SKP1
-
Official Full Name
S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a component of SCF complexes, which are composed of this protein, cullin 1, a ring-box protein, and one member of the F-box family of proteins. This protein binds directly to the F-box motif found in F-box proteins. SCF complexes are involved in the regulated ubiquitination of specific protein substrates, which targets them for degradation by the proteosome. Specific F-box proteins recognize different target protein(s), and many specific SCF substrates have been identified including regulators of cell cycle progression and development. Studies have also characterized the protein as an RNA polymerase II elongation factor. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants. A related pseudogene has been identified on chromosome 7.
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
Background
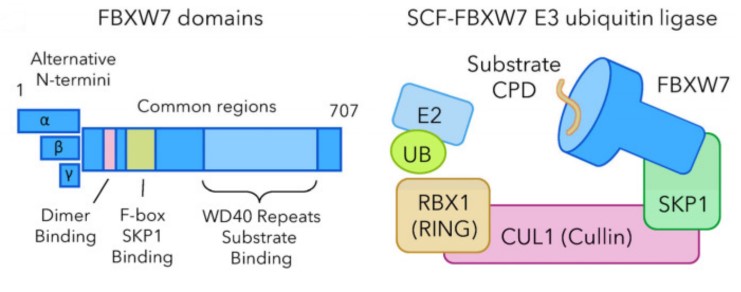
Fig1. Domains of the FBXW7 protein include three different N-termini produced from alternative isoforms and common regions that include the dimerization domain, F-box domain, and WD40 repeat domain. (Claire C de la Cova, 2023)
What is SKP1 protein?
SKP1 (S-phase kinase associated protein 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5q31. This gene encodes a component of SCF complexes, which are composed of this protein, cullin 1, a ring-box protein, and one member of the F-box family of proteins. This protein binds directly to the F-box motif found in F-box proteins. The SKP1 protein is an important cell cycle regulatory protein, mainly involved in the regulation of the S phase (DNA replication phase) and G2 phase (pre-cell division phase) of the cell cycle. The SKP1 protein is consisted of 163 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 18.7 kDa.
What is the function of SKP1 protein?
SKP1 protein can bind to CDK (cell cycle dependent kinase) to form SKP1-CDK complex, thus promoting the process of cell cycle. It can also bind to other proteins (such as NANOG, Oct4, and SOX2) to form complexes that regulate stem cell self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, maintaining the state of stem cells. SKP1 is also involved in the regulation of brain nerve development.
SKP1 Related Signaling Pathway
SKP1, as a component of the SCF complex, interacts with Cullin, F-box proteins, and CDK to regulate ubiquitination and degradation of substrate proteins and promote cell cycle progression. It can also be involved in the association of Bcl-2 family proteins and Caspase family proteins related to apoptosis pathways. At the same time, SKP1 is also involved in the tumorigenic pathways, including PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and Ras/MAPK signaling pathway.
SKP1 Related Diseases
SKP1 protein is abnormally expressed in some types of tumors and may be involved in the genesis and development of tumors. For example, high expression of SKP1 protein is associated with the occurrence of tumors such as breast cancer and colorectal cancer. It may also lead to immune system diseases and neurological diseases, such as autism and intellectual disability. In addition, the abnormal function of SKP1 protein may affect the normal function of hematopoietic cells, resulting in the occurrence of blood system diseases.
Bioapplications of SKP1
SKP1 protein is involved in multiple signaling pathways and can be used as a target to screen small molecule compounds. At present, a number of small molecule inhibitors targeting SKP1 protein have entered clinical trials for the treatment of certain types of tumors.
Case Study
Case study 1: Jie Li, 2023
Intracellular degradation of proteins and organelles by the autophagy-lysosome system is essential for cellular quality control and energy homeostasis. Besides degradation, endolysosomal organelles can fuse with the plasma membrane and contribute to unconventional secretion. But the function of mammalian SKP1 in the endolysosome is unclear. In this study, the researchers the phosphorylation events of SKP1 were determined under nutrient-poor conditions and nutrient-rich conditions.
Here, we identify a function for mammalian SKP1 in endolysosomes that is independent of its established role as an essential component of the family of SCF/CRL1 ubiquitin ligases. And this study implicates SKP1 phosphorylation as a switch between autophagy and unconventional secretion in a manner dependent on cellular nutrient status.
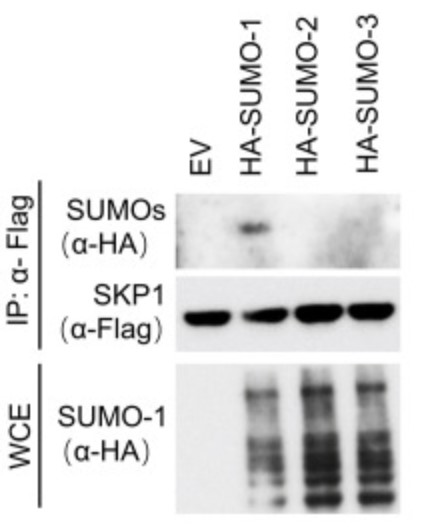
Fig1. Immunoblot after IP with Flag tag from HEK293T cells transfected with Flag-SKP1, Myc-UBC9, SLX4, and hemagglutinin (HA)–tagged SUMO-1, SUMO-2, or SUMO-3.
Case study 2: Huihong Zhai, 2017
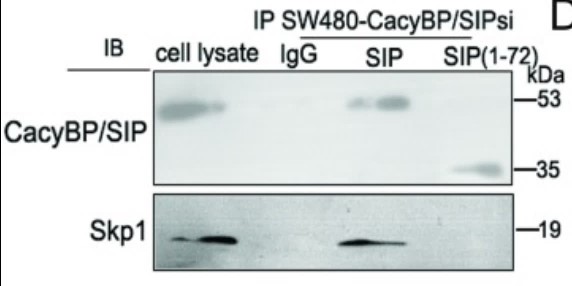
CacyBP/SIP is a component of the ubiquitin pathway and is overexpressed in several transformed tumor tissues, including colon cancer, which is one of the most common cancers worldwide. It is unknown whether CacyBP/SIP promotes the proliferation of colon cancer cells. SKP1 is also involved in related cancer-promoting pathways, so it is not clear whether CacyBP/SIP is directly related to SKP1. This study examined the expression level, subcellular localization, and binding activity of CacyBP/SIP in human colon cancer cells in the presence and absence of the hormone gastrin.
The fingdings revealed gastrin stimulation triggered the translocation of CacyBP/SIP to the nucleus, and enhanced interaction between CacyBP/SIP and SKP1, a key component of ubiquitination pathway which further mediated the proteasome-dependent degradation of p27kip1 protein. These results suggest that CacyBP/SIP may be promoting growth of colon cancer cells by enhancing ubiquitin-mediated degradation of p27kip1.
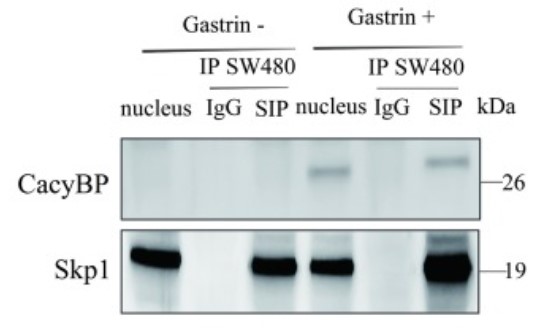
Fig3. Physical interaction between Skp1 and CacyBP/SIP in colon cancer cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
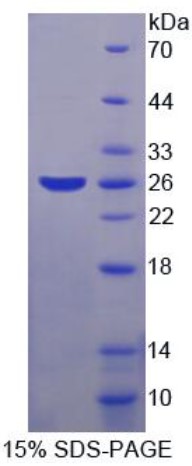
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SKP1-367H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
SKP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SKP1 participated on our site, such as Cell cycle,Oocyte meiosis,Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SKP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | HUWE1,TCEB2,RHOBTB1,FBXO4,UBE2F,SAE1,UBE3B,SIAH2L,UBE2E2,UBE2O |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | SSR1,UBE2E3,MAN1A1,UBE2G1,CAPN1,LMAN1L,RAD23B,XBP1,SEC61AL2,ATF4 |
| Herpes simplex infection | GTF2I,HLA-DRB1,EIF2AK1,IFN-a,TLR2-1,IL15,RNASEL,TLR9,IFNA13,IFIT1 |
| Cell cycle | CDC26,MLF1IP,BRE,PLK1,RAD9B,LEMD3,CDC20,GADD45A,TMPO,CLASP1A |
| Oocyte meiosis | RPS6KA1,YWHAE,CUL1A,PPP2R1A,YWHABA,CALM3A,RPS6KA2,PPP2R5EB,PPP2R5D,YWHAB |
| Circadian rhythm | RORA,PER1,PRKAA1,RORC,NPAS2,CSNK1E,FBXL3,BTRC,NR1D1,CLOCK |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | ACVR1,TGFBR1A,BMP8A,SMAD3A,INHBA,SMAD9,BMP7A,MYCB,IFNG,PPP2R1A |
| Wnt signaling pathway | WNT11R,NKD2B,WNT9B,TCF7L2,FZD3B,PPP3R1,SFRP1A,PLCB4,NKD1,LRP6 |
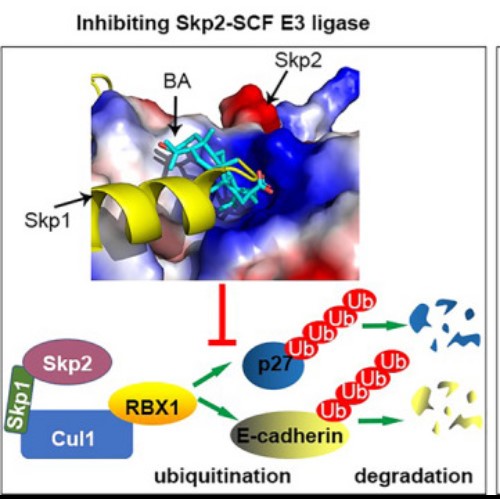
Fig2. Schematic identification of betulinic acid as a novel Skp2-SCF E3 ligase inhibitor to inhibit proliferation and metastasis of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). (Dan-Hua He, 2021)
Protein Function
SKP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,ubiquitin-protein transferase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SKP1 itself. We selected most functions SKP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SKP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | RNF181,FBXL3,UBE2E1,ZNF738,PEX2,FBXO7,LTN1,STUB1,ARIH1L,ARIH2 |
| protein binding | NR2E3,LHFPL5,GPC3,PATL1,VAMP7,CDKAL1,BRSK1,C2orf51,UBL5,CBL |
Interacting Protein
SKP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SKP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SKP1.
SKP2;CUL1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Hamorsky, KT; Kouokam, JC; et al. N-Glycosylation of cholera toxin B subunit in Nicotiana benthamiana: impacts on host stress response, production yield and vaccine potential. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 5:-(2015).
- Min, CK; Kwon, YJ; et al. Multiple Orientia tsutsugamushi Ankyrin Repeat Proteins Interact with SCF1 Ubiquitin Ligase Complex and Eukaryotic Elongation Factor 1 alpha. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).



