What is HMGB1 Protein
In the intricate tapestry of the human body, proteins play an indispensable role in orchestrating various physiological processes. Among these, the High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) protein emerges as a multifaceted molecular player with profound implications for human health and disease.
What is HMGB1 Protein?
HMGB1 protein, a highly conserved nuclear protein in eukaryotes, has transcended its traditional role in DNA regulation to become a pivotal player in both intracellular and extracellular processes. Structurally, HMGB1 boasts two DNA-binding domains, Box A and Box B, along with a negatively charged C-terminal tail, allowing it to interact with DNA in a non-sequence-specific manner.
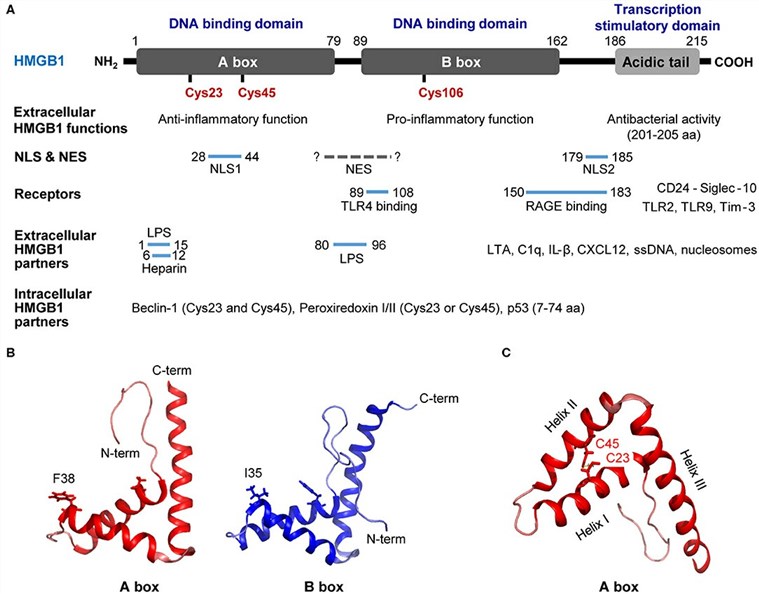
Figure 1. Structure of HMGB1. (Kwak, M.S., et al. 2020)
The Function of HMGB1 Protein
- Nuclear Function
Within the nucleus, HMGB1 acts as a chromatin architectural protein, wielding influence over DNA repair, recombination, and transcriptional regulation. It facilitates the binding of transcription factors to their respective DNA sequences, orchestrating the formation of functional transcriptional complexes vital for cellular processes.
- Extracellular Function
Beyond the nucleus, HMGB1 takes on a new identity as an extracellular signaling molecule. Released actively or passively into the extracellular environment, HMGB1 serves as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP), alerting the immune system to cellular stress or injury. Its interactions with receptors like RAGE and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) initiate inflammation and immune responses, unveiling its role as a sentinel in the body's defense mechanisms.
HMGB1-Related Diseases
- Inflammatory Disorders
The extracellular role of HMGB1 as a mediator of inflammation is prominently implicated in inflammatory disorders. Binding to receptors such as RAGE and TLRs, HMGB1 activates pro-inflammatory pathways, contributing to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
- Cancer
HMGB1's connection to cancer is multifaceted. Elevated levels correlate with increased tumor aggressiveness, and its ability to confer resistance to cell death promotes cancer cell survival. Understanding these mechanisms opens avenues for targeted therapies in cancer treatment.
- Neurological Disorders
In the realm of neurological disorders, HMGB1's presence is noteworthy. Elevated levels in conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease contribute to neuroinflammation and neuronal damage, unraveling potential therapeutic targets for these devastating diseases.
- Autoimmune Diseases
HMGB1's immune-activating properties position it as a potential contributor to autoimmune diseases. In systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), for instance, heightened HMGB1 levels may perpetuate autoimmune responses, implicating it in the pathogenesis of these conditions.
HMGB1 Related Signaling Pathways
- RAGE Signaling
Interaction with the receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) sets off a cascade of events leading to the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and other pro-inflammatory pathways. This RAGE signaling axis amplifies inflammatory responses, playing a pivotal role in various disease processes.
- TLR Signaling
HMGB1's interaction with Toll-like receptors, particularly TLR2 and TLR4, initiates signaling pathways that converge on transcription factors like NF-κB. This intricate signaling cascade contributes to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, further fueling inflammatory responses.
- MAPK Signaling
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are implicated in HMGB1-mediated cellular responses. Activation of these pathways contributes to cell survival, proliferation, and the production of inflammatory mediators, offering potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Applications of HMGB1 in Biomedical Research
- Diagnostic Biomarker
Elevated HMGB1 levels in various diseases position it as a potential diagnostic biomarker. Measuring HMGB1 levels in bodily fluids offers a non-invasive method for early detection and monitoring, with applications in conditions like cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Prognostic Indicator
The association of HMGB1 with disease severity and prognosis makes it a promising prognostic indicator. Monitoring changes in HMGB1 levels during disease progression provides valuable insights into the course of the condition, guiding clinicians in making informed decisions regarding treatment strategies.
- Therapeutic Target
The involvement of HMGB1 in various diseases positions it as a promising therapeutic target. Inhibitors targeting HMGB1 release or antagonists disrupting its interactions with receptors are being explored for their potential to modulate inflammation and immune responses, offering new avenues for therapeutic interventions.
- Cancer Therapy
In the realm of cancer therapy, strategies targeting HMGB1 are gaining traction. Inhibiting HMGB1-mediated survival pathways or enhancing immune responses against HMGB1-expressing cancer cells presents a promising frontier for developing innovative cancer therapies.
The enigmatic HMGB1 protein, with its dual roles in the nucleus and extracellular environment, unravels as a central figure in health and disease. From intricate signal pathways to applications in diagnostics and therapeutics, HMGB1's significance resonates across the biomedical landscape, promising breakthroughs in our understanding of diseases and the development of targeted interventions.
Recommended Products for HMGB1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMGB1-452H | Human | Active Recombinant Human High-Mobility Group Box 1, HIgG1 Fc-tagged | CHO | Fc |
| HMGB1-752H | Human | Recombinant Human HMGB1, Fc tagged | Human Cell | Fc |
| HMGB1-13841H | Human | Recombinant Human HMGB1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| HMGB1-3827H | Human | Active Recombinant Human HMGB1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| Hmgb1-1134M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Hmgb1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | HEK293T | MYC/DDK |
| Hmgb1-6947M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Hmgb1 protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | His |
| HMGB1-001R | Rat | Active Recombinant Rat HMGB1, HIgG1 Fc-tagged | CHO | Fc |
| Hmgb1-292R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Hmgb1, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| HMGB1-589C | Cynomolgus Monkey | Recombinant Cynomolgus HMGB1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | His |
| HMGB1-2108R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus monkey HMGB1 Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Kwak, M.S., et al. Immunological Significance of HMGB1 Post-Translational Modification and Redox Biology. Front Immunol. 2020, 11: 1189.

