Fungal Toxin Test Service
Background on Fungal Toxins and Their Risk in Food Products
Fungal toxins, commonly referred to as mycotoxins, are toxic secondary metabolites produced by certain species of fungi, notably Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium. These contaminants thrive in food and medicinal raw materials, particularly under warm and humid conditions. Often invisible to the naked eye, mycotoxins can be present even in trace amounts, yet still pose significant health risks to humans—including liver toxicity, immunosuppression, and carcinogenic effects.
The history of mycotoxin poisoning dates back to medieval Europe, marking its recognition as a longstanding public health concern. To date, scientists have identified and classified over 2,000 different types of fungal toxins, based on their chemical structures and biological effects.

Figure 1. Examples of mycotoxins. (a) Grapefruit infected with green mold (Penicillium digitatum). (b) A severe case of powdery mildew on a zinnia. (c) A barley infected with stem rust. (d) Muscodor albus fungi produces chemicals that inhibit the growth of grey mold on table grapes.
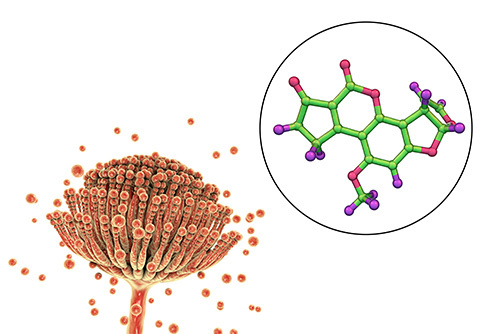
Figure 2. Fungi Aspergillusproducing Aflatoxin B1.
Mycotoxin contamination typically results from improper storage conditions, such as elevated moisture and inadequate ventilation, which facilitate fungal growth. Contaminated products may appear outwardly unaffected, yet the presence of toxins can lead to the spoilage of agricultural commodities, diseases in grain crops, and serious health threats to both humans and animals. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), more than 25% of global food production is contaminated with mycotoxins, leading to economic losses estimated in the billions of U.S. dollars annually.
One of the most significant fungal toxins is aflatoxin, a secondary metabolite produced by Aspergillus flavus. Aflatoxin is commonly found in grains, nuts, spices, and dried fruits. To date, more than 20 types of aflatoxin variants have been identified, with B1, B2, G1, G2, M1, and M2 being the most prevalent. Aflatoxin can cause acute hepatitis, hemorrhagic necrotic hepatitis, bile duct proliferation, and cirrhosis. Other fungal toxins, such as T-2 toxin and zearalenone, can also severely damage human organs and the immune system.
Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive list of Fungal Toxin Test Services that can detect trace amount of fungal toxin accurately. Our services include five major aflatoxin variants (B1, B2, G1, G2, and M1) and some other common fungal toxins.
Explore Our Fungal Toxin Test Service
Service Procedure

Targeted Mycotoxins We Analyze
We offer a full spectrum of Fungal Toxin Test Service tailored to meet your study design and regulatory goals, including:
-
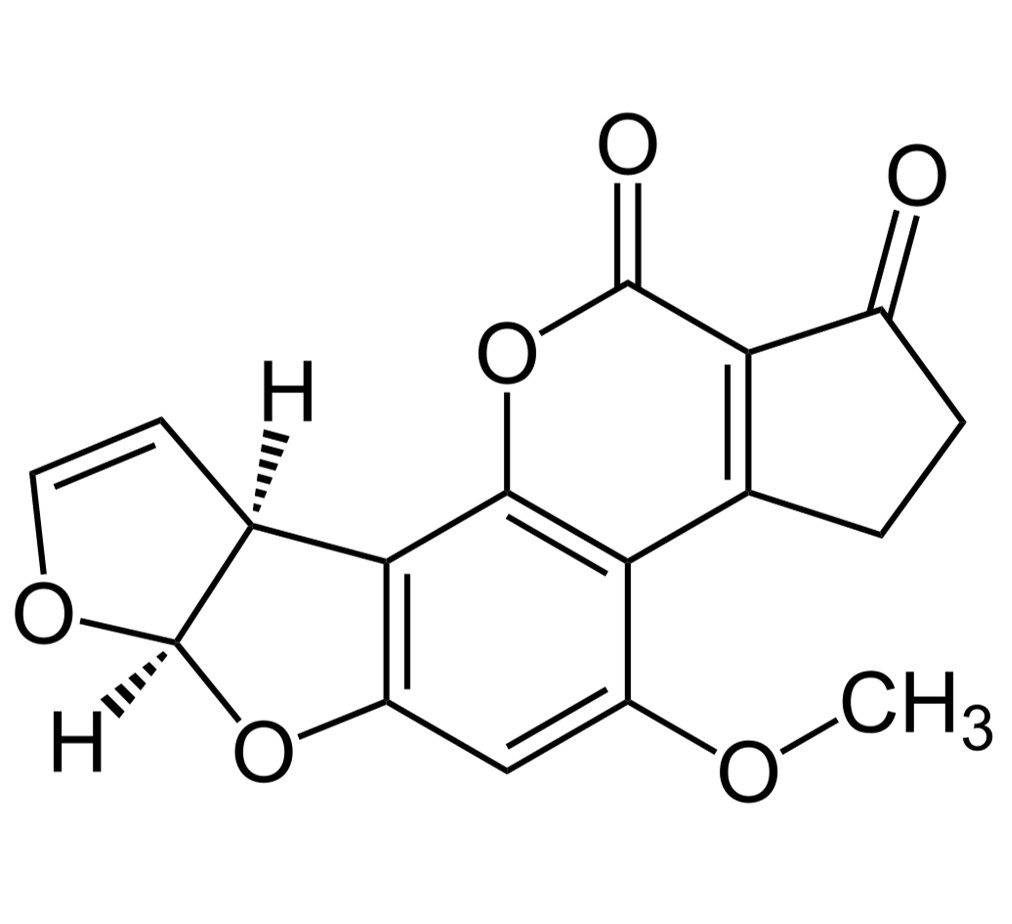
Aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, G2, M1)
-
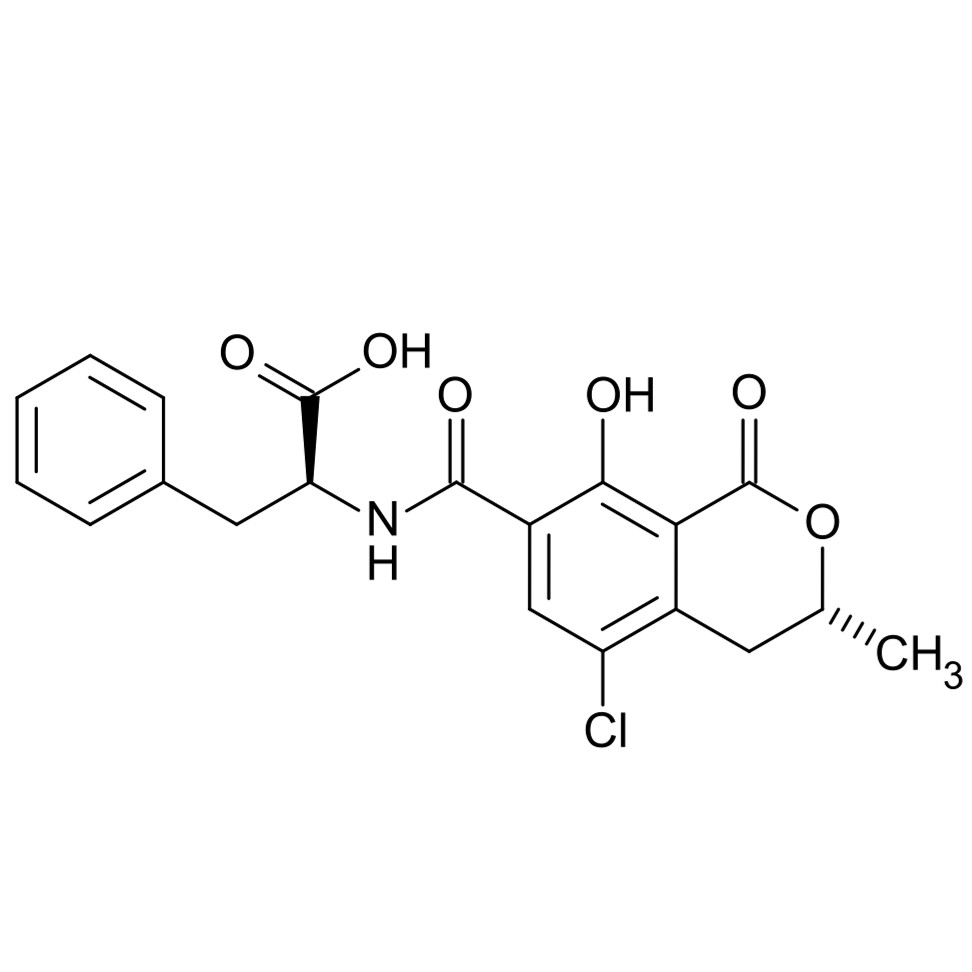
Ochratoxin A (OTA)
-
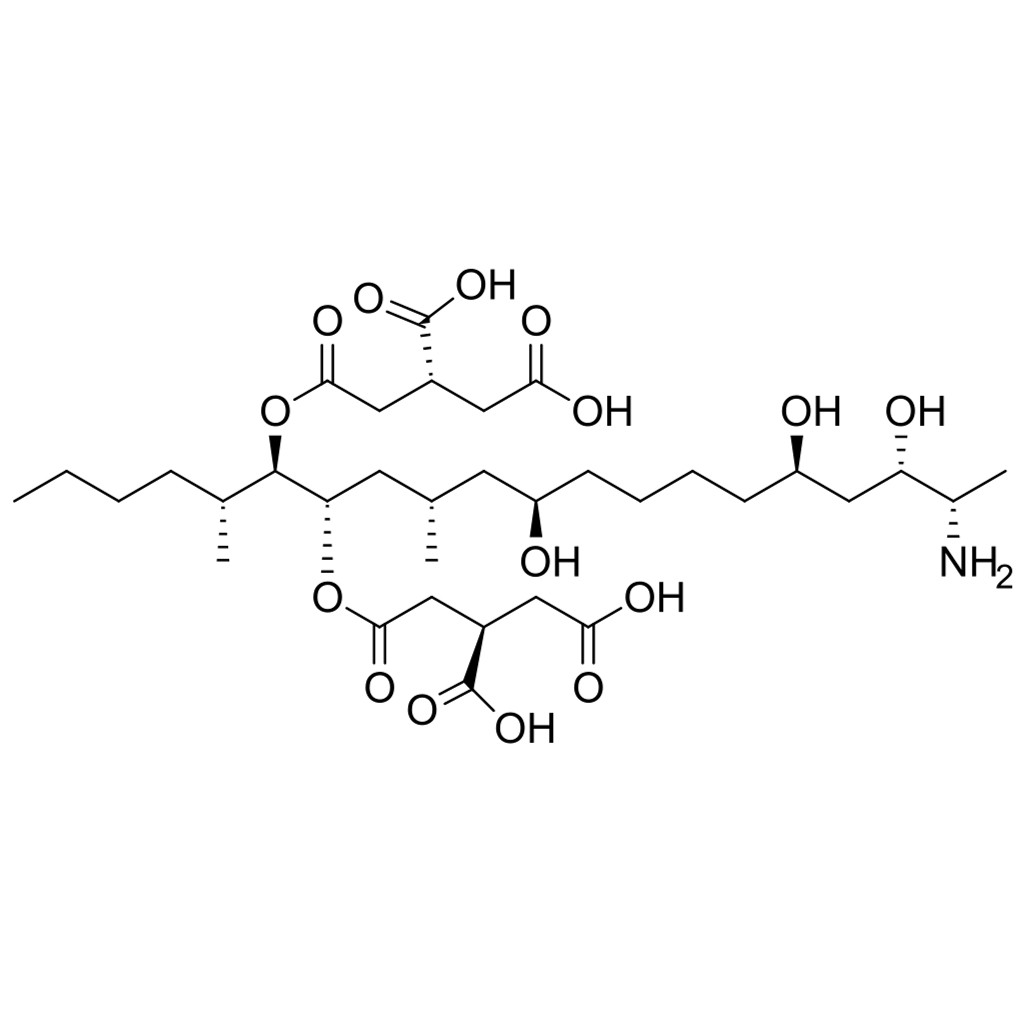
Fumonisins (B1, B2, B3)
-
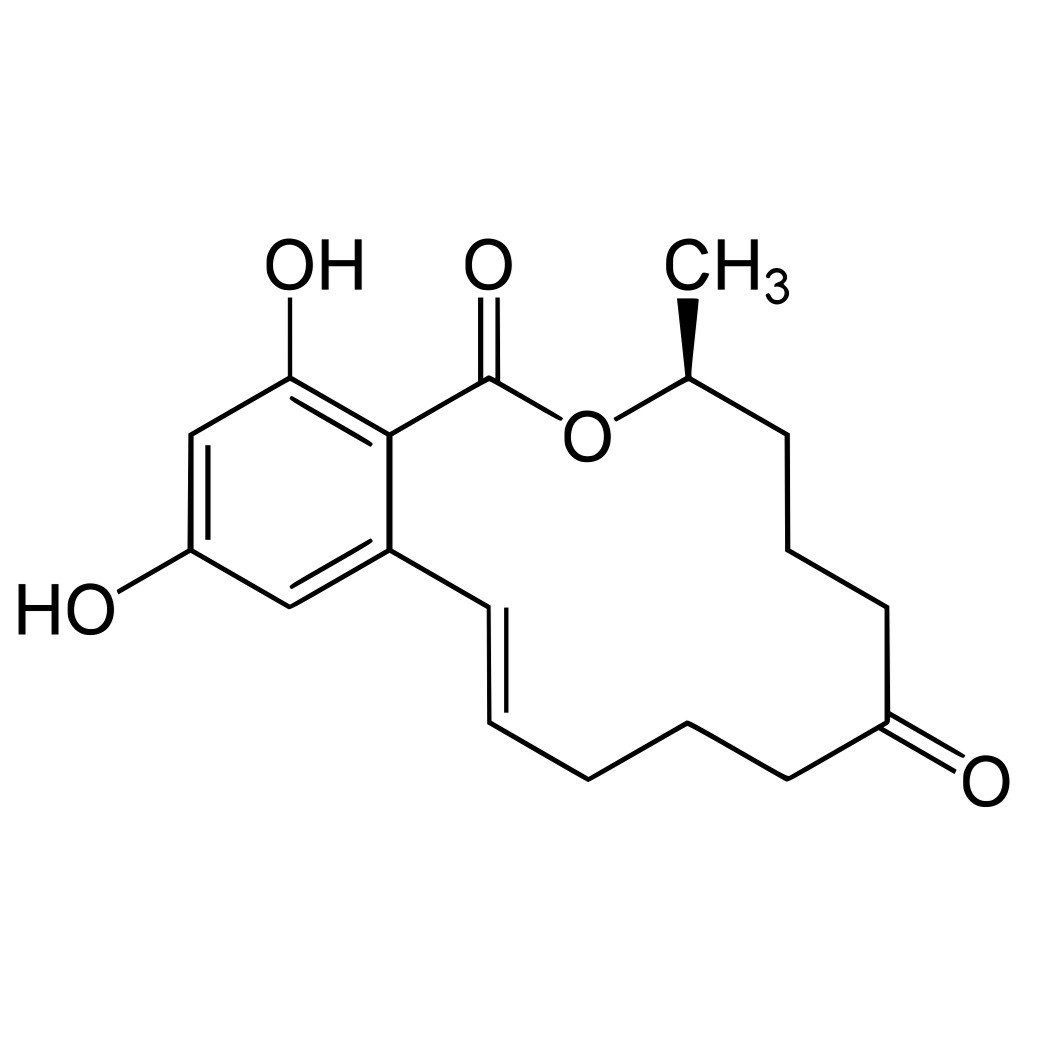
Zearalenone (ZEA)
-
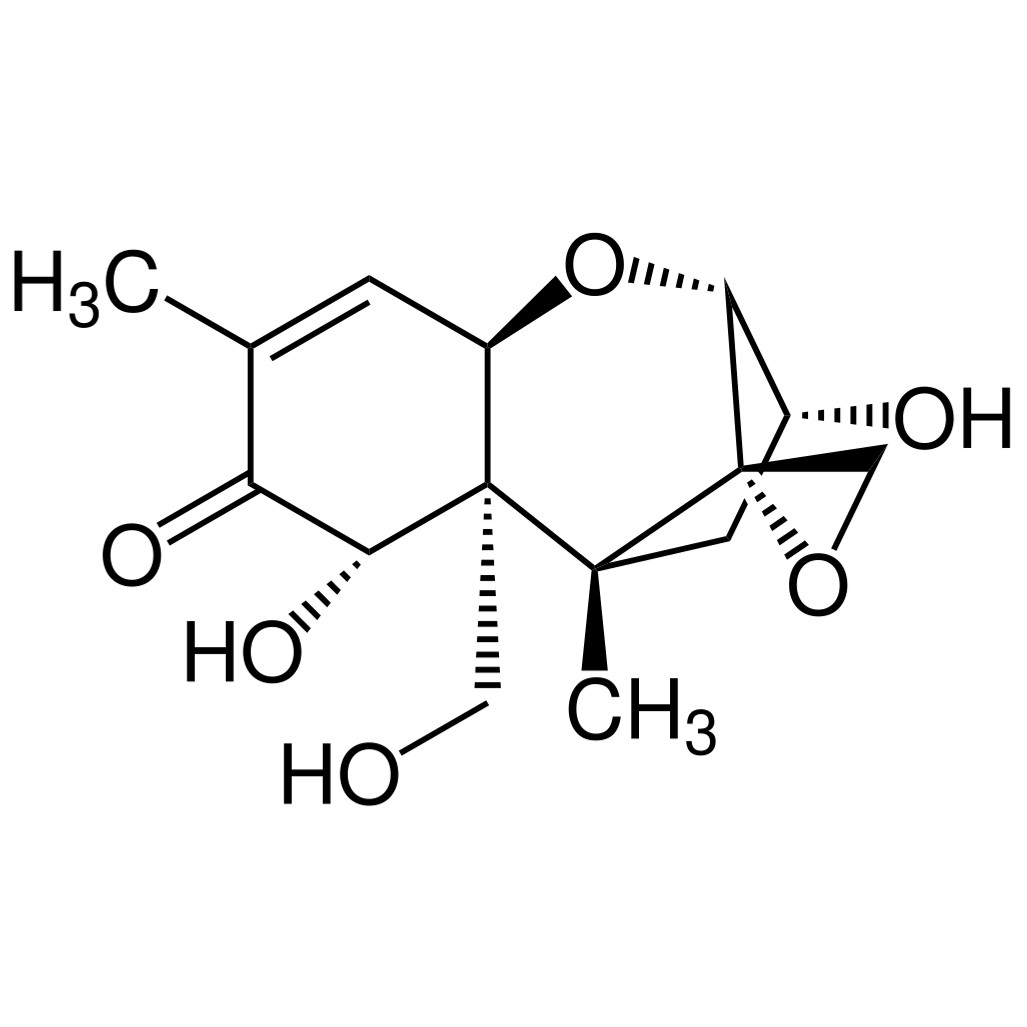
Deoxynivalenol (DON / Vomitoxin)
-
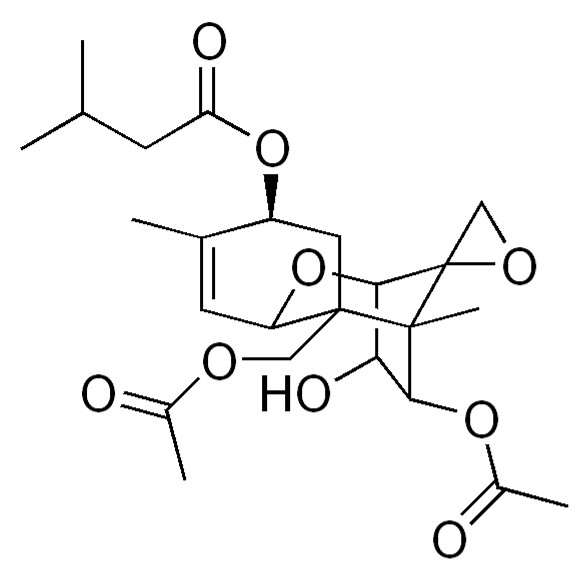
T-2 and HT-2 Toxins
-
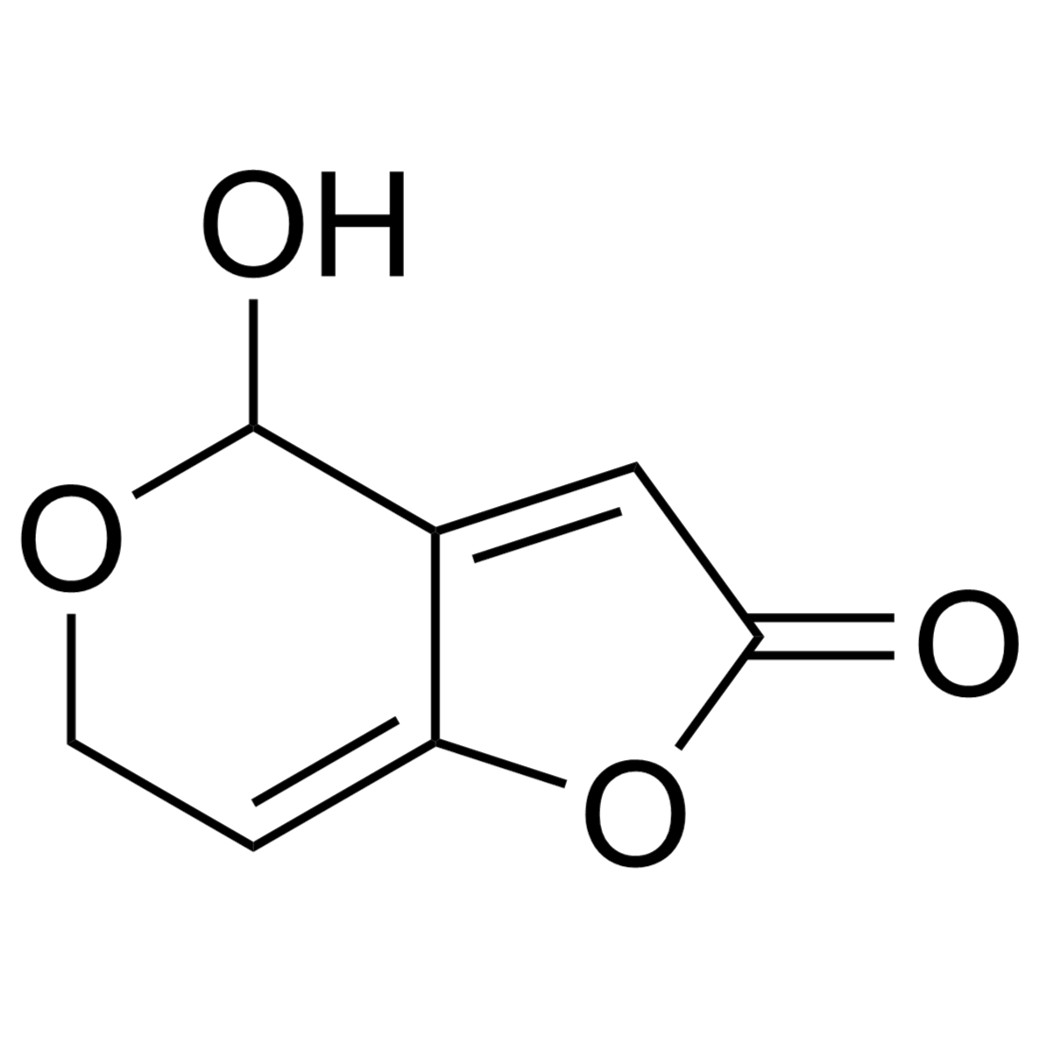
Patulin
-
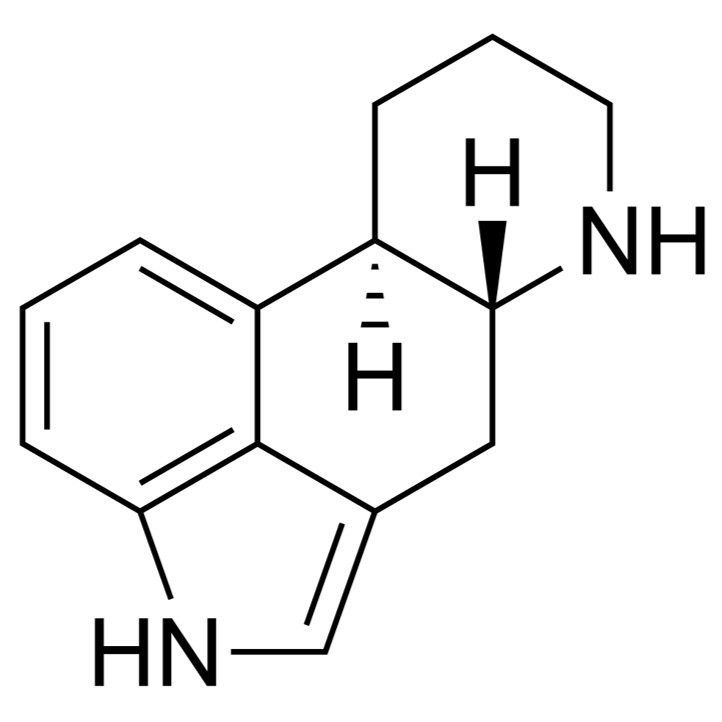
Ergot Alkaloids
Testing Technologies We Use
We combine scientific precision with real-world efficiency to ensure reliable results:
-

HPLC-FLD
Targeted detection of aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in food and TCM
-

LC-MS/MS
Multi-toxin profiling in complex matrices like herbal extracts, spices, supplements
-

ELISA
Rapid screening for regulatory compliance
Sample Types We Support
Our testing is customized for food and healthcare products, including:
- Food Products: Grains, cereals, nuts, dried fruits, spices, coffee, tea, dairy products
- Functional Foods: Nutritional supplements, probiotics, fortified foods
- Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM): Raw herbs, granules, decoctions
- Health Foods: Herbal drinks, tablets, capsules
- Natural Extracts: Plant-based ingredients used in healthcare formulations
Advantages of Our Fungal Toxin Test Service
- Multi-Toxin Screening: Simultaneous detection of 20+ mycotoxins using LC-MS/MS for broad coverage and cost-effective analysis.dt
- Specialized Expertise: Experts in food safety and herbal toxicology ensure accurate, industry-specific testing and interpretation for complex product matrices.
- Customized Solutions: Flexible testing plans tailored to your specific products, sample matrices, and regulatory requirements.
- Fast & Flexible Turnaround: Standard results in 5–7 days; expedited testing available within 48–72 hours for urgent compliance or production needs.dt
- Rigorous Quality Control: Each test includes validated methods, internal standards, and strict QC to ensure reliable and reproducible results.
- Global Compliance Ready: Tests aligned with EU, FDA, and Codex standards to support international market access.dt
Case Studies on Detecting Aflatoxins, T-2 Toxin, and More
* NOTE: We prioritize confidentiality to safeguard our clients’ technology and intellectual property. As an alternative, we present selected published research articles as representative case studies. For details on the assay services and products used in these studies, please refer to the relevant sections of the cited literature.
Case 1: Single kernel aflatoxin and fumonisin detection in corn
Chavez et al., 2022. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108393
Aflatoxin and fumonisin contamination in corn is unevenly distributed, making it difficult to detect using bulk testing alone. To address this, researchers analyzed 864 individual corn kernels using UV–Vis–NIR spectroscopy and quantified toxin levels with ELISA. Results showed that only 1% of kernels contained ≥20 ppb aflatoxin and 5% had ≥2 ppm fumonisin. Despite the variability, aggregated single-kernel data aligned closely with bulk test results, indicating no significant systematic bias.
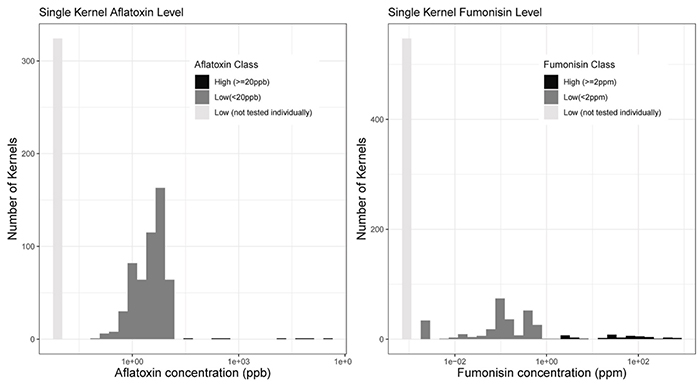
Figure. 3. Distribution of aflatoxin and fumonisin levels in single kernels from commercial corn from Texas. (Left) Distribution of aflatoxin contaminated kernels stratified by ≥ 20 ppb and <20 ppb aflatoxin. (Right) Distribution of fumonisin contaminated kernels stratified by ≥ 2 ppm and <2 ppm fumonisin. (Chavez et al., 2022)
Case 2: Levels of T-2 toxin and its metabolites in the Czech Republic
Pernica et al., 2022. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2021.103875
This study examined T-2 toxin and its related metabolites in Fusarium-infected Czech spring barley using HPLC-MS/MS and ELISA methods. Out of 152 barley samples from the 2018 harvest, 15 exceeded the EU's safety limit (200 µg/kg for T-2 and HT-2 toxins combined) and were further analyzed. The predominant fungal species identified were Fusarium poae and F. tricinctum, with lower occurrences of F. sporotrichioides and F. langsethiae. The average concentration of T-2 and HT-2 toxins was 107.7 µg/kg.
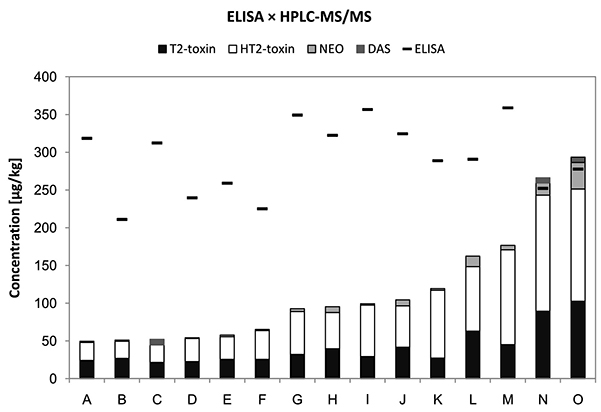
Figure 4. Concentrations of mycotoxins as determined by ELISA and HPLC-MS/MS in the most contaminated barley samples from the Czech Republic inform the 2018 harvest. (Pernica et al., 2022)
What Clients Say About Our Reliable Mycotoxin Testing Services
"We relied on their mycotoxin testing service to validate a batch of herbal extracts for aflatoxin B2 and zearalenone. Their LC-MS/MS method detected trace levels that our in-house equipment missed. The detailed report helped us avoid a costly recall. Their scientific rigor and regulatory familiarity make them a trusted testing partner."
— Quality Control Manager | Herbal Supplement Manufacturer
"Our R&D team was developing a new botanical formulation for export, and fungal toxin testing was a key requirement for EU market entry. The Creative BioMart team provided multi-toxin screening covering 20+ mycotoxins, including ochratoxin A and fumonisin B1. The turnaround was fast, and the report was ready for immediate submission."
— Director of Product Development | Global Nutraceutical Company
"We use Creative BioMart’s fungal toxin testing regularly for raw ingredient verification—especially high-risk items like chili powder and dried figs. Their results consistently match third-party validation, and the QC data in their reports give our auditors complete confidence. The customer service is also refreshingly responsive."
— Procurement Director | Organic Food Brand
"We ran into an urgent batch release issue involving aflatoxin M1 in a dairy-based nutraceutical. Creative BioMart’s priority service delivered results within 48 hours, complete with method traceability and standard references. That speed and accuracy kept our production on schedule."
— Head of Manufacturing QA | Functional Food Enterprise
FAQs on Our Fungal Toxin Test
-
Q: What types of products can you test for fungal toxins?
A: We specialize in testing food products, herbal raw materials, health foods, and nutritional supplements, including grains, nuts, spices, TCM, extracts, and capsules. -
Q: Which mycotoxins do you test for?
A: We test for over 20 common fungal toxins, including aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, G2, M1), ochratoxin A, zearalenone, T-2 toxin, fumonisins, and more. -
Q: Can you test multiple toxins in one analysis?
A: Yes. Our multi-toxin screening can detect 20+ mycotoxins in a single run, saving you time and cost without sacrificing detail. -
Q: What testing methods do you use?
A: We use LC-MS/MS, HPLC-FLD, and ELISA, selecting the best method for your sample matrix and detection requirements. -
Q: How long does the testing process take?
A: Our standard turnaround time is 5–7 working days. For urgent projects, we offer priority service with results in 72 hours. -
Q: Are your reports suitable for regulatory submission?
A: Yes. Our reports are compliant with international standards (ISO, EU, FDA, GB) and are formatted for regulatory, audit, and certification use. -
Q: How do you ensure the accuracy and reliability of test results?
A: All tests are conducted under strict quality control, with validated methods, internal standards, and duplicate analyses to ensure precision and reproducibility. -
Q: Do you offer customized testing plans?
A: Absolutely. We tailor each test plan based on your product type, regulations, and target markets—ensuring optimal compliance and relevance.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References:
- Chavez RA, Cheng X, Herrman TJ, Stasiewicz MJ.Single kernel aflatoxin and fumonisin contamination distribution and spectral classification in commercial corn. Food Control. 2022;131:108393. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108393
- Pernica M, Kyralová B, Svoboda Z, et al.Levels of T-2 toxin and its metabolites, and the occurrence of Fusarium fungi in spring barley in the Czech Republic. Food Microbiology. 2022;102:103875. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2021.103875
Contact us or send an email at for project quotations and more detailed information.
Quick Links
-

Papers’ PMID to Obtain Coupon
Submit Now -

Refer Friends & New Lab Start-up Promotions

