SMAD1
-
Official Full Name
SMAD family member 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene mothers against decapentaplegic (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein mediates the signals of the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are involved in a range of biological activities including cell growth, apoptosis, morphogenesis, development and immune responses. In response to BMP ligands, this protein can be phosphorylated and activated by the BMP receptor kinase. The phosphorylated form of this protein forms a complex with SMAD4, which is important for its function in the transcription regulation. This protein is a target for SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin ligases, such as SMURF1 and SMURF2, and undergoes ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
SMAD1;SMAD family member 1;BSP1;JV41;BSP-1;JV4-1;MADH1;MADR1;mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1;MAD homolog 1;Mad-related protein 1;TGF-beta signaling protein 1;mothers against DPP homolog 1;SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 1;MAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1;transforming growth factor-beta signaling protein 1;transforming growth factor-beta-signaling protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Cattle
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- GST
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is SMAD1 protein
Short for 'Small Mothers Against Decapentaplegic', SMAD1 belongs to a family of similar proteins that play key roles within the body, primarily in signal transduction.Firstly, let's look at the SMAD1 protein itself. SMAD1 was discovered as part of a group of homologous proteins known colloquially as SMADs in the 1990s. The name 'SMAD' is a portmanteau; it is a combination of two previously discovered proteins - the Caenorhabditis elegans protein 'Sma' and the Drosophila protein 'Mothers Against Decapentaplegic (Mad)'.
The background of the SMAD proteins spans back to genetic studies in the fruit fly and nematodes. In these organisms, important developmental pathways, controlled by the TGFβ signaling pathway, were understood for the first time. Mutations in this pathway in the nematode led to 'small' phenotypes, while in the fly they led to disruptions in embryogenesis. Thus, Sma and Mad together became SMAD - the name for a family of proteins that carry signals from the TGFβ receptors on the cell surface to the nucleus.
The SMAD1 gene is located on the human chromosome 4q31.21. It is an intronless gene that encodes a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-specific SMADs, a subgroup within the broader SMAD family.
Structurally, SMAD1 protein, like all SMAD proteins, comprises two primary domains: the MH1 (Mad homology 1) domain and the MH2 domain. The MH1 domain at the N-terminus binds to DNA, while the MH2 domain at the C-terminus possesses the most diversity amongst the SMAD proteins and has a critical role in the propagation of receptor-specific signals.
What are the functions of SMAD1 protein?
Now that we have an understanding of what SMAD1 protein is, let's look at its functions. As mentioned earlier, SMAD1, like all SMAD proteins, plays a key role in signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus in response to BMP. This process impacts cell growth, cell differentiation, apoptosis and morphogenesis, and therefore can influence many biological processes such as embryonic development and tissue homeostasis.
The SMAD1 protein is activated via phosphorylation by bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type-I receptors. Once activated, SMAD1 forms a complex with another activated SMAD1 molecule, or with the similar SMAD5 or SMAD8 molecules, as well as the common SMAD4 molecule. This complex is transported into the nucleus where it functions as a transcriptional regulator of BMP-responsive genes.
SMAD1 protein related diseases
In regard to related diseases, there are several pathological conditions where the dysregulation or disruption of SMAD1 signaling has been implicated. Among them are certain types of cancers, fibrosis, and developmental disorders. In various cancers, SMAD1 pathways can be disrupted or inactivated, either through mutations or epigenetic modifications, thereby contributing to cancer growth, progression, and resistance to therapy. On the other hand, recent studies show that high levels of SMAD1 may promote fibrosis, a condition marked by the uncontrolled formation of excess fibrous connective tissue.
Osteoporosis: Mutations reducing SMAD1 activity impair BMP signaling, leading to decreased bone mineral density and increased fracture risk.
Osteopenia: Heterozygous SMAD1 mutations have been linked to low bone mass disorders like osteopenia.
Craniosynostosis: Mutations cause premature fusion of skull bones by disrupting BMP-driven intramembranous bone formation.
SMAD1 protein's application
From a medical perspective, the understanding of the SMAD1 protein has proved to be rather insightful. The SMAD1 protein's central role in signal transduction has made it an attractive target for potential therapeutic approaches in genetic or developmental disorders and certain types of cancers. Scientists, carrying out specialized research in oncology, cell biology, and immunology, frequently utilize SMAD1 protein to understand disease mechanisms, discover potential drug targets, and develop treatment strategies.
Research into the development of pharmacological inhibitors and agonists of the SMAD/BMP signaling pathway is increasing. These drugs aim to manipulate SMAD1 signaling to correct pathological imbalances in cells and tissues. SMAD1 is therefore an intriguing protein, with the future potential for targeted therapeutics and drug discovery efforts.
- Bone tissue engineering: Overexpressing SMAD1 can help promote osteoblast differentiation of stem cells for bone grafts/implants.
- Fracture healing: Modulating SMAD1 activity may enhance endogenous BMP signaling and accelerate fracture repair.
- Osteoporosis treatment: Drugs that selectively activate SMAD1 could help increase bone density in osteoporosis patients.
- Dental regeneration: Similar approach may help regeneration of dentin-pulp complex or enamel via precise BMP-SMAD1 stimulation.
Case Study
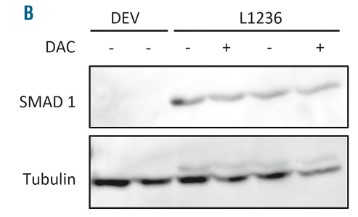
(Magdalena M, 2021)
Fig2. SMAD1 expression at the protein level after no treatment (-) or treatment with 1 mM decitabine (+) for 96 h of two HL cell lines as determined by western blotting. Results from two independent experiments are exemplified. Decitabine-treated samples of the DEV cell line are not shown because of lack of protein after demethylating treatment.
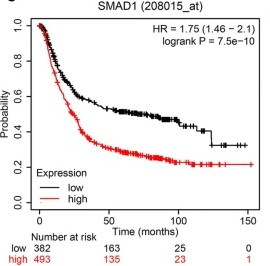
(Wanjing Chen, 2022)
Fig3. Correlation between SMAD1 expression and the survival of patients with GC according to data in TCGA-STAD
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: SMAD1-656C)
Involved Pathway
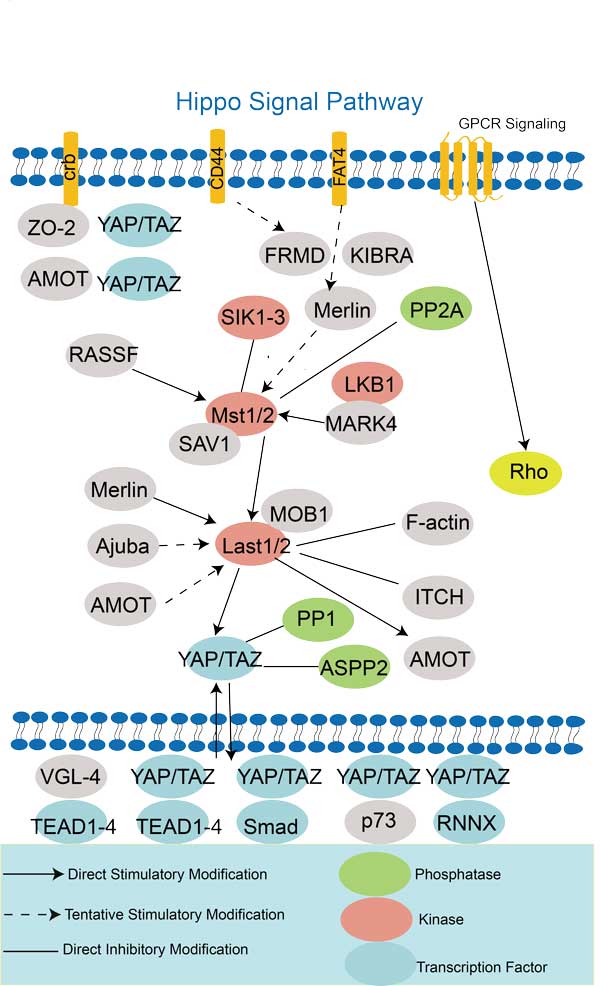
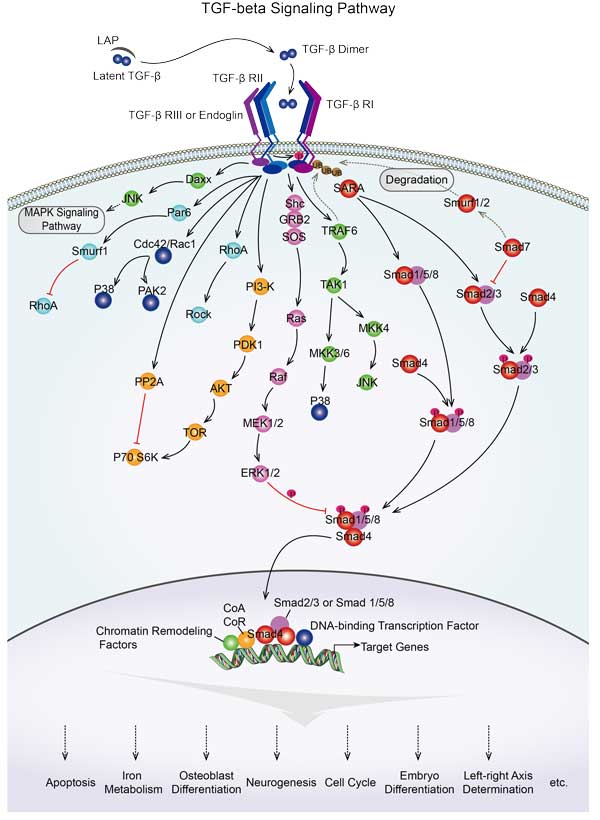
SMAD1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SMAD1 participated on our site, such as TGF-beta signaling pathway,Hippo signaling pathway,Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SMAD1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | MAP2K1,BMP4,STAT3,GSK3B,ZFHX3,Fzd4,ID3,ISL1,FGFR4,WNT16 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | PROM1,FUS,LDB1,MET,PFTK1,PTK2,MEIS1,RUNX1T1,HIST1H3G,HIST2H3A |
| Hippo signaling pathway | CDH1,FZD3,ACTG1,Fzd4,PPP2R1A,ITGB2,BMP8B,FZD5,GDF7,SOX2 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | TGFBR1A,THBS1,ACVR1L,AMHR2,BAMBIB,PPP2R1A,BMP8A,RPS6KB1,AMH,ACVR2AA |
Protein Function
SMAD1 has several biochemical functions, for example, I-SMAD binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SMAD1 itself. We selected most functions SMAD1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SMAD1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | TAL1,TCF7L2,HNF4A,SOX8,HOXB3,GATA6,TP53,GATA1,HEYL,SP3 |
| identical protein binding | SMAD6,NLRC4,ST13,ASMT,PTPRG,ESYT2,GSTM3,LZTFL1,JMJD6,ZNF3 |
| I-SMAD binding | SMAD4,TGFBR1,CTNNB1,AXIN2,TGFB1I1,SMAD2,SMAD7,SMURF1,AXIN1,SMAD6 |
| metal ion binding | DPF2L,ZFP326,ZFP27,ZNF26,YME1L1,HERC2,NANOS1,NRP1B,RSAD1,ZFP12 |
| protein kinase binding | PTPN23,BCL2L1,JIP1,EEF2,TNIP2,ACTA2,CAV1,ELAVL1,TNNI3,BCAR1 |
| co-SMAD binding | TRIM33,FOXH1,TGIF1,SMAD3,CITED1,USP9X,SMAD2,SMAD6,GATA4 |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | NR4A3,ONECUT2,PGR,PATZ1,GCM1,TCF4,ETV4,ETV2,PITX1,DBP |
| protein heterodimerization activity | TCF12,IKBKG,UGT1A9,SNX5,BAXB,TGFB1,PPP1CBL,HIST1H2AL,TAP1,ATF1 |
| protein binding | CFI,LYVE1,C1QBP,SERPINB5,C21orf2,FSD2,FGB,P2RX4,TTR,PRCP |
Interacting Protein
SMAD1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SMAD1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SMAD1.
SMAD4;GSK3B;AR
SMAD1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kaneko, K; Higuchi, C; et al. Hyaluronan inhibits BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation. FEBS LETTERS 589:447-454(2015).
- Xu, LL; Liu, Y; et al. U0126 promotes osteogenesis of rat bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by activating BMP/Smad signaling pathway. CELL AND TISSUE RESEARCH 359:537-545(2015).