What is FLT4 Protein
The FLT4 protein, also known as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3), is a key orchestrator of cellular processes.
What is FLT4 Protein?
FLT4, a member of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family, acts as a linchpin in cellular communication. Predominantly expressed in the endothelial cells of the lymphatic system, FLT4 plays a paramount role in lymphangiogenesis—the intricate process of forming new lymphatic vessels.
The Structure of FLT4 Protein
The FLT4 protein consists of several domains, each contributing to its specific functions. The extracellular region contains immunoglobulin-like domains that facilitate ligand binding, with the ligands primarily being members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family. The intracellular region, on the other hand, contains the kinase domain, responsible for phosphorylating tyrosine residues and initiating downstream signaling events.
The Function of FLT4 Protein
- Lymphangiogenesis
FLT4's foremost function is the regulation of lymphangiogenesis. Ligands such as VEGF-C and VEGF-D bind to FLT4, initiating downstream signaling that propels the proliferation, migration, and survival of lymphatic endothelial cells—a critical process for the development and repair of the lymphatic system.
- Maintenance of Lymphatic Vessels
Beyond its role in lymphangiogenesis, FLT4 is instrumental in the maintenance of existing lymphatic vessels. Proper FLT4 signaling is indispensable for ensuring the integrity and functionality of these vessels, crucial for efficient fluid drainage and immune cell trafficking.
FLT4-Related Diseases
Dysregulation of FLT4 signaling unveils a spectrum of diseases and disorders, underscoring its indispensable role in maintaining homeostasis.
- Lymphedema
Mutations or aberrations in the FLT4 gene manifest as lymphedema—a condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, leading to debilitating swelling. This pathology underscores FLT4's pivotal role in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of lymphatic vessels.
- Cancer Metastasis
Elevated FLT4 expression in certain cancers implicates its role in tumor metastasis. Tumor cells exploit FLT4 signaling to induce the growth of new lymphatic vessels, providing a pathway for metastatic spread.
FLT4 Related Signaling Pathways
Understanding the signaling pathways associated with FLT4 is essential for unraveling its roles in health and disease. The VEGF-C/VEGF-D and FLT4 axis is a major pathway through which FLT4 transduces signals. The following summarizes the key steps in this signaling pathway:
- Ligand Binding
Ligands such as VEGF-C and VEGF-D bind to the extracellular domain of FLT4, inducing receptor dimerization.
- Receptor Dimerization
Ligand binding triggers the dimerization of FLT4 receptors, bringing the kinase domains into close proximity.
- Phosphorylation
The kinase domains of FLT4 phosphorylate tyrosine residues on the receptor itself, creating docking sites for downstream signaling molecules.
- Downstream Signaling
Phosphorylated FLT4 activates various intracellular signaling pathways, including the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways, which in turn regulate cellular processes such as proliferation, survival, and migration.
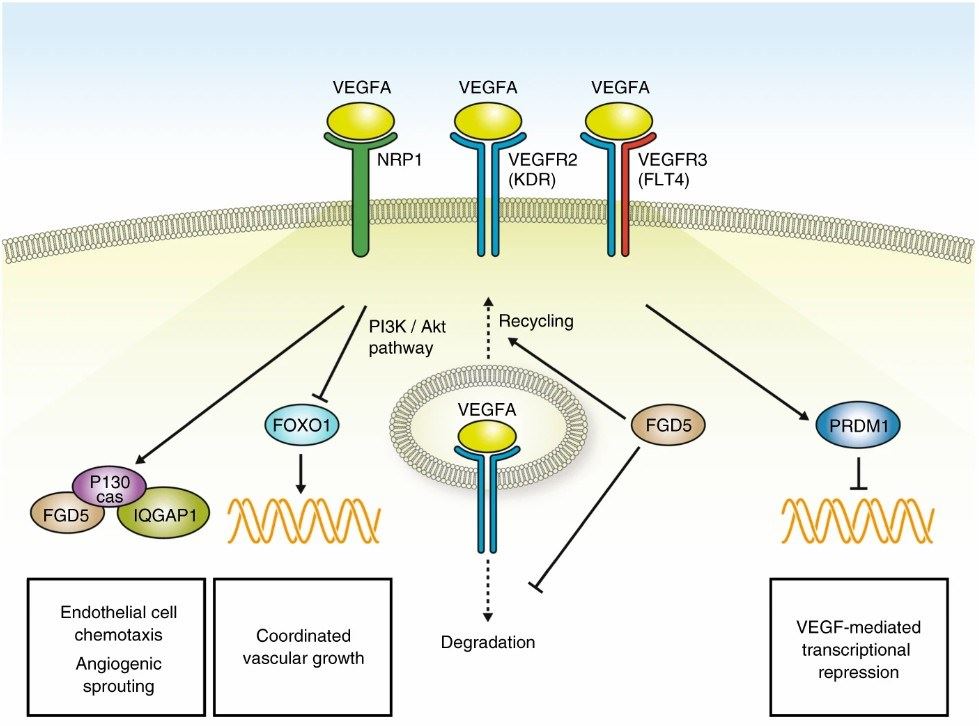
Figure 1. VEGF pathway. (Reuter, M.S., et al. 2019)
Applications of FLT4 in Biomedical Research
The unique attributes of FLT4 position it as an enticing target for therapeutic interventions and innovative biomedical applications.
- Target for Cancer Therapy
In light of FLT4's role in cancer metastasis, targeted therapies inhibiting FLT4 signaling emerge as a promising avenue for impeding tumor-induced lymphangiogenesis and metastatic spread.
- Treatment of Lymphedema
Deciphering the molecular underpinnings of FLT4-associated lymphedema unveils prospects for targeted therapies, offering potential relief for individuals grappling with this debilitating condition.
- Biomedical Imaging
The specific expression of FLT4 in the lymphatic system renders it an invaluable target for molecular imaging techniques. FLT4-specific probes could revolutionize diagnostic imaging, providing insights into lymphatic vessel dynamics.
- Drug Delivery and Vascular Targeting
Exploiting FLT4 expression for targeted drug delivery holds promise. Designing therapies that interact specifically with FLT4-expressing cells could pave the way for precision medicine approaches, optimizing therapeutic efficacy.
From its structural intricacies to its pivotal role in health and disease, FLT4 unveils a tapestry of possibilities for advancing our understanding of cellular dynamics and revolutionizing therapeutic interventions in biomedicine.
Recommended Products for FLT4 Protein
Reference
- Reuter, M.S., et al. Haploinsufficiency of vascular endothelial growth factor related signaling genes is associated with tetralogy of Fallot. Genet Med. 2019, 21: 1001–1007.

