What is CRTC3 Protein
CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 3 (CRTC3) was discovered following the initial identification of two homologous proteins, CRTC1 and CRTC2. All three proteins belong to the CRTC family that plays a pivotal role in modulating CREB-dependent gene transcription. However, CRTC3, encoded by the CRTC3 gene, upholds unique functions, distinguishing itself from its relatives.
Gene Locus
The human CRTC3 gene resides on the chromosomal region 15q26. CRTC3's gene locus, otherwise referred to as its specific location on chromosome 15, is crucial to understanding any genetic alterations that may influence protein functions and contribute to disease genomics.
Protein Structure of CRTC3
CRTC3 is a multi-domain protein highlighting two primary areas, the N-terminal CREB-binding domain, and the C-terminal transactivation domain. The N-terminal domain combines with CREB to initiate the transcription of target genes. Two TORC conserved regions (TCR) are found in this area that play a significant function in regulating gene expression. The C-terminal domain is heavily phosphorylated, thereby controlling the cellular localization of CRTC3.
Function of the CRTC3 Protein
The basic function of the CRTC3 protein is to co-activate CREB-dependent gene transcription. This event occurs in response to an increase in intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) concentrations. However, the function is not restricted to this. Its roles in metabolism, inflammation regulation, and lymphocyte development echo its potential throughout the body.
CRTC3 also plays a critical part in the regulation of genes involved in metabolism and energy balance. When CRTC3 is inactivated, it augments the thermogenic program in adipose tissues, supporting enhanced energy expenditure and providing resistance to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance.
CRTC3 Protein Related Signal Pathway
The CRTC3 protein operates within the cAMP signaling pathway. cAMP, a secondary messenger, is essential for several biological responses, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, and glucose and lipid metabolism. cAMP modulates the interaction of CRTC3 with the family of CREB transcription factors, which in turn affects the transcription of target genes.
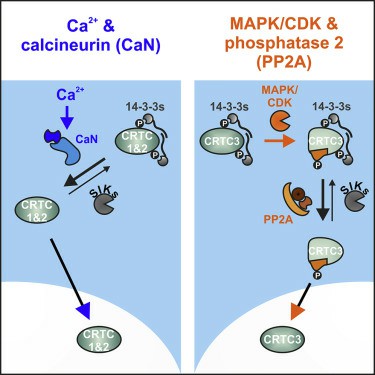
Fig1. CRTC3 Signaling Pathway (Sonntag, T., et al. 2019)
CRTC3 Protein Related Diseases
Notably, abnormalities and dysregulations involving CRTC3 are linked with various pathophysiological conditions. Researchers have identified associations between CRTC3 and several diseases, including obesity and type 2 diabetes, due to mutations in the regulatory genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. CRTC3 gene polymorphisms were discovered to heighten the risk of developing obesity in humans.
Beyond metabolic diseases, misregulated CRTC3 has also been implicated in Everolimus-resistant breast cancer. CRTC3 encodes a critical component in a signal transduction pathway resulting in Everolimus resistance, suggesting that this protein could serve as a potential therapeutic target for overcoming drug resistance in breast cancer patients.
CRTC3 Protein's Applications in Biomedical
Given its function in regulating metabolic processes, and its association with various diseases, CRTC3 holds a significant potential for therapeutic targeting. Direct attention is being focused on developing drugs that manipulate CRTC3 activity, primarily to treat metabolic disorders and certain types of cancer.
For instance, tailoring therapeutic interventions to inactivate CRTC3 could defend against obesity and insulin resistance. Moreover, identifying strategies to counteract CRTC3 function in cancer cells could prove critical in cancer treatment and enhancing patients' response to current therapeutic modalities.
In conclusion, the CRTC3 protein, with its complex structure and varied functionality, is undoubtedly an essential player in human health and disease. Its effects, particularly in metabolism and disease pathogenesis, divulge a wealth of promising areas for future biomedical research and therapeutic innovation. Its manipulation can lead to novel treatment strategies and improve the health outcomes in patients with conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and cancer. With further investigations in this realm, the mysteries of the CRTC3 protein continue to unfold, promising new ways to improve and safeguard human health.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRTC3-32H | Recombinant Human CRTC3 protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CRTC3-1114H | Recombinant Human CRTC3 protein, His & T7-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/T7 |
| CRTC3-1992M | Recombinant Mouse CRTC3 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Sonntag, T., Ostojić, J., Vaughan, J. M., Moresco, J. J., Yoon, Y., Yates, J. R., & Montminy, M. (2019). Mitogenic Signals Stimulate the CREB Coactivator CRTC3 through PP2A Recruitment. IScience, 11, 134-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.012

