What is C2 Protein?
Background and Discovery of C2 Protein
The C2 protein is named after the second component of human complement, where it was initially discovered. In 1968, the presence of a heat-labile serum factor that contributes to immune response and inflammation linked with the complement system was identified, which was later recognized as C2. It is encoded by the C2 gene, located in the HLA class III region at chromosome 6p21.33.
The C2 protein primarily consists of a chain of 752 amino acids and has a modular structure with different functional domains. The overall structure includes a catalytic serine protease domain (SP), followed by a 'handle' region, two contiguous complement control protein modules (CCPs), a fragment of collagen-like structure and a C-terminal C345c domain.
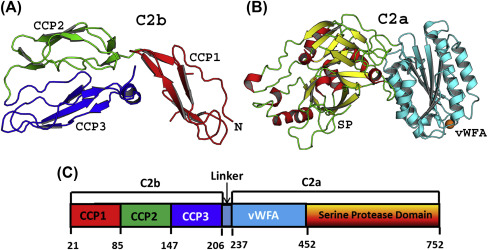
Fig1. C2 Protein
What Is The Function of C2 Protein?
The key function of C2 protein is its involvement in the complement system, a potent effector of the innate immune response. The complement system's core purpose is to defend the body against microbial intruders, induce inflammation, and clear out immune complexes and dead cells. The C2 protein acts as an essential player in the classical and mannose-binding lectin pathway of the complement activation.
C2 protein related signal pathway
The C2 protein performs a pivotal role in signal transduction pathways aiding cellular communications within the body. It cleaves C4 protein into C4a and C4b; C4b combines with C2 to form the C3 convertase (C4b2a) in the classical pathway of the complement system. Additionally, C2 domains serve as universal Ca2+-dependent lipid-binding domains that target proteins to cell membranes in diverse cellular processes, including signal transduction, vesicle trafficking, and lipid metabolism.
C2 protein related diseases
Anomalies in the C2 protein can lead to diverse diseases. Deficiency of the C2 protein is the most common complement system abnormality linked to autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), various types of vasculitis, and infectious diseases like meningitis and pneumonia. Due to the location of the C2 gene in the MHC class III region, variations may affect susceptibility to diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and diabetes. Consequently, C2a, the active fragment of the C2 protein, plays a role in age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
C2 protein's applications in biomedical
In terms of biomedical applications, researchers use the understanding of the C2 protein for drug development and therapy design. Tools such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant proteins to block or regulate the complement system have started to emerge based on the comprehension of the essential complement components like C2 protein. For example, eculizumab, an inhibitor of the terminal complement pathway, is used for treating paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Another potential application is developing therapeutic strategies for AMD, where specifically inhibiting the C3 convertase component (C2a) could be beneficial.
Moreover, understanding the C2 protein's role in immune response has valuable implications in vaccine design. As a part of the complement system, C2 protein enhancement may form a crucial aspect of effective vaccine strategies to boost the immune response.
In conclusion, the C2 protein, initially discovered as an essential component of the immune system's complement process, is a crucial determinant in numerous biological processes and numerous diseases. Its role in signal transduction, lipid binding, and immune response makes it an attractive point of study in the field of biomedicine, promising potential avenues of research into disease treatment and prevention strategies.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2-6878H | Recombinant Human C2, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| C2-26739TH | Recombinant Human C2 | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| C2-599H | Recombinant Human Complement Component 2, Fc Chimera | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| C2-7265H | Recombinant Human C2 protein, hFc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | hFc |
| C2-7846H | Recombinant Human C2 protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| C2-1032H | Active Recombinant Human C2 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Manne, K., & Narayana, S. V. (2017). C2. The Complement FactsBook (Second Edition), 127-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-810420-0.00013-4

