PTPRF
-
Official Full Name
protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, F -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. PTPs are known to be signaling molecules that regulate a variety of cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, mitotic cycle, and oncogenic transformation. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region contains three Ig-like domains, and nine non-Ig like domains similar to that of neural-cell adhesion molecule. This PTP was shown to function in the regulation of epithelial cell-cell contacts at adherents junctions, as well as in the control of beta-catenin signaling. An increased expression level of this protein was found in the insulin-responsive tissue of obese, insulin-resistant individuals, and may contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene, which encode distinct proteins, have been reported. -
Synonyms
PTPRF;protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, F;LAR;receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase F;LCA-homolog;leukocyte common antigen related;leukocyte antigen-related (LAR) PTP receptor;leukocyte antigen-related tyrosine phosphatase;receptor-linked protein-tyrosine phosphatase LAR;protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, F polypeptide;FLJ43335;FLJ45062;FLJ45567
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is PTPRF protein?
PTPRF (protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p34. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. This PTP possesses an extracellular region, a single transmembrane region, and two tandem intracytoplasmic catalytic domains, and thus represents a receptor-type PTP. The extracellular region contains three Ig-like domains, and nine non-Ig like domains similar to that of neural-cell adhesion molecule. This PTP was shown to function in the regulation of epithelial cell-cell contacts at adherents junctions, as well as in the control of beta-catenin signaling. The PTPRF protein is consisted of 1907 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 212.9 kDa.
What is the function of PTPRF protein?
An increased expression level of this protein was found in the insulin-responsive tissue of obese, insulin-resistant individuals, and may contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. PTPRF, as a tyrosine phosphatase, regulates a variety of cell signaling pathways, such as growth factor signaling, cell cycle regulation, and cytoskeletal remodeling. By regulating cytoskeleton recombination and cell-extracellular matrix interaction, the migration ability of cells is affected. PTPRF protein can promote apoptosis in some cases, especially under certain stress conditions.
PTPRF Related Signaling Pathway
Ras/MAPK pathway: PTPRF protein can interact with a variety of growth factor receptors, dephosphorylating these receptors through its phosphatase activity, which in turn affects the downstream Ras/MAPK signaling cascade. This pathway plays a central role in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation and survival.
PI3K/Akt pathway: PTPRF protein can also interact with PI3K to regulate its activity, thereby affecting the downstream Akt signaling pathway. This pathway plays an important role in cell growth, survival, metabolism and migration.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway: Some studies have shown that PTPRF may be involved in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, thereby affecting cell proliferation and differentiation.
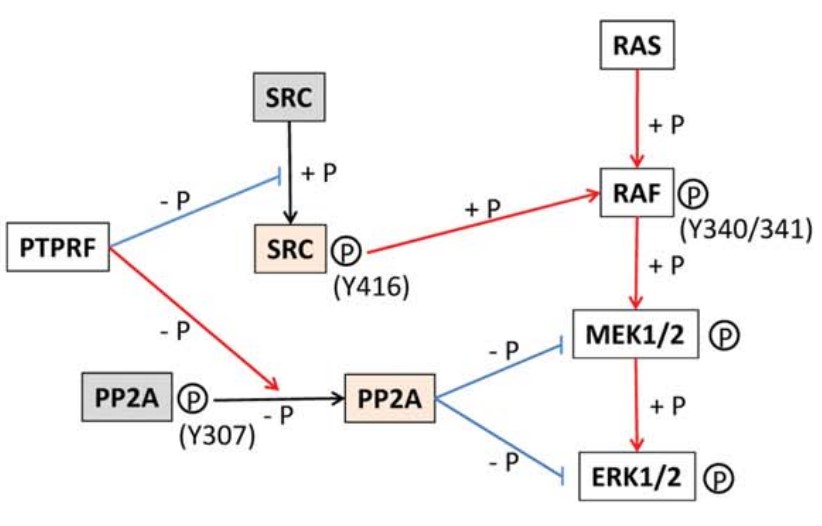
Fig1. Schematic diagram shows the proposed mechanism whereby PTPRF suppresses ERK1/2 activation by way of SRC and PP2A. (Rabindranath Bera, 2014)
PTPRF Related Diseases
PTPRF expression is altered in many tumors, including breast, lung, and gastric cancers. The function of PTPRF in nerve cells has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. PTPRF may be involved in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases such as angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. PTPRF may also be associated with a variety of other diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, diabetes, pulmonary fibrosis, and certain genetic disorders.
Bioapplications of PTPRF
Because of its universal expression on all white blood cells, PTPRF is often used as a diagnostic marker for blood diseases. In addition, therapeutic strategies targeting PTPRF are being investigated to improve certain types of leukemia and other immune-related diseases. In organ transplantation, monitoring PTPRF expression helps to assess the risk of immune rejection and thus guide the use of immunosuppressive drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mai Quynh Nguyen, 2022
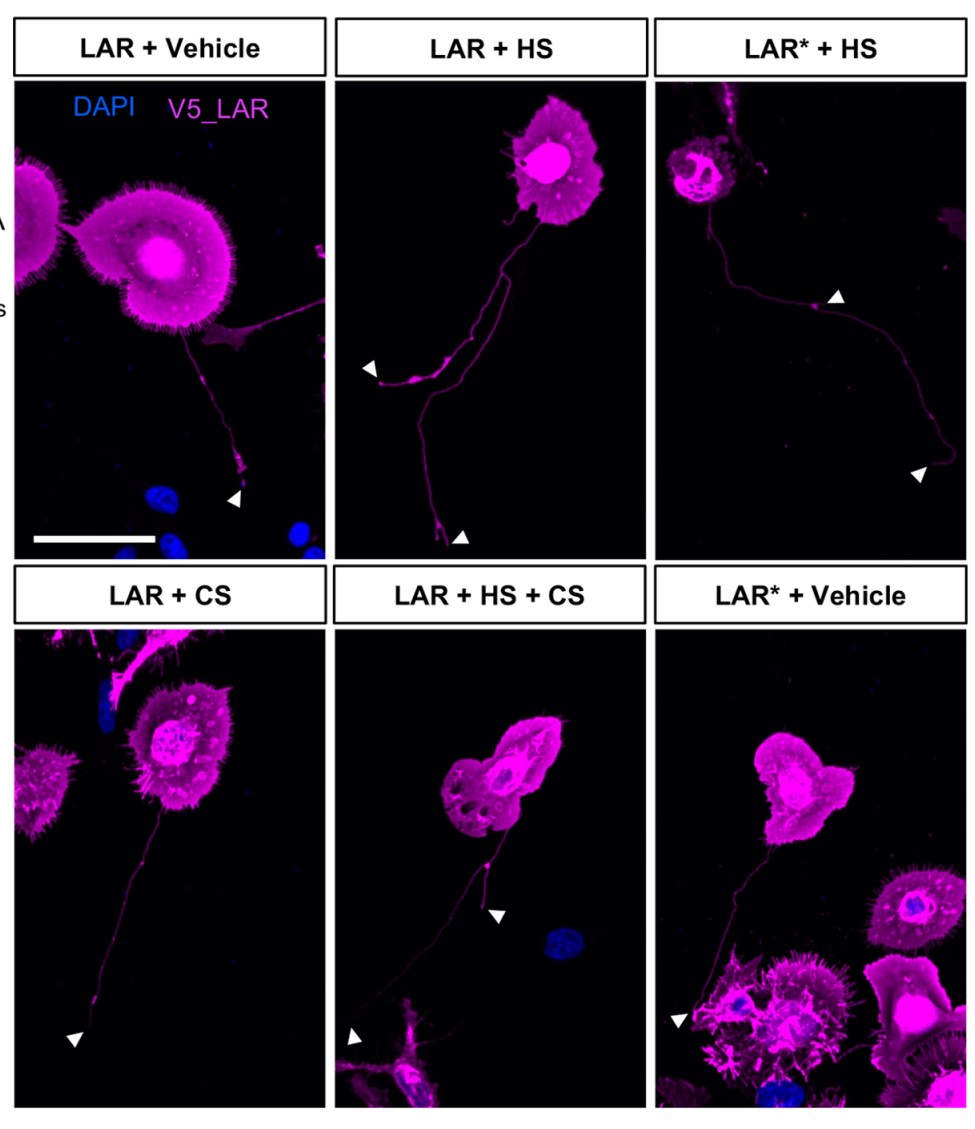
Actin-based protrusions called cytonemes are reported to function in cell communication by supporting events such as morphogen gradient establishment and pattern formation. Despite the crucial roles of cytonemes in cell signaling, the molecular mechanism for cytoneme establishment remains elusive. In this study, the researchers showed that the leukocyte common antigen-related (LAR) receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase plays an important role in cytoneme-like protrusion formation. Overexpression of LAR in HEK293T cells induced the formation of actin-based protrusions, some of which exceeded 200 μm in length and displayed a complex morphology with branches. Upon focusing on the regulation of LAR dimerization or clustering and the resulting regulatory effects on LAR phosphatase activity, they found that longer and more branched protrusions were formed when LAR dimerization was artificially induced and when heparan sulfate was applied. Interestingly, although the truncated form of LAR lacking phosphatase-related domains promoted protrusion formation, the phosphatase-inactive forms did not show clear changes, suggesting that LAR dimerization triggers the formation of cytoneme-like protrusions in a phosphatase-independent manner.
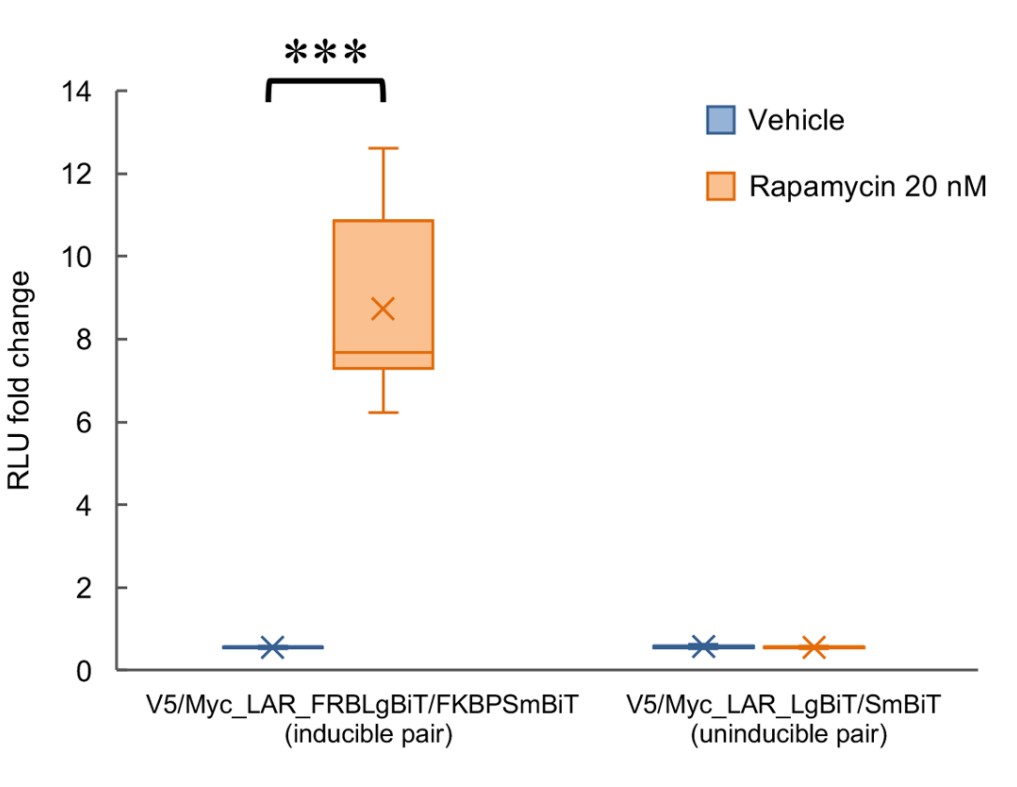
Fig1. Analytical results of the changes in detected luminescence upon rapamycin application to induce LAR dimerization followed by reconstitution and restoration of luciferase enzymatic activity (at 60 min post application).
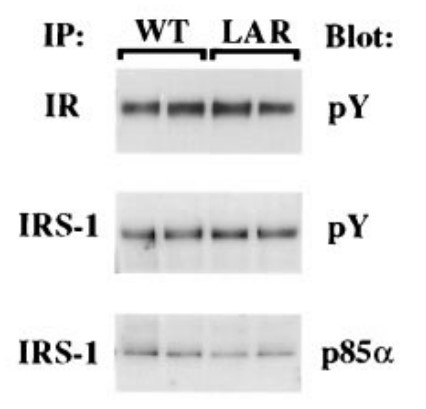
Case Study 2: J M Zabolotny, 2001
Previous reports indicate that the expression and/or activity of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) LAR are increased in insulin-responsive tissues of obese, insulin-resistant humans and rodents, but it is not known whether these alterations contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. To address this question, the researchers generated transgenic mice that overexpress human LAR, specifically in muscle, to levels comparable to those reported in insulin-resistant humans. In LAR-transgenic mice, fasting plasma insulin was increased 2.5-fold compared with wild-type controls, whereas fasting glucose was normal. Whole-body glucose disposal and glucose uptake into muscle in vivo were reduced by 39-50%. Insulin injection resulted in normal tyrosyl phosphorylation of the insulin receptor and insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) in muscle of transgenic mice. However, phosphorylation of IRS-2 was reduced by 62%, PI3' kinase activity associated with phosphotyrosine, IRS-1, or IRS-2 was reduced by 34-57%, and association of p85alpha with both IRS proteins was reduced by 39-52%. Thus, overexpression of LAR in muscle causes whole-body insulin resistance, most likely due to dephosphorylation of specific regulatory phosphotyrosines on IRS proteins.
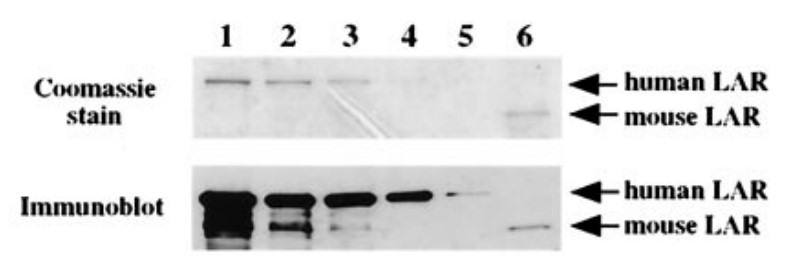
Fig3. Reactivity of anti-human LAR antibody to human and mouse LAR.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
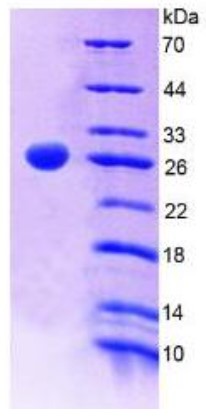
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PTPRF-463H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
PTPRF involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PTPRF participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Adherens junction,Insulin signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PTPRF were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | NEO1,MPZL1L,CD8B1,Siglec1,PECAM1,NLGN1,GLG1,CLDNK,MAG,ITGA6 |
| Insulin resistance | RPS6KB2,PTPN11B,GSK3B,SOCS3B,PTPN11A,PIK3CB,MTOR,PPP1CC,CREB3L3,PYGB |
| Insulin signaling pathway | PHKB,FBP2,PRKAA1,G6PC,TSC1A,MAPK8B,SHC1,PIK3R3A,FBP1,AKT1 |
| Adherens junction | PVRL1,PTPRM,CTNNA2,MET,RAC1B,RAC2,RHOAB,INSRA,RHOAC,WASF3B |
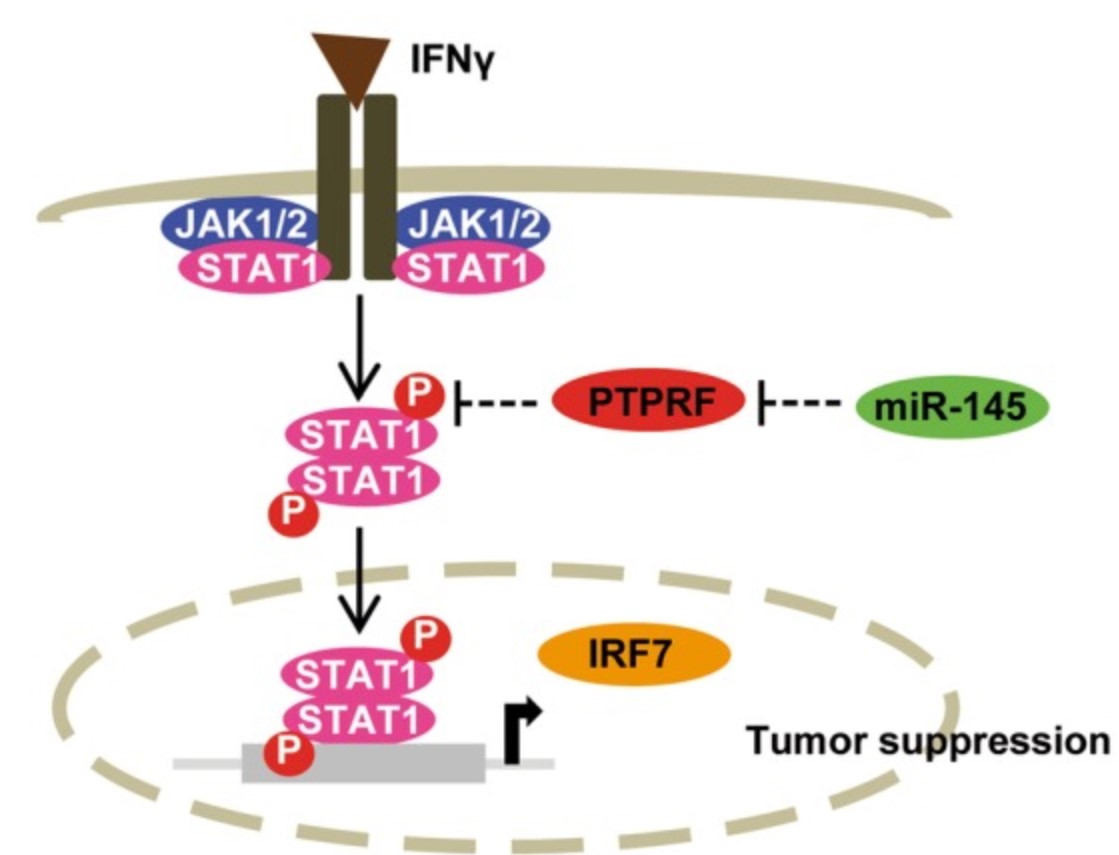
Fig1. Schematic model of miR-145-5p-mediated activation of STAT1 signaling. (Benjamin Goeppert, 2019)
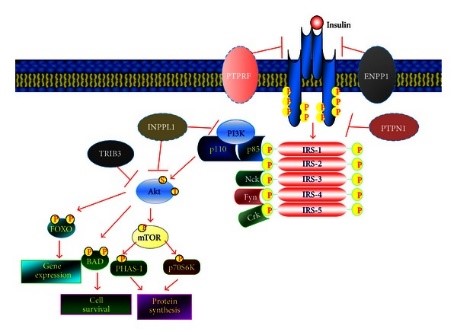
Fig2. Schematic representation of the insulin-signaling pathway. (Carlo de Lorenzo, 2013)
Protein Function
PTPRF has several biochemical functions, for example, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binding,heparin binding,protein complex binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PTPRF itself. We selected most functions PTPRF had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PTPRF. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan binding | COL20A1,PTN,SEMA5A |
| heparin binding | WISP1,APOB,ZNF207,ABP1,MSTN,OVALX,FN1,PGF,PF4V1,AZU1 |
| protein complex binding | PRMT5,RBM10,TRADD,NRAS,LRP1,CDH2,PLK2,CRTAP,KLHL8,GRIN2A |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | PTPRUB,PTPRE,PTPRC,PTPRM,PTPN6,PTPRN2,PTPRA,PTPRB,PTPRD,PTPRO |
| protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | PTPN13,SSH3,DUSP22A,DUSP5,PTPMT1,DUSP2,PTPN14,PTPRM,SSH1,PTPN4B |
Interacting Protein
PTPRF has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PTPRF here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PTPRF.
CAV1;Irs1;PRPF40A;SKIL;ZNF512B;EGFR
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Westgaard, IH; Dissen, E; et al. The lectin-like receptor KLRE1 inhibits natural killer cell cytotoxicity. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 197:1551-1561(2003).
- Jewett, A; Cacalano, NA; et al. Coengagement of CD16 and CD94 receptors mediates secretion of chemokines and induces apoptotic death of naive natural killer cells. CLINICAL CANCER RESEARCH 12:1994-2003(2006).



