.
- Activins and Inhibins are involved in regulating cell differentiation and growth in various tissues, including the nervous system, reproductive system, and immune system.
- Growth and Differentiation Factors (GDFs) are also involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue development.
Immune Response and Inflammation
TGF-beta family regulators play important roles in immune regulation and inflammation.
- TGF-beta itself is a potent immunosuppressive cytokine that regulates immune cell function, promotes regulatory T cell differentiation, and suppresses immune responses.
- The Activin/TGF-beta signaling pathway is involved in regulating immune cell development, function, and inflammation.
- Inflammatory cytokines, such as Interleukin-1 (IL-1), can induce the expression of TGF-beta family regulators, including TGF-beta itself, to modulate the immune response.
Wound Healing and Tissue Repair
TGF-beta family regulators play critical roles in wound healing and tissue repair processes.
- TGF-beta signaling is involved in promoting the migration, proliferation, and differentiation of various cell types, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, during wound healing.
- Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) is a downstream target of TGF-beta signaling and is involved in fibroblast activation, extracellular matrix production, and tissue remodeling during wound healing.
Tissue Homeostasis and Regeneration
TGF-beta family regulators are involved in maintaining tissue homeostasis and regulating tissue regeneration.
- During tissue injury or damage, TGF-beta signaling is activated to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
- TGF-beta regulates the balance between stem cell self-renewal and differentiation in various tissues, such as the intestine, skin, and liver.
These examples highlight the diverse roles of TGF-beta family regulators in different biological processes. By modulating the activity and signaling of TGF-beta ligands, these regulators contribute to the regulation of development, cell proliferation and differentiation, immune response and inflammation, wound healing, tissue homeostasis, and tissue regeneration. Understanding the functions of TGF-beta family regulators is crucial for unraveling the complex biology of TGF-beta signaling and its implications in health and disease.
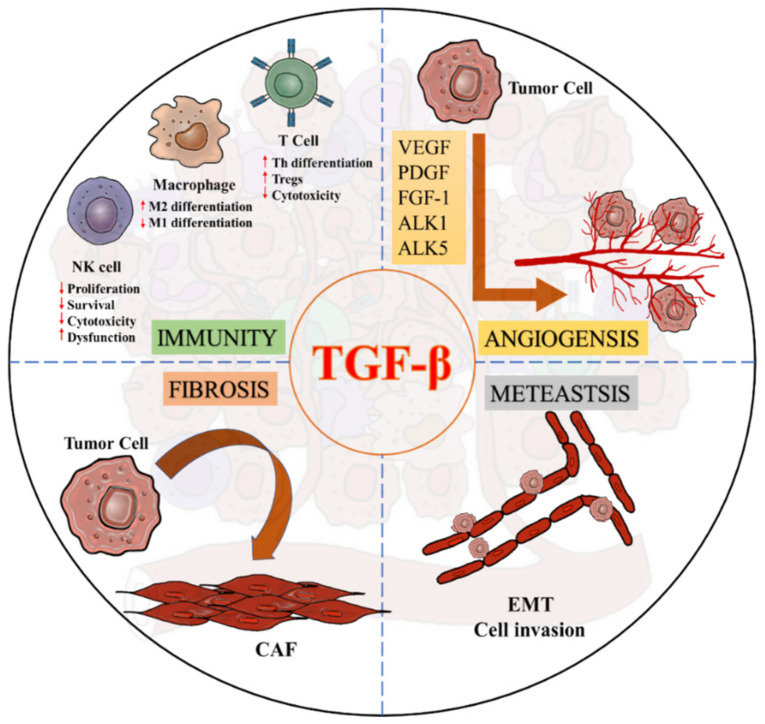 Fig.2 Diverse roles of TGF-β signaling in a pro-tumoral TME. (Chung JY, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Diverse roles of TGF-β signaling in a pro-tumoral TME. (Chung JY, et al., 2021)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Chung JY, Chan MK, Li JS, et al. TGF-β signaling: from tissue fibrosis to tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7575. Published 2021 Jul 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22147575
- Chang C. Agonists and antagonists of TGF-β family ligands[J]. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 2016, 8(8): a021923.

